|
4/4/2022 The nationalism in Putin's Russia that scholars could not find but which invaded UkraineRead Now by Taras Kuzio
The roots of Russian President Vladimir Putin’s invasion of Ukraine are to be found in the elevation of Tsarist imperial nationalist and White Russian émigré views, which deny the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians.[1] The Soviet Union recognised Ukrainians as a people separate but close to Russians. Russian imperial nationalists hold a Jekyll-and-Hyde view of Ukraine. While denigrating Ukraine in a colonial manner that would make even Soviet-era Communist Party leaders blush, Russian leaders at the same time claim to hold warm feelings towards Ukrainians, whom they see as the closest people to them. In this light, ‘bad’ Ukrainians are nationalists and neo-Nazis who want their country to be part of Europe; ‘good’ Ukrainians are obedient Little Russians who know their place in the east Slavic hierarchy and want to align themselves with Mother Russia. In other words, ‘good’ Ukrainians are those who wish their country to emulate Belarus. In practice, during the invasion, cities such as Kharkiv and Mariupol that have resisted the Russian incursion have been pulverised irrespective of the fact they are majority Russian-speaking. In turn, the fact of this resistance means to Russia’s leaders that these cities are inhabited by ‘Nazis’, not Little Russians who would have greeted Russian troops—and who should therefore be destroyed. Without an understanding of the deepening influence of Tsarist imperial nationalism in Russia since 2012, and especially following Crimea’s annexation in 2014, scholars will be unable to grasp or explain why Putin has been so obsessed with returning Ukraine to the Russian World—a concept created as long ago as 2007 as a body to unite the three eastern Slavs, which underpinned his invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Putin’s invasion did not come out of nowhere, but had been nurtured, discussed, and raised by Putin and Russian officials since the mid-2000s in derogatory dismissals of Ukrainians, and in territorial claims advanced against Ukraine. Unfortunately, few scholars took these at face value until summer 2021, when Putin published a long 6,000-word article[2] detailing his thesis about Russians and Ukrainians constituting one people with a single language, culture, and common history.[3] Ukrainians were a ‘brotherly nation’ who were ‘part of the Russian people.’ ‘Reunification’ would inevitably take place, Putin told the Valdai Club in 2017.[4] The overwhelming majority of scholarly books and journals have dismissed, ignored, or downplayed Russian nationalism as a temporary phenomenon.[5] Richard Sakwa claimed Putin was not dependent upon Russian nationalism, ‘and it is debatable whether the word is even applicable to him.’[6] Other scholars described it as a temporary phenomenon that had disappeared by 2015–16.[7] A major book on Russian nationalism published after the 2014 crisis included nothing on the incorporation of Tsarist imperial nationalist and White Russian émigré discourse that dismissed the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians.[8] Russia’s invasion of Ukraine backed by Russian nationalist rhetoric has led to many Western academics suggesting that the Russian forces have ended up—or will end up—with egg on their faces. Why they felt the need to take this angle has varied, ranging from elaborate political science theories popular in North America about the nature of the Russian regime to the traditional Russophilia found among a significant number of Euro-American scholars writing about Russia.[9] As Petro Kuzyk pointed out, in writing extensively about Ukrainian regionalism, scholars have tended to exaggerate intra-Ukrainian regional divisions. [10] This has clearly been seen during the invasion, when Russia has found no support among Russian-speakers in cities such as Kharkiv, Mariupol, Odesa, and elsewhere. Furthermore, the prevailing consensus prior to the invasion among scholars and think tankers was eerily similar to that in Moscow; namely, that Ukraine would be quickly occupied, President Volodymyr Zelenskyy would flee, and Kyiv would be captured by Russian troops. That this did not happen again shows a a serious scholarly miscalculation about the strength of Ukrainian identity, and an overestimation of the strength of Russian military power.[11] Nationalism in Putin’s Russia has integrated Tsarist imperial and Soviet nationalisms into an eclectic ruling ideology that drives the invasion. Putin, traditionally viewed as nostalgic for the Soviet Union, has also exhibited some pronounced anti-Soviet tendencies, above all in criticising Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin for creating a federal union of republics that included ‘Russian lands’ in the south-east, and artificially creating a ‘fake’ Ukrainian people. Putin’s invasion goal of ‘denazification’[12] aimed to correct this mistake by destroying the ‘anti-Russia’ nurtured by the West.[13] Both scholars and Russian leaders have been baffled as to how to understand and explain the tenacity of Ukrainian identity that has fought the Russian army to a standstill, and is now in the position of launching counterattacks. What is particularly difficult for Russian political leaders and media journalists to explain is how a people that supposedly does not exist (Ukrainians) could greet the ‘special military operation’ (Putin’s dystopian term for the invasion of Ukraine) not with bouquets of flowers but met it with armed resistance. Instrumentalism: Russian Nationalism as a Temporary Phenomenon Sakwa[14] writes that ‘the genie of Russian nationalism was firmly back in the bottle’ by 2016. Pal Kolstø and Marlene Laruelle, along similar lines, write that the nationalist rhetoric of 2014 was novel and subsequently declined.[15] Meanwhile, Henry Hale[16] also believes Putin was only a nationalist in 2014, not prior to the annexation of the Crimea or since 2015. Laruelle[17] concurs, writing that by 2016, Putin’s regime had ‘circled back to a more classic and pragmatic conservative vision’. Laruelle describes Putin’s regime as nationalistic only in the period 2013–16, arguing that ‘since then [it] has been curtailing any type of ideological inflation and has adopted a low profile, focusing on much more pragmatic and Realpolitik agendas at home and abroad.’[18] Paul Chaisty and Stephen Whitefield write, ‘Putin is not a natural nationalist’ and ‘[w]e do not see the man and the regime as defined by principled ideological nationalism.’[19] Sakwa[20] is among the foremost authors who deny that Putin is a nationalist, describing him as not an ideologue because he remains rational and pragmatic—which sharply contrasts with an invasion that most commentators view as irrational. Allegedly, moreover, there has been a ‘crisis’ in Russian nationalism.[21] Other scholars, meanwhile, believed that Putin ‘lost’ nationalist support.[22] In reality, the opposite took place. Russian imperial nationalism deepened, penetrated even further into Russian society and became dominant in Putin’s regime during the eight years between the invasions of Crimea and Ukraine. Russian imperial nationalist denials of the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians became entrenched and have driven the invasion of Ukraine. Patriots and Conservatives - Not Nationalists Scholars described Russian nationalists as ‘patriots’ and western-style ‘conservatives.’ In the same year that the constitution was changed to allow Putin to remain president until 2036, Laruelle writes ‘the Putin regime still embodies a moderate centrist conservatism.’[23] Petro, Sakwa, and Robinson analogously describe a ‘conservative turn’ in Russian foreign policy.[24] If contemporary British conservatives annexed part of Ireland and denied the existence of the Irish people, “conservatism” would no longer fully capture the ideology they represented. By the same token, the Putin regime’s annexation of Crimea and denial of the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians has sharply steered Russian conservatism towards the conceptual centrality of imperial nationalism. In their analyses, Sakwa and Anna Matveeva could only identify ‘militarised patriotism’ or elites divided into ‘westerners’ and ‘patriots.’[25] Following his 2012 re-election, Sakwa writes that Putin only spoke of ‘Russian identity discourse’ and Putin’s ‘conservative values’ which he believes should be not confused with a Russian nationalist agenda.[26] Sakwa has generally avoided using the term ‘nationalist’ when discussing Russian politicians. This created problems in explaining why a ‘non-nationalist’ Putin might choose to support a wide range of far-right and a smaller number of extreme left political movements in Europe and the US, ranging from national-conservatives, populist-nationalists, irredentist imperialists to neo-Nazis in Europe. Sakwa[27] attempts to circumvent this conundrum by relying on a portfolio of euphemistic alternatives, describing these far-right and extreme left movements as ‘anti-systemic forces,’ ‘radical left,’ ‘movements of the far right,’ ‘European populists,’ ‘traditional sovereigntists, peaceniks, anti-imperialists, critics of globalisation,’ ‘populists of left and right,’ and ‘values coalition.’ Putin’s Imperial Nationalist Obsession with Ukraine The Soviet regime recognised a separate Ukrainian people, albeit one that always retained close ties to Russians. The Ukrainian SSR was a ‘sovereign’ republic within the Soviet Union. In 1945, Joseph Stalin negotiated three seats at the UN for the USSR (representing the Russian SFSR), Ukrainian SSR, and Belarusian SSR. In the USSR, there was a Ukrainian lobby in Moscow, while this has been wholly absent under Putin.[28] Soviet nationality policy defined Ukrainians and Russians as related, but nevertheless separate peoples; this was no longer the case in Putin’s Russia. In the USSR, Ukraine, and the Ukrainian language ‘always had robust defenders at the very top. Under Putin, however, the idea of Ukrainian national statehood was discouraged.’[29] Although the USSR promoted Russification, it nevertheless recognised the existence of the Ukrainian language. For a decade prior to the invasion, the Ukrainian language was disparaged by the Russian media and political leaders as a dialect that was artificially made a language in the Soviet Union.[30] Russian nationalist myths and stereotypes underpinning the February 2022 invasion of Ukraine had been raised, discussed, and threatened for over a decade prior to the ‘special military operation’. When Putin returned as president in 2012, he portrayed himself as the ‘gatherer of Russian [i.e., eastern Slavic] lands.’ Ukraine’s return to the Russian World, alongside Crimea and Belarus, was Putin’s unfinished business that he needed to accomplish before entering Russia’s history books. Ukraine, as a ‘Russian land’, should fall within the Russian World and remain closely aligned to Russia. Ukrainians, on this account, had no right to decide their own future. Russia sought to accomplish Ukraine’s return to the Russian World through the two Minsk peace agreements signed in 2014–15. Ukrainian leaders resisted Russian pressure to implement the agreements because they would have created a weak central government and federalised state where Russia would have inordinate influence through its proxy Donetsk Peoples Republic and Luhansk Peoples Republic. The failure of Russia’s diplomatic and military pressure led to a change in tactics in October 2021. Early that month, former President Dmitri Medvedev, now deputy head of Russia’s Security Council, penned a vitriolic attack on Ukrainian identity as well as an anti-Semitic attack on Jewish-Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, ruling out further negotiations with Kyiv.[31] Medvedev claimed Ukrainian leaders were US puppets, and that therefore the Kremlin needed to negotiate directly with their alleged ‘puppet master’—Washington. Meanwhile, Russia would ‘wait for the emergence of a sane leadership in Ukraine,’ ‘who aims not at a total confrontation with Russia on the brink of war…but at building equal and mutually beneficial relations with Russia.’[32] Medvedev was revealing that Russia’s goal in any future military operation would be regime change, replacing an ‘anti-Russia’ leadership with a pro-Kremlin leader.[33] In early November 2021, Russia’s foreign policy machine mobilised and made stridently false accusations about threats from Ukraine and its ‘Western puppet masters.’ Russia began building up its military forces on the Ukrainian border and in Belarus. In December 2021, Russia issued two ultimatums to the West, demanding a re-working of European security architecture. The consensus within Euro-American commentary on the invasion has been that this crisis was completely artificial. NATO was not about to offer Ukraine membership, even though Ukraine had held periodic military exercises with NATO members for nearly three decades, while the US and NATO at no point planned to install offensive missiles in Ukraine. The real cause of the crisis was the failure of the Minsk peace process to achieve Ukraine’s capitulation to Russian demands that would have placed Ukraine within the Russian sphere of influence. After being elected president in April 2019, Zelenskyy had sought a compromise with Putin, but he had come round to understanding that this was not on offer. The failure of the Minsk peace process meant Ukraine’s submission would now be undertaken, in Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov’s words, by ‘military-technical means’—that is, the ‘special military operation’ that began on 24 February 2022. Russian Imperial and White Émigré Nationalism Captures Putin’s Russia Downplaying, marginalising, and ignoring Russian nationalism led to the ignoring of Russian nationalism’s incorporation of Tsarist and White Russian émigré denials of the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians. Marginal nationalism in the 1990s became mainstream nationalism in Russia in the 2000s under Putin when the ‘emergence of a virulent nationalist opposition movement took the mainstream hostage.’[34] The 1993 coup d’état against President Boris Yeltsin was led by a ‘red-brown’ coalition of pro-Soviet and far-right nationalists and fascists. The failure of the coup d’état and the electoral defeat of the Communist Party leader Gennadiy Zyuganov in the 1996 elections condemned these groups to the margins of Russian political life. At the same time, from the mid 1990s, the Yeltsin presidency moved away from a liberal to a nationalist foreign and security approach within Eurasia and towards the West. This evolution was discernible in the support given to a Russian-Belarusian union during the 1996 elections and in the appointment of Yevgeny Primakov as foreign minister. Therefore, the capture of Russia by the Soviet siloviki began with the Chairman of the Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), Primakov, four years before the chairman of the Federal Security Service (FSB), Putin, was elected president. Under Primakov, Russia moved from defining itself as part of the ‘common European home’ to the country at the centre of Eurasia. Under Putin, the marginalised ‘red-brown’ coalition gradually increased its influence and broadened to include ‘whites’ (i.e., nostalgic supporters of the Tsarist Empire). Prominent among the ideologists of the ‘red-white-brown’ coalition was the fascist and Ukrainophobe Alexander Dugin, who has nurtured national-Bolshevik and Eurasianist political projects.[35] In the 2014 crisis, Dugin, then a professor at Moscow State University, stated: ‘We should clean up Ukraine from the idiots,’ and ‘The genocide of these cretins is due and inevitable… I can’t believe these are Ukrainians. Ukrainians are wonderful Slavonic people. And this is a race of bastards that emerged from the sewer manholes.’[36] During the 2000s the ‘red-white-brown’ coalition came to prominence and Putin increasingly identified with its denial of Ukraine and Ukrainians. Tsarist imperial nationalism was integrated with Soviet nostalgia, Soviet traditions and symbols and historical myths, such as the Great Patriotic War. Since the mid 2000s, only five years into his rule, Putin spearheaded the rehabilitation of the White Russian émigré movement and reburial of its military officers, writers, and philosophers in Russia. These reburials took place at the same time as the formation of the Russian World Foundation (April 2007) and unification of the Russian Orthodox Church with the émigré Russian Orthodox Church (May 2007). These developments supercharged nationalism in Putin’s Russia, reinforced the Tsarist element in the ‘red-white-brown’ coalition and fuelled the growing disdain of, and antipathy towards Ukraine and Ukrainians that was given state support in the media throughout the two decades before the invasion.[37] Putin personally paid for the re-burial of White Russian émigré nationalists and fascists Ivan Ilyin, Ivan Shmelev, and General Anton Deniken, who called Ukraine ‘Little Russia’ and denied the existence of a separate Ukrainian nation. These chauvinistic views of Ukraine and Ukrainians were typical of White Russian émigrés. Serhy Plokhy[38] writes, ‘Russia was taking back its long-lost children and reconnecting with their ideas.’ Little wonder, one hundred descendants of White Russian émigré aristocrats living in Western Europe signed an open letter of support for Russia during the 2014 crisis. Putin was ‘particularly impressed’ with Ilyin, whom he first cited in an address to the Russian State Duma as long ago as 2006. Putin recommended Ilyin to be read by his governors, senior adviser Vladislav Surkov, and Prime Minister Dmitri Medvedev. The intention was to use Ilyin’s publications in the Russian state programme to inculcate ‘patriotism’ and ‘conservative values’ in Russian children. Ilyin was integrated into Putin’s ideology during his re-election campaign in 2012 and influenced Putin’s re-thinking of himself as the ‘gatherer of Russian lands;’ that is, integrating Belarus and Ukraine into the Russian World, and specifically his belief that the three eastern Slavs constituted a pan-Russian nation.[39] Laruelle has downplayed the importance of Ilyin’s ideology, writing that he did not always propagate fascism, and that Putin only quoted him five times.[40] Yet Putin has not only cited Ilyin, but also asked Russian journalists whether they had read Deniken’s diaries, especially the parts where ‘Deniken discusses Great and Little Russia, Ukraine.’[41] Deniken wrote in his diaries, ‘No Russian, reactionary or democrat, republican or authoritarian, will ever allow Ukraine to be torn away.’[42] In turn, Tsarist imperial nationalist and White Russian émigré denials of Ukraine and Ukrainians were amplified in the Russian media and in its information warfare for over a decade prior to the invasion. Ukraine and Ukrainians were mocked in the Russian media in a manner ‘typical in coloniser-colonised relationships.’[43] Russia and Russians were cast as superior, modern, and advanced, while Ukraine and Ukrainians were portrayed as backward, uneducated, ‘or at least unsophisticated, lazy, unreliable, cunning, and prone to thievery.’ As a result of nearly two decades of Russian officials and media denigrating Ukraine and Ukrainians these Russian attitudes towards Ukraine and Ukrainians ‘are widely shared across the Russian elite and populace.’[44] This is confirmed by a March 2022 survey conducted by Russia’s last remaining polling organisation, the Levada Centre, which found that an astronomical 81% of Russians supporting Russian military actions in Ukraine. Among these supporters, 43% believe the ‘special military operation’ was undertaken to protect Russophones, 43% to protect civilians in Russian-occupied Donbas, 25% to halt an attack on Russia, and 21% to remove ‘nationalists’ and ‘restore order.’[45] Russian Imperial Nationalist Denigration and Denial of Ukraine and Ukrainians Russian imperial nationalist views of Ukraine began to reappear as far back as the 2004 Ukrainian presidential elections, when Russian political technologists worked for pro-Russian Viktor Yanukovych’s election campaign, producing election posters designed to scare Russian speakers in south-eastern Ukraine about the prospect of an electoral victory by ‘fascist’ and ‘nationalist’ Viktor Yushchenko. This was when Russia revived Soviet ideological propaganda attacks against Ukrainian nationalists as ‘Nazi collaborators.’ Putin’s cult of the Great Patriotic War has been intricately linked to the promotion of Russia as the country that defeated Nazism in World War II (this is not true as all the Soviet nations contributed to the defeat) and which today is fighting contemporary Nazis in Ukraine, Poland, the three Baltic states, and beyond. Ukraine’s four de-communisation laws adopted in 2015 were despised in Moscow for many reasons. The most pertinent to this discussion was one law that equated Nazi and Soviet crimes against humanity (which contradicted Putin’s cult of Stalin[46]) and another law that moved the terminology of Ukraine’s wartime commemorations from the 1941–45 ‘Great Patriotic War’ to ‘World War II’ of 1939–45.[47] One of the 2004 election posters, reproduced below, imagines Ukraine in typical Russian imperial nationalist discourse as divided into three parts, with west Ukraine as ‘First Class’ (that is, the top of the pack), central Ukraine as ‘Second Class’ and south-eastern Ukraine as ‘Third Class’ (showing Russian speakers living in this region to be at the bottom of the hierarchy). Poster Prepared by Russian Political Technologists for Viktor Yanukovych’s 2004 Election Campaign Text:Yes! This is how THEIR Ukraine looks. Ukrainians, open your eyes! The map of Ukraine in the above 2004 election poster is remarkably similar to the traditional Russian nationalist image of Ukraine reproduced below: Map of Russian Imperial Nationalist Image of Ukraine Note: From right to left: ‘New Russia’ (south-eastern Ukraine in red), ‘Little Russia’ (central Ukraine in blue), ‘Ukraine’ (Galicia in orange), ‘Sub-Carpathian Rus’ (green).
Putin’s Growing Obsession with Ukraine Ignored by Scholars Imperial nationalism came to dominate Russia’s authoritarian political system, including the ruling United Russia Party. Putin’s political system copied that of the late USSR, which in turn had copied East European communist regimes that had created state-controlled opposition parties to provide a fake resemblance of a multi-party system. In 1990, the USSR gave birth to the Liberal Democratic Party of the Soviet Union, becoming in 1992 the Liberal Democratic Party of the Russian Federation (LDPRF). Led by Vladimir Zhirinovsky, the LDPRF repeatedly made loud bellicose statements about Ukraine and the West. The LDPRF’s goal has always been to attract nationalists who would have otherwise voted for far-right political parties not controlled by the state. In the 1993 elections following the failed coup d’état, the LDPRF received 22.9% - more than the liberal Russia’s Choice Party (15%) and the Communist Party (KPRF). Under Putin, these state-sponsored political projects expanded to the extreme left through the national-Bolshevik Motherland Party, whose programme was written by Dugin, and the Just Russia Party, which was active in Russian-occupied Donbas. Putin’s authoritarian regime needs internal fifth columnists and external enemies. Domestically, these include opposition leaders such as Alexei Navalny, and externally ‘anti-Russia’ Ukraine and the West. Changes to the Russian constitution in summer 2020 extended the ability of Putin to remain president for fifteen years, but in effect made him president for life. Political repression and the closure of independent media increased after these changes, as seen in the attempted poisoning of Navalny, and grew following the invasion of Ukraine. In 2017, The Economist said it was wrong to describe Russia as totalitarian;[48] five years later The Economist believed Russia had become a totalitarian state.[49] A similar evolution has developed over whether Putin’s Russia could be called fascist. In 2016, Alexander J. Motyl’s article[50] declaring Russia to be a fascist state met with a fairly tepid reception. and widespread scholarly criticism.[51] Laruelle devoted an entire book to decrying Russia as not being a fascist state, which was ironically published a few weeks after Russia’s invasion.[52] By the time of the invasion, all the ten characteristics Motyl had defined as constituting a fully authoritarian and fascist political system in Russia were in place:
Fascists rely on projection; that is, they accuse their enemies of the crimes which they themselves are guilty of. This has great relevance to Ukraine because Russia did not drop its accusation of Ukraine as a ‘Nazi’ state even after the election of Zelenskyy, who is of Jewish-Ukrainian origins and whose family suffered in the Holocaust.[54] Indeed, civilian and military Ukrainians describe Russian invaders as ‘fascists,’ ‘racists’, and ‘Orks’ (a fictional character drawn from the goblins found in J.R.R. Tolkien’s Lord of the Rings). After shooting and severely wounding a Ukrainian civilian, the Russian soldier stood over him saying ‘We have come to protect you.’[55] Another Russian officer said to a young girl captive: ‘Don’t be afraid, little girl, we will liberate you from Nazis.’[56] Putin and the Kremlin’s justification for their ‘special military operation’ into Ukraine was based on many of the myths and chauvinistic attitudes to Ukraine and Ukrainians that had been disseminated by Russia’s media and information warfare since the mid 2000s. Of the 9,000 disinformation cases the EU database has collected since 2015, 40% are on Ukraine and Ukrainians.[57] The EU’s Disinformation Review notes, ‘Ukraine has a special place within the disinformation (un)reality,’[58] and ‘Ukraine is by far the most misrepresented country in the Russian media.[59] Russia’s information warfare and disinformation has gone into overdrive since the 2014 crisis. ‘Almost five years into the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, the Kremlin’s use of the information weapon against Ukraine has not decreased; Ukraine still stands out as the most misrepresented country in pro-Kremlin media.’[60] Since the mid 2000s, Russian media and information warfare has dehumanised Ukraine and Ukrainians, belittling them as unable to exist without external support.[61] In colonialist discourse, Ukrainians were mocked as dumb peasants who had no identity, did not constitute a real nation, and needed an ‘elder brother’ (US, Russia) to survive. Such discourse was reminiscent of European imperialists when discussing their colonies prior to 1945. Ukraine was repeatedly ridiculed as an artificial country and a failed, bankrupt state. Putin first raised this claim as far back as in his 2008 speech to the NATO-Russia Council at the Bucharest NATO summit.[62] Ukraine as a failed state is also one of the most common themes in Russian information warfare.[63] In 2014, the Ukrainian state allegedly collapsed, requiring Russia’s military intervention. The Ukrainian authorities were incapable of resolving their problems because Ukraine is not a real state and could not survive without trade with Russia. Russian disinformation claimed that Ukraine’s artificiality meant it faced territorial claims from all its neighbours. Central-Eastern European countries would put forward territorial claims towards western Ukraine. Russia has made territorial claims to south-eastern Ukraine (Novorossiya [New Russia] and Prichernomorie [Black Sea Lands]) since as far back as the 2008 NATO summit[64] and increased in intensity following the 2014 invasion of Crimea. Putin repeatedly condemned Lenin for including south-eastern Ukraine within the Soviet Ukrainian republic, claiming the region was ancient ‘Russian’ land.[65] Another common theme in the Russian media was that Ukraine was a land of perennial instability and revolution where extremists run amok, Russian speakers were persecuted, and pro-Russian politicians and media were repressed and closed. Ukrainian ‘nationalist’ and ‘neo-Nazi’ rule over Ukraine created an existentialist threat to Russian speakers. Putin refused to countenance the return of Ukrainian control over the Russian-Ukrainian joint border because of the alleged threat of a new ‘Srebrenica-style’ genocide of Russian speakers.[66] Putin used the empirically unsubstantiated claim that Russian speakers were subject to an alleged ‘genocide’ as justification for the ‘special military operation.’ On 16 March, the UN’s highest court, the International Court of Justice, threw out the Russian claim of ‘genocide’ and demanded Russia halt its war.[67] Putin and the Kremlin adopted the discourse of an artificial Ukrainian nation created as an anti-Russian conspiracy. Putin said: ‘The Ukrainian factor was specifically played out on the eve of World War I by the Austrian special service. Why? This is well-known—to divide and rule (the Russian people).’[68] Putin and the Kremlin incorporated these views of Ukraine and Ukrainians a few years after they had circulated within the extreme right in Russia. The leader of the Russian Imperial Movement, Stanislav Vorobyev said, ‘Ukrainians are some socio-political group who do not have any ethnos. They are just a socio-political group that appeared at the end of the nineteenth century by means of manipulation of the occupying Austro-Hungarian administration, which occupied Galicia.’[69] Vorobyev and Putin agreed with one another that ‘Russians’ were the most divided people in the world and believed Ukrainians were illegally occupying ‘Russian’ lands.[70] These nationalist myths were closely tied to another, namely that the West created a Ukrainian puppet state in order to divide the pan-Russian nation. Russia’s ‘special military operation’ is allegedly not fighting the Ukrainian army but ‘nationalists,’ ‘neo-Nazis and drug addicts’ supported by the West.[71] Putin has even gone so far as to deny that his forces are fighting the Ukrainian army at all, and has called on Ukrainian soldiers to rebel against the supposed ‘Nazi’ regime led by Zelenskyy—an especially cruel slur given that several generations of the latter’s family were murdered during the Holocaust. The Russian nationalist myth of a Ukrainian puppet state is a reflection of viewing it as a country without real sovereignty that only exists because it is propped up by the West. Soviet propaganda and ideological campaigns also depicted dissidents and nationalists as puppets of Western intelligence services. Russian information warfare frequently described former President Petro Poroshenko and President Zelenskyy as puppets of Ukrainian nationalists and the West. [72] These Russian nationalist views have also percolated through into the writings of some Western scholars. Stephen Cohen, a well-known US historian of Russia and the Soviet Union, described US Vice President Joe Biden as Ukraine’s ‘pro-consul overseeing the increasingly colonised Kyiv.’[73] President Poroshenko was not a Ukrainian leader, but ‘a compliant representative of domestic and foreign political forces,’’ who ‘resembles a pro-consul of a faraway great power’ running a ‘failed state.’[74] Cohen, who was contributing editor of the left-wing The Nation magazine, held a derogatory view towards Ukraine as a Western puppet state, which is fairly commonly found on the extreme left in the West, and which blamed the West (i.e., NATO, EU enlargement) for the 2014 crisis, rather than Putin and Russia. Soviet propaganda and ideological campaigns routinely attacked dissidents and nationalist opposition as ‘bourgeois nationalists’ who were in cahoots with Nazis in the Ukrainian diaspora and in the pay of Western and Israeli secret services. Ukraine has been depicted in the Russian media since the 2004 Orange Revolution as a country ruled by ‘fascists’ and ‘neo-Nazis.’[75] A ‘Ukrainian nationalist’ in the Kremlin’s eyes is the same as in the Soviet Union; that is, anybody who supports Ukraine’s future outside the Russian World and USSR. All Ukrainians who supported the Orange and Euromaidan Revolutions and are fighting Russia’s ‘special military operation’ were therefore ‘nationalists’ and ‘Nazis.’ Conclusion Between the 2004 Orange Revolution and Putin’s re-election in 2012, Russian imperial nationalism rehabilitated Tsarist imperial and White Russian émigré dismissals of Ukraine and Ukrainians into official discourse, military aggression, and information warfare. In 2007, the Russian World Foundation was created and two branches of the Russian Orthodox Church were re-united. Returning to the presidency in 2012, Putin believed he would enter Russian history as the ‘gatherer of Russian lands’ which he proceeded to undertake with Crimea (2014), Belarus (2020), and Ukraine (2022). The origins of Putin’s obsession with Ukraine lie in his eclectic integration of Tsarist imperial and Soviet nationalisms. The former provides the ideological bedrock for the denial of the existence of Ukraine and Ukrainians while the latter provides the ideological discourse to depict as Nazis all those Ukrainians who resist being defined as Little Russians. Putin believed his military forces would be greeted as liberators by Little Russians eager to throw off the US imposed nationalist and neo-Nazi yoke, the artificial Ukrainian state would quickly disintegrate, and the country and capital city of Kyiv would be taken within two days. Russian troops brought parade uniforms to march down Kyiv’s main thoroughfare and victory medals to be awarded to troops. This was not to be, because Putin’s denial of a Ukrainian people is—put simply—untrue. The Russo-Ukrainian war is a clash between twenty-first century Ukrainian patriotism and civic nationalism, as evidenced by Zelenskyy’s landslide election, and rooted in a desire to leave the USSR behind and be part of a future Europe, and nineteenth-century Russian imperial nationalism built on nostalgia for the past. Unfortunately, many scholars working on Russia ignored, downplayed, or denied the depth, direction, and even existence of nationalism in Putin’s Russia and therefore find unfathomable the ferocity, and goals behind the invasion of Ukraine. This was because many scholars wrongly viewed the 2014 crisis as Putin’s temporary, instrumental use of nationalism to annex Crimea and foment separatism in south-eastern Ukraine. Instead, they should have viewed the integration of Tsarist imperial and Soviet nationalisms from the mid 2000s through to the invasion as a continuous, evolutionary process that has led to the emergence of a fascist, totalitarian, and imperialist regime seeking to destroy Ukrainian identity. [1] See Taras Kuzio, Russian Nationalism and the Russian-Ukrainian War: Autocracy-Orthodoxy-Nationality (London: Routledge, 2022). [2] Vladimir Putin, ‘Pro istorychnu yednist rosiyan ta ukrayinciv,’ 12 July 2021. http://kremlin.ru/events/president/news/66182?fbclid=IwAR0Wj7W_7QL2-IFInLwl4kI1FOQ5RxJAemrvCwe04r8TIAm03rcJrycMSYY [3] Y.D. Zolotukhin, Bila Knyha. Spetsialnykh Informatsiynykh Operatsiy Proty Ukrayiny 2014-2018, 67-85. [4] Vladimir Putin, ‘Speech to the Valdai Club,’ 25 October 2017. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvY184FQsiA [5] Anna Matveeva, A. (2018). Through Times of Trouble. Conflict in Southeastern Ukraine Explained From Within (Lanham, MA: Lexington Books, 2018), 182, 218, 221, 223, 224, 277. [6] Richard Sakwa, Russia Against the Rest. The Post-Cold War Crisis of World Order. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017), 125. [7] Pal Kolsto, ‘Crimea vs. Donbas: How Putin Won Russian Nationalist Support—and Lost It Again,’ Slavic Review, 75: 3 (2016), 702-725; Henry E. Hale, ‘How nationalism and machine politics mix in Russia,’ In: Pal Kolstø and Helge Blakkisrud eds., The New Russian Nationalism. Imperialism, Ethnicity and Authoritarianism (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2016), 221-248, at p.246; Marlene Laruelle, ‘Making Sense of Russia's Illiberalism,’ Journal of Democracy, 31: 3 (2020: 115-129. [8] P. Kolstø and H. Blakkisrud eds., The New Russian Nationalism. Imperialism, Ethnicity and Authoritarianism (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2016). [9] For a full survey see T. Kuzio, ‘Euromaidan Revolution, Crimea and Russia-Ukraine War: Why it is Time for a Review of Ukrainian-Russian Studies,’ Eurasian Geography and Economics, 59: 3-4 (2018), 529-553 and Crisis in Russian Studies? Nationalism (Imperialism), Racism, and War (Bristol: E-International Relations, 2020), https://www.e-ir.info/publication/crisis-in-russian-studies-nationalism-imperialism-racism-and-war/ [10] See Petro Kuzyk, ‘Ukraine’s national integration before and after 2014. Shifting ‘East–West’ polarization line and strengthening political community,’ Eurasian Geography and Economics, 60: 6 (2019), 709-735/ [11] T. Kuzio, ‘Putin's three big errors have doomed this invasion to disaster,’ The Daily Telegraph, 15 March 2022. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2022/03/15/putins-three-big-errors-have-doomed-invasion-disaster/ [12] ‘Do not resist the liberation,’ EU vs Disinfo, 31 March 2022. https://euvsdisinfo.eu/do-not-resist-the-liberation/ [13] T. Kuzio, ‘Inside Vladimir Putin’s criminal plan to purge and partition Ukraine,’ Atlantic Council, 3 March 2022. https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/ukrainealert/inside-vladimir-putins-criminal-plan-to-purge-and-partition-ukraine/ [14] R. Sakwa, Russia Against the Rest, 159. [15] P. Kolsto, ‘Crimea vs. Donbas: How Putin Won Russian Nationalist Support—and Lost It Again’ and M. Laruelle, ‘Is Nationalism a Force for Change in Russia?’ Daedalus, 146: 2 (2017, 89-100. [16] H. E. Hale, ‘How nationalism and machine politics mix in Russia.’ [17] M. Laruelle, ‘Making Sense of Russia's Illiberalism,’126. [18] M. Laruelle, ‘Ideological Complimentarity or Competition? The Kremlin, the Church, and the Monarchist Idea,’ Slavic Review, 79: 2 (2020), 345-364, at p.348. [19] Paul Chaisty and Stephen Whitefield, S. (2015). ‘Putin’s Nationalism Problem’ In: Agnieszka Pikulicka-Wilczewska and R. Sakwa eds., Ukraine and Russia: People, Politics, Propaganda and Perspectives (Bristol: E-International Relations, 2015), 165-172, at pp. 157, 162. [20] R. Sakwa, Frontline Ukraine. Crisis in the Borderlands (London: I.B. Tauris, 2015) and Russia Against the Rest. [21] Robert Horvath, ‘The Euromaidan and the crisis of Russian nationalism,’ Nationalities Papers, 43: 6 (2015), 819-839. [22] P. Kolsto, ‘Crimea vs. Donbas: How Putin Won Russian Nationalist Support—and Lost It Again’ and H. E. Hale, ‘How nationalism and machine politics mix in Russia.’ [23] M. Laruelle, ‘Making Sense of Russia's Illiberalism,’126. [24] R. Sakwa, ‘Is Putin an Ism,’ Russian Politics, 5: 3 (2020): 255-282, at pp.276-277; Neil Robinson, ‘Putin and the Incompleteness of Putinism,’ Russian Politics, 5: 3 (2020): 283-300, at pp.284-285, 287, 289, 293, 299); Nicolai N. Petro, ‘How the West Lost Russia: Explaining the Conservative Turn in Russian Foreign Policy,’ Russian Politics, 3: 3 (2018): 305-332. [25] A. Matveeva, Through Times of Trouble, 277 and Sakwa, Russia Against the Rest, 119. [26] R. Sakwa, Russia Against the Rest, 125, 189. [27] Ibid., 60, 75, 275, 276. [28] Mikhail Zygar, All the Kremlin’s Men. Inside the Court of Vladimir Putin (New York: Public Affairs, 2016), 87. [29] Ibid., [30] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/report/ukrainian-literary-language-is-an-artificial-language-created-by-the-soviet-authorities/ [31] https://www.kommersant.ru/doc/5028300 [32] Ibid., [33] Taras Kuzio, ‘Medvedev: The Russian-Ukrainian War will continue until Ukraine becomes a second Belarus,’ New Eastern Europe, 20 October 2021. https://neweasterneurope.eu/2021/10/20/medvedev-the-russian-ukrainian-war-will-continue-until-ukraine-becomes-a-second-belarus/ [34] Charles Clover, Black Wind, White Snow. The Rise of Russia’s New Nationalism (New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 2016), 287. [35] M. Laruelle, ‘The three colors of Novorossiya, or the Russian nationalist mythmaking of the Ukrainian crisis,’ Post-Soviet Affairs, 3: 1 (2016), 55-74. [36] Mykola Riabchuk, ‘On the “Wrong” and “Right” Ukrainians,’ The Aspen Review, 15 March 2017. https://www.aspen.review/article/2017/on-the-wrong-and-right-ukrainians/ [37] Anders Aslund, ‘Russian contempt for Ukraine paved the way for Putin’s disastrous invasion,’ Atlantic Council, 1 April 2022. https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/ukrainealert/russian-contempt-for-ukraine-paved-the-way-for-putins-disastrous-invasion/ [38] Serhy Plokhy, Lost Kingdom. A History of Russian Nationalism from Ivan the Great to Vladimir Putin (London: Penguin Books, 2017), 327. [39] Ibid., 332. [40] M. Laruelle, ‘In Search of Putin’s Philosopher,’ Intersection, 3 March 2017. https:// www.ponarseurasia.org/article/search-putins-philosopher [41] S. Plokhy, Lost Kingdom, 326. [42] Ibid., [43] Alena Minchenia, Barbara Tornquist-Plewa and Yulia Yurchuk ‘Humour as a Mode of Hegemonic Control: Comic Representations of Belarusian and Ukrainian Leaders in Official Russian Media’ In: Niklas Bernsand and B. Tornquist-Plewa eds., Cultural and Political Imaginaries in Putin’s Russia (Leiden and Boston: Brill Academic Publishers, 2018), 211-231, at p.225. [44] Ibid, 25 and Igor Gretskiy, ‘Lukyanov Doctrine: Conceptual Origins of Russia’s Hybrid Foreign Policy – The Case of Ukraine,’ Saint Louis University Law Journal, 64:1 (2020), 1-22, at p.21. [45] https://www.levada.ru/2022/03/31/konflikt-s-ukrainoj/ [46] T. Kuzio, ‘Stalinism and Russian and Ukrainian National Identities,’ Communist and Post-Communist Studies, 50, 4 (2017), 289-302 . [47] Anna Oliynyk and T. Kuzio, ‘The Euromaidan Revolution of Dignity, Reforms and De-Communisation in Ukraine,’ Europe-Asia Studies, 73: 5 (2021), 807-836. [48] Masha Gessen is wrong to call Russia a totalitarian state,’ The Economist, 4 November 2017. https://www.economist.com/books-and-arts/2017/11/02/masha-gessen-is-wrong-to-call-russia-a-totalitarian-state [49] ‘The Stalinisation of Russia,’ Economist, 12 March 2022. https://www.economist.com/leaders/2022/03/12/the-stalinisation-of-russia [50] Alexander J. Motyl, ‘Putin’s Russia as a fascist political system,’ Communist and Post-Communist Studies, 49: 1 (2016), 25-36. [51] I was guest editor of the special issue of Communist and Post-Communist Studies and remember the controversies very well as to whether to publish or not publish Motyl’s article. [52] M. Laruelle, Is Russia Fascist ? Unraveling Propaganda East and West (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2022). [53] Olga Kryshtanovskaya and Stephen White, ‘Putin's Militocracy,’ Post-Soviet Affairs, 19: 4 (2003), 289-306. [54] Zelenskyy is the grandson of the only surviving brother of four. The other 3 brothers were murdered by the Nazi’s in the Holocaust. [55] https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/mar/19/we-have-to-come-to-protect-you-russian-soldiers-told-ukrainian-man-theyd-shot [56] https://www.nytimes.com/2022/03/20/world/europe/russian-soldiers-video-kyiv-invasion.html [57] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/ukraine-will-turn-into-a-banana-republic-ukrainian-elections-on-russian-tv/?highlight=ukraine%20land%20of%20fascists [58] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/what-didnt-happen-in-2017/?highlight=What%20didn%26%23039%3Bt%20happen%20in%202017%3F [59] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/ukraine-under-information-fire/ [60] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/ukraine-under-information-fire/?highlight=ukraine [61] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/dehumanizing-disinformation-as-a-weapon-of-the-information-war/?highlight=Ukraine%20has%20a%20special%20place%20within%20the%20disinformation%20%28un%29reality [62] https://www.unian.info/world/111033-text-of-putin-s-speech-at-nato-summit-bucharest-april-2-2008.html [63] Yuriy D. Zolotukhin Ed., Bila Knyha. Spetsialnykh Informatsiynykh Operatsiy Proty Ukrayiny 2014-2018 (Kyiv: Mega-Pres Hrups, 2018), 302-358. [64] https://www.unian.info/world/111033-text-of-putin-s-speech-at-nato-summit-bucharest-april-2-2008.html [65] T. Kuzio, Russian Nationalism and the Russian-Ukrainian War,1-34. [66] ‘Putin fears second “Srebrenica” if Kiev gets control over border in Donbass,’ Tass, 10 December 2019. https://tass.com/world/1097897 [67] https://www.icj-cij.org/en/case/182 [68] V. Putin, ‘Twenty questions with Vladimir Putin. Putin on Ukraine,’ Tass, 18 March 2020. https://putin.tass.ru/en [69] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZD62ackWGFg [70] V. Putin, ‘Ukraina – samaya blyzkaya k nam strana,’ Tass, 29 September 2015. https://tass.ru/interviews/2298160 and ‘Speech to the Valdai Club,’ 25 October 2015. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvY184FQsiA [71] ‘Putin references neo-Nazis and drug addicts in bizarre speech to Russian security council – video,’ The Guardian, 25 February 2022. https://www.theguardian.com/world/video/2022/feb/25/putin-references-neo-nazis-and-drug-addicts-in-bizarre-speech-to-russian-security-council-video [72] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/report/zelenskyys-ruling-is-complete-failure-nazis-feel-well-ukraine-remains-anti-russia/ [73] Stephen Cohen, War with Russia?: From Putin & Ukraine to Trump and Russiagate (New York: Skyhorse Publishing, 2019), 145. [74] Ibid., p. 36. [75] https://euvsdisinfo.eu/ukraine-will-turn-into-a-banana-republic-ukrainian-elections-on-russian-tv/?highlight=ukraine%20land%20of%20fascists by Joanne Paul
 A lot can be said about the relationship between utopianism and ideology, and Gregory Claeys covered much of it in his comprehensive and detailed contribution to this blog.[1] As with all discussions of utopianism, however, participants cannot help but acknowledge the roots of the concept in the originator of the term, Thomas More’s masterfully enigmatic Utopia (full title: On the Best State of the Commonwealth and on the New Island of Utopia). Whether it was More himself who coined the term (it has been suggested it was in fact Erasmus), and acknowledging the longer (and global) history of imagined ideal states, any consideration of utopianism must at some point trace itself to More’s sixteenth-century text. This can make for some awkward anachronistic connections, especially for anyone concerned particularly with the importance of contextualism in the analysis of historic texts (as I am). Even the question of whether there is an ‘ideology’ present in More’s text can immediately be countered with the charge of anachronism. This is, of course, an issue with the term itself. However, much like we might acknowledge utopias (or utopian thinking) prior to 1516, we might also entertain the suggestion that ideology as a concept (if not a term) might have existed prior to the Enlightenment, and that various contemporary ideologies might also have their roots in the Renaissance, even if More would have been perplexed—but likely intrigued—by the term itself. The purpose of this piece, then, is to explore two interrelated questions. First, whether we can think about ideology and Utopia without giving ourselves entirely over to anachronism and thus a reading of the text that cannot be substantiated. Second, in a similar vein, to test the waters with a variety of ‘ideologies’ with which Utopia has been associated: republicanism, liberalism, totalitarianism/authoritarianism, socialism/communism, and, of course, utopianism. In this ‘testing’, the first criteria will be consistency within the text itself, but in establishing this, I will be reading the text in the context of More’s times and other works. Utopia is too frequently read as a stand-alone text despite—or perhaps because of—More’s substantial oeuvre. It is an intentionally ambiguous work, which is why so many different and even opposed ideologies can be read into it. In order to test the legitimacy of these readings, we must understanding Utopia in the context of More’s work more widely. A short caveat: none of this, of course, precludes the use of Utopia as an inspiration or foundation for a variety of ideological arguments, and Claeys has repeatedly made an impassioned and vitally important argument for the role of utopian thinking in meeting the environmental challenges of the twenty-first century (along with another contribution to this blog by Mathias Thaler)[2]. Political theorists and philosophers have—often very good—reasons for playing harder and faster with the ‘rules’ of historical contextualism (for more on this, see in particular the work of Adrian Blau).[3] There are, however, also good reasons to want to be attentive to the particularities of an utterance in its historical context, which I will not rehearse here, but which I hope are evident in what follows. Ideology and Utopia Does the idea of ‘ideology’ fit with a sixteenth-century intellectual mindset? More was not unfamiliar with the notion of ‘-isms’, often seen as the shorthand for identifying ideologies (though not in the explicitly modern sense).[4] Most of these ‘-isms’ were religious, not just less ‘ideological’ words like baptism, but those that more accurately fit the definition of a ‘system of beliefs’ such as ‘Judaism’, which More used in his Confutation of Tyndale’s Answer (1532).[5] It was the Reformation, Harro Höpfl has noted, which saw the widespread use of ‘isms’ to refer to ‘theological or religious positions considered heretical, and also to refer to the doctrines of various philosophical schools’.[6] Indeed More used the term ‘sophism’ (see the excerpt from the concordance above) in a way that arguably had ideological connotations, and not expressly or necessarily religious ones.[7] That being said, Ideology’s association with political ideas as wholly distinct from religious ones might have not squared with More’s worldview. Any religion can fit the definition of an ‘ideology’ and religious ideas permeated every aspect of More’s world, including—and especially—politics. The way in which Utopia can and has been read as an especially secular text is part of what makes it an enduringly popular text to study, certainly more than More’s other—obviously (and vehemently) religious—writings. There is something attractively secular about More’s pre-Christian island, which is based more obviously on classical pagan influences than medieval Christian ones. For this reason, it is temptingly easy to read a series of ideologies into this short book. The interesting question for a historian like myself becomes whether these were ideas available and attractive to More himself. Republicanism The island of Utopia is obviously and expressly a republic, and the neo-classical humanist More would have fully understood what this entailed. Both books of the text articulate, as Quentin Skinner has demonstrated, arguments for a Ciceronian vita activa, on which republicanism is based.[8] Although each Utopian city is ruled by a princeps, they are elected, and rule in consultation with an assembly of elected ‘tranibors’. The island as a whole is ruled by a General Council, made up of representatives elected from each city. This description of Utopia is framed by a discussion about the merits of the active life in the context of a monarchy, echoing similar discussions in Isocrates, Cicero, Erasmus, and others.[9] Does this align Utopia with ‘republicanism’ as an ideology? Certainly, the text deserves an important place in the development of that ideology from its ‘Athenian and Roman roots’, especially when read in the context of More’s other writings, which express a conciliarism that clearly has overlaps with classical republicanism. In his Latin Historia Richardi Tertii, More writes that parliament, which he calls a senatus, has ‘supreme and absolute’ authority, and in his religious polemics, he is keen to draw a connection between the parliament and the General Council.[10] The latter, he writes, has the power to depose the Pope and, whereas the Pope’s primacy can be held in doubt, ‘the general councils assembled lawfully… the authority thereof ought to be taken for undoubtable’.[11] Both parliament and the General Council are authorised representatives of the whole community, whether the church or the realm.[12] More also expresses ideas in line with what has come to be known as ‘republican liberty’: ‘non-domination’ or ‘that freedom within civil associations’, impling the lack of an ‘arbitrary power’ which would reduce ‘the status of free-man to that of slaves’.[13] In his justification of the importance of law, More writes, that ‘if you take away the laws and leave everything free to the magistrates… they will rule by the leading of their own nature… and then the people will be in no way freer, but, by reason of a condition of servitude, worse’.[14] This aligns with the Renaissance view of tyranny as ruling according to one’s own willful passions, rather than right reason. More certainly saw unfreedom in the rule of licentia (or license) over reason.[15] This could be found both in the rule of a single tyrant and in the anarchy of pluralism, a situation he feared would arise from Lutheranism.[16] As such, a firmly established structure of self-government, like that in Utopia, was the ideal way to ensure his notion of freedom, one that was largely in accordance with the republican tradition. Liberalism This is in contrast with notion of freedom advanced in Utopia by the character Raphael Hythloday, which we might think of as more in line with a ‘liberal’ perspective. He does not want to ‘enslave’ himself to a king and prefers to ‘live as I please’, certainly more ‘license’ than ‘liberty’ in More’s perspective.[17] There is an inherent contradiction between republican and liberal notions of liberty. In so far as More can be said to express something of the former, he is deeply against the latter. Individualism sits at the heart of liberalism; it is, as Michael Freeden and Marc Stears have suggested (though not without qualification), ‘an individualist creed’, seeking to enshrine ‘individual rights, social equality, and constraints on the interventions of social and political power’.[18] Liberalism was a product of the Enlightenment, and so More could not properly be said to be its opponent, but he did powerfully critique what we might see as its nascent constitute parts. In his other works, More often repeats a distinction between the people (populus) and ‘anyone whatever’ (quislibet), to the derision of the authority of the latter.[19] This lies at the heart of his fear of anarchy and Lutheranism, which he accuses of transferring ‘the authority of judging doctrines… from the people and deliver[ing] it to anyone whatever’.[20] In Utopia, we can see this critique of proto-individualism in his central message about pride, which he (with Augustine) takes to be the root of all sin, as it necessarily cuts across the bonds that should unite the populus. Pride is not just self-love, but self-elevation, a form of comparative arrogance that seeks to mark one out from others (a sin he associates with the scholastics, vice-ridden nobility, Lutherans, and indeed most of his opponents). Utopia has thus been read as a repressive regime which quashes—rather than upholds—freedom. This is from the perspective of post-Enlightenment liberalism, and takes Utopia perhaps more literally than it is meant. Read as a critique of the pride which we might associate with a sort of proto-individualism, it offers a powerful critique of an ideology which is—it must be acknowledged—in need of a reassessment. Totalitarianism/Authoritarianism It is for its anti-liberal qualities that Utopia has ended up associated with some of the darkest ideologies of the 20th century. More’s biographer, Richard Marius, called his views about education—certainly present in Utopia—‘an authoritarian concept, suitable for an authoritarian age’. Others have associated Utopia explicitly with totalitarianism.[21] Of the two, authoritarianism might be the more likely. There is a very clear desire in the setting out of the Utopian political and social system to have laws inculcated. The emphasis on what is referred to as ‘education’ or ‘training’ [institutis] might make 21st century readers think instead of socialisation or, more pessimistically, indoctrination. Priests, for example, are responsible for children’s education, and must ‘take the greatest pains from the very first to instil into children’s minds, while still tender and pliable, good opinions which are also useful for the preservation of the commonwealth.’[22] For this, not only are laws and institutions employed, but also public opinion. In a land where everything is public, nothing is private, and thus all is subject to public opinion: ‘being under the eyes of all, people are bound either to be performing the usual labor or to be enjoying their leisure in a fashion not without decency’.[23] This ‘universal behaviour’ is the secret to Utopia’s success. What I think More wanted to draw attention to in Utopia is the way in which this happens anyway, and to reorient the inculcation of values (or ‘opinions’) towards ‘truer’ or more ‘eternal’ (of course even ‘divine’) values. Utopians laugh at gems and precious metals because they associate them with fools and chamber pots. We value them because we associate them with the wealthy and powerful. The Utopians are ‘made’ to be dutiful citizens. As Book One suggests, ‘When you allow your youths to be badly brought up and their characters, even from early years, to become more and more corrupt, to be punished, of course, when, as grown-up men, they commit the crimes from boyhood they have shown every prospect of committing, what else, I ask, do you do but first create thieves and then become the very agents of their punishment?’.[24] In both cases, More suggests in Utopia and elsewhere, these values (or opinions) are built on a sort of ‘consensus’. The suggestion that this is authoritarian stems from a post-Enlightenment perspective that looks to see the liberal individual protected (as set out in part III above), of which More is many ways presenting a sort of ‘proto-critique’. While the republicanism of Utopia would, to some minds (and I would suspect to More’s), prevent it from being accurately labelled authoritarian—the citizenry is, after all, involved in its governance—to others this would not suffice. Would More have minded an ‘authoritarian’ society, if the values it inculcated with the ‘right’ ones? Perhaps not. More’s point, however, that we all submit to and are shaped by various sources of authority, and that the power to reorient the values cultivated by these authorities has been and continues to be a powerful one. Socialism/communism The early socialist thinkers were inspired by More to think that they might make people better through their organisation of society and its institutions (primarily education). In this historical context, we also have to contend, at least for a moment, with utilitarianism, and the Utopian’s ‘hedonism’ (or more properly Epicureanism). Jeremy Bentham, of course, held stock in the factory of utopian socialist Robert Owen. Helen Taylor (stepdaughter of J.S. Mill) wrote that in Utopia More ‘lays down a completely Utilitarian system of ethics’ as well as an ‘eloquently and yet closely reasoned defense of Socialism’. More was not an Epicurean (nor, of course, a utilitarian), though was interested to get back to more ‘real’ or ‘true’ pleasures over those false ones (we might think again of Utopians’ views of gems and precious metals). What I have called his republicanism might have also meant he was more interested in the good of the many over the few, though perhaps not quite in those terms (instead, the common good over any individual good). This emphasis on ‘common good’, of course, translates into ‘common goods’ in Utopia, where everything is held in common. This abolition of anything private (and thus private property) has led him to be read as a socialist and/or communist thinker, the latter not least by Marx and Engels. Beyond Utopia, however, More does make some very un-socialist comments. Through the central figure of Anthony in his Dialogue of Comfort (1534), More suggests in an Aristotelian vein that economic inequality is essential for the commonwealth; there must be ‘men of substance… for else more beggars shall you have’.[25] The golden hen must not be cut up for the few riches one might find inside. The larger point More wants to make in this text, however, is that even the richest do not ‘own’ their property. Property is a fiction and needs to be seen as such. Thus a rich man can keep his wealth so long as he recognises it is only his by the fictions of the society in which he lives, and ought (therefore) to be used to benefit the commonwealth. Wealth, position, and so on, More advocates, ‘by the good use thereof, to make them matter of our merit with God’s help in the life after.’ This is not a socialist nor a communist position, and it is certainly not materialist. More’s entire argument seeks to cultivate a conscious neglect of material realities in favour of the decidedly immaterial. Utopia, then, serves as a reminder of the immaterial realities underneath the social fictions generated in Europe (property, money, social hierarchy, etc). Living in that—shall we say—‘fictive reality’, however, means using those falsities towards the higher ends. As More’s friend John Colet put it: ‘use well temporal things. Desire eternal things.’ Utopianism Utopianism is at once an ideology, has characteristics similar to ideology, might encompass all ideologies, and is entirely opposed to it.[26] I will not rehearse the arguments of Sargent and Claeys here, but the three ‘faces’ that they speak of: utopian literature, utopian communities/practice, and utopian social theory are of course drawn from More’s 1516 text, and Sargent even suggests that ‘the meaning of [utopia] has not changed significantly from 1516 to the present’. So can we accept the obvious, then, that utopianism, as an ideology, is present in More’s text? Unfortunately, this question would seem to hinge on the fraught question of More’s sincerity in setting out the merits of the island of Utopia and the extent to which it is a community that he intended his readers to emulate. In many ways, our answer to this question has the power to overturn the very notion of any ideology being present in at least a surface reading of Utopia. If we were to conclude that Utopia is pure satire, and that the only arguments made in it are negative deconstructive ones, we would be hard-pressed to find any ideology within it at all.[27] I have made my own arguments about the central argument of Utopia, which I will not rehearse here, but the good news is that we can engage with the issue of utopianism in Utopia without answering this seemingly unanswerable question. Say what you will about the difficult question of More’s intentions, it would be difficult indeed to suggest that he was putting forward a blueprint of any kind for the construction of a practical community or endorsing the direct adoption of any of the practices exhibited in Utopia. The idea that Utopia exhibits—to use the words of Crane Brinton—‘a plan [that] must be developed and put into execution’ creates a sense of unease, to say the least. Afterall, More famously ends his text with the conclusion that ‘in the Utopian commonwealth there are very many features that in our own societies I would wish rather than expect to see’.[28] Despite the consensus that this passage is central to our understanding of Utopia, scholars have generally not attempted to read this statement in the context of More’s other works. When we do, we see that More applied this phrase elsewhere as well, and provided more of an explanation than he does in Utopia. In his Apology of 1533, More tells his reader that it would be wonderful if the world was filled with people who were ‘so good’ that there were no faults and no heresy needing punishment. Unfortunately, ‘this is more easy to wish, than likely to look for’.[29] Because of this reality, all one can do is ‘labour to make himself better’ and ‘charitably bear with others’ where he can. It is an internal reorganisation of priorities, drawn in large part from More’s reading of Augustine; what is common and shared must be prioritised over that which is one’s own. This, I have argued elsewhere, is what sits at the heart of More’s oeuvre, and we should be unsurprised to find it in Utopia as well. It is not the case, then, that More is advocating for what we might recognise as utopianism, but rather than Utopia is re-enforcing the arguments he makes elsewhere: the destructive power of pride and the personal need to prioritise the common over the individual. Conclusion: Moreanism? Does this mean, at last, we have come to an ideology in Utopia? A sort of republicanism-light, a proto-communitarianism, an anti-liberalism? I leave it to political theorists to hash out what More’s view might be termed—or indeed if a label is useful at all. Utopia can, indeed, be read in a variety of ways, which support a diversity of ideological positions. It becomes more difficult, I think, to read these positions into More’s thought as a whole. When we examine his corpus, we see a preoccupation with the common good, expressed through representative quasi-republican institutions, and the eternal/immaterial, but also a pragmatism (even ‘realism’?) about the artificialities of the world in which we live. It is the work of a much larger piece to flesh this out in whole, and this small article has instead focused largely on what More cannot be said to be. Hopefully, however, this is in itself a utopian exercise. In understanding Not-More, we might better understand More himself. [1] ‘Utopianism as a Political Ideology: An Attempt at Redefinition’, IDEOLOGY THEORY PRACTICE, accessed 8 February 2022, http://www.ideology-theory-practice.org/1/post/2021/04/utopianism-as-a-political-ideology-an-attempt-at-redefinition.html. [2] ‘“We Are Going to Have to Imagine Our Way out of This!”: Utopian Thinking and Acting in the Climate Emergency’, IDEOLOGY THEORY PRACTICE, accessed 8 February 2022, http://www.ideology-theory-practice.org/1/post/2021/09/we-are-going-to-have-to-imagine-our-way-out-of-this-utopian-thinking-and-acting-in-the-climate-emergency.html. [3] Adrian Blau, ‘Interpreting Texts’, in Methods in Analytical Political Theory, ed. Adrian Blau (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017), 243–69, https://doi.org/10.1017/9781316162576.013. [4] H. M. Höpfl, ‘Isms’, British Journal of Political Science 13, no. 1 (January 1983): 1–17, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007123400003112. [5] Thomas More, The Yale Edition of the Complete Works of St. Thomas More: The Confutation of Tyndale’s Answer, ed. Louis A. Schuster, Richard C. Marius, and James P. Lusardi, vol. 8 (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1973), 782. [6] Höpfl , ‘Isms’, 1; most of these do not appear in More’s work, though ‘papist’ does (24 times), which is a derivation of ‘papism’; likewise ‘donatists’ (26 times) from ‘donatism’ see https://thomasmorestudies.org/concordance/. Of course, this discussion is of English ‘isms’, and Utopia, along with a handful of More’s other writing, is Latin. Ism itself is a Latin (from Greek, and into French) derivation, for the suffix ‘-ismus’ (masculine). However, text-searches and concordances did not turn up many of these either, nor do ‘isms’ appear in the text of translations consulted. [7] ‘Concordances’, Thomas More Studies (blog), accessed 8 February 2022, http://thomasmorestudies.org/concordance-home/. [8] Quentin Skinner, ‘Thomas More’s Utopia and the Virtue of True Nobility’, in Visions of Politics: Volume 2: Renaissance Virtues (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002), 213–44. [9] Joanne Paul, Counsel and Command in Early Modern English Thought (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020), chapter 1. [10] More, Letters, 321. In the Confutation, 287 he justifies this approach, suggesting that ‘senatus Londinensis’ could be translated ‘as mayor, aldermen, and common council’. [11] More, Letters, 213. [12] More, Confutation, 146, 937. [13] Quentin Skinner, Hobbes and Republican Liberty (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008), ix-x. This is not inconsistent with the fact that free-men could indeed become slaves in Utopia. In fact, the presence of slaves only highlights the emphasis on the sort of freedom enjoyed by law-abiding Utopian citizens.[13] Slaves are drawn from either within Utopia - those condemned of ‘some heinous offence’ - or without – captured prisoners of war, those who have been condemned to death in their own country or, thirdly, those who volunteer for it as a preferable option to poverty elsewhere.[13] Notably, in none of these cases is slavery hereditary and slaves cannot be purchased from abroad; Thomas More, More: Utopia, ed. George M. Logan and Robert M. Adams (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002), 77. [14] More, Responsio Ad Lutherum, 277. All references to More’s works taken from the Yale Collected Works series, unless otherwise indicated. [15] Skinner, Hobbes and Republican Liberty, 30-1. [16] Joanne Paul, Thomas More (Cambridge: Polity, 2016), 98-9. [17] More, Utopia, 13. [18] Michael Freeden and Marc Stears, ‘Liberalism’, in The Oxford Handbook of Political Ideologies (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013), https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199585977.013.0020. [19] Paul, Thomas More, 99. [20] More, Responsio, 613. [21] Richard Marius, Thomas More: a biography (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 199), p. 235; Wolfgang E. H. Rudat, ‘Thomas More and Hythloday: Some Speculations on Utopia’, Bibliothèque d’Humanisme et Renaissance 43, no. 1 (1981): 123–27; J. C. Davis, Utopia and the Ideal Society: A Study of English Utopian Writing 1516-1700 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1981); Hanan Yoran, Between Utopia and Dystopia: Erasmus, Thomas More, and the Humanist Republic of Letters (Lexington Books, 2010), 13, 167, 174, 182-3. [22] More, Utopia, 229. [23] More, Utopia, 46. [24] More, Utopia, 71. [25] More, Dialogue of Comfort, 179. [26] Lyman Tower Sargent, ‘Ideology and Utopia’ in The Oxford Handbook of Political Ideologies (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013), https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199585977.013.0020. [27] This leads me to address the Erasmus-shaped elephant in the room: what about humanism? Even if Utopia is entirely critical, then the ‘ism’ that might be left standing would be humanism. It’s important to note, however, that humanism has been rather unfortunately named, as scholars agree that it is most definitely not a defined or coherent system of beliefs, but rather a curriculum of learning, an approach to the study of texts and at most a series of questions to which ‘humanists’ provided a variety of answers. One of those question does indeed address the best state of the commonwealth, to which Utopia is a – thoroughly enigmatic – answer. [28] ‘in Utopiensium republica, quae in nostris civitatibus optarim verius, quam sperarim.’ [29] More, Apology, 166. by Erik van Ree
Measured against the number of those who called themselves his followers, and given the speed with which these “Marxists” after 1917 laid hands on a substantial part of the globe, Karl Marx, in death if not in life, was one of the most successful people that ever lived. He falls in the category of conquerors, Alexander the Great and Genghis Khan, or of religious prophets with the stature of Jesus of Nazareth and Mohammed. The spectacular collapse of much of the communist world, of course, substantially detracts from Marx’s posthumous success, but it doesn’t annul “Marxism’s” earlier triumphs.
Marx’s twentieth-century followers reconfigured his ideas (as far as these were available to them at all) to the point of unrecognisability. The fact that both Pol Pot and Mikhail Gorbachev could wrap themselves in the master’s flag speaks volumes. But the fact remains that on whatever grounds and with whatever degree of justification, dozens of millions worldwide, on an historically rather abrupt time scale, began to call themselves “Marxists”. We follow Karl Marx. Why did these millions make this person their emblem? The question has no easy answer, if only because Marx’s worldwide success is part of the larger question of why communism, Marxist or not, for a time became the world’s wave of the future. The fact that the radically estranged twins, social democracy and communism, made spectacular strides in the late nineteenth and the twentieth centuries, as such, surely, has little to do with anything Karl Marx ever did or wrote. But why did so many socialists precisely select him and not, for example, Ferdinand Lassalle, Mikhail Bakunin or any other well-known radical onto whom to project their hopes and aspirations? I know why I did. If I remember correctly, I regarded myself as a Marxist from the age of eighteen. Undergoing a rapid process of radicalisation, I served as a member of various Maoist groups in the Netherlands between 1973 and 1981. In the wake of this experience I lost my sympathies not only for the Chairman but also for the alleged founder of the movement, Karl Marx. But I do remember what attracted me to him. My first political love as a youth was anarchism. What, in my imagination, made Marx so much more attractive was the way he managed to combine radical combativeness, also found in anarchism, with a sober, scientific perspective. Obviously, personal experiences of half a century ago represent nothing more than that—one person’s history. But not only do memories and experiences inevitably colour any researcher’s work, they may even be quite helpful in formulating hypotheses. I believe with Karl Popper that, as long as hypotheses are testable, their original inspiration can never be held against them.[1] What, then, did Marx have to offer potential “followers”? He was, I believe, one of the modern era’s great visionaries. Marx was a man of unusually broad interests and activities, engaging as he did in philosophy, economics, law, political analysis, journalism, and radical activism. What made him stand out among other potential world-level socialist gurus was the breadth and enormous diversity and scope of his vision, the extraordinarily multifaceted quality of his work, potentially appealing to people living in very different kinds of societies and of very different social position, views and temperament. Many Marxes The literature about Marx’s life and thought is so extensive that it is impossible to oversee even for researchers who have dedicated their whole life to the subject, a category the present author does not belong to. But it seems to me that the main existing academic interpretations of Karl Marx insufficiently bring out what made this man special and fascinating to so many people. I find four interpretations of Marx of special interest and interpretive power, even though I do not feel completely comfortable with any of them. The first, Social Democratic Marx is to be met, for example, in Geoff Eley’s Forging Democracy. This Marx recognised the futility of Blanquist secret societies and insurrectionary committees, while instead embracing the model of the political party of the working class. Marxist Social Democratic parties wisely made good use of their parliamentary positions.[2] This Marx furthermore made socialism dependent on the material conditions created by industrial capitalism, thus altogether ruling out proletarian revolution outside the industrialised world. Wolfgang Leonhard was one authoritatively (and quite rigidly) to characterise Marx thus, back in 1962.[3] That Marx predicated proletarian revolution upon the conditions of developed industrialism has become something of an established truth. Recently the thesis was repeated, for example, by Terry Eagleton and Steve Paxton.[4] Social Democratic Marx was, furthermore, a radical democrat. If he sporadically referred to the “dictatorship of the proletariat” he was merely referring to the rule of the working class, i.e. to majority rule.[5] The second, Revolutionary Marx was a Bolshevik avant la lettre. This frame is less well represented in the academic literature but is certainly not to be ignored. Central in Michael Löwy’s reading of the insurrectionist Marx is the “permanent revolution”. Löwy’s Marx accepted that, in principle, proletarian-socialist revolution was doomed to remain a fantasy without a preceding, protracted stage of capitalist development and/or a bourgeois revolution. However, Marx nurtured some “brilliant but unsystematised intuitions”[6] to the effect that the proletariat might yet induce a “telescoped sequence”[7] compressing the two stages into one and seizing power before the bourgeoisie had completed its historical task.[8] Reidar Larsson perceptively observes that, when between 1846 and 1852 Marx was creating strategies for proletarian revolution in Germany and France these countries were still industrially backward themselves. According to Larsson, Marx believed that by the 1840s, capitalism, even if still underdeveloped, yet had reached the limit of its capacity for development, which is what made the proletarian revolution timely even then.[9] Even if I personally find the Revolutionary reading of Marx more convincing than the Social Democratic one, both readings are convincing enough, referring us as they do to different aspects of Marx’s thinking and practice. Alvin Gouldner’s attractive thesis of “The Two Marxisms” is built on the idea of two spirits coexisting in Marx’s breast, both real, the one objectivist, relying on historical-economic laws, and the other voluntarist and emphasising human agency. Gouldner leaves open the question of whether Marx’s ambivalent ideas were irreducibly fragmented or, perhaps, expressive of some deeper coherence. The great merit of his work from my point of view lies in clearly establishing the multifaceted, diverse quality of Marx’s thinking.[10] The third Marx, Man of the Nineteenth Century, was born in 2013. Biographer Jonathan Sperber reads Marx’s life and thought as the product of an era impressed with the French Revolution, philosophically coloured by G.W.F. Hegel, and shaken out of balance by early industrialisation. This biographer sidesteps the whole question of the possible influence of Marx’s ideas on the modern world, as essentially irrelevant.[11] Sperber’s focus on what caused “Marxism” rather than on what it brought about seems to echo Quentin Skinner’s suggestion that historians do better to explore what authors meant to convey and achieve in their own times, than to lose themselves in imaginary, universal, and timeless elements of these authors’ ideas beyond their context of origination.[12] But, then again, irrespective of what historians may believe, millions of others did think that Marx’s ideas were worth following, and they patterned their actions on what they believed were his guiding thoughts. Even if they may have been misrepresenting these thoughts, we must discover the secret of their extraordinary attractiveness. Finally, the fourth, Demystified Marx, created by Terrell Carver, was an activist journalist locked in everyday life. His “thinking” was valuable enough, even for radicals today, but it was action-oriented and lacked the academic rigour even to be called a “thought”. Most of Marx’s more theoretical writings were never published in his lifetime and were mere messy fragments without much coherence or consistency. After Marx’s death in 1883 an everyday activist was souped-up into the great, world-class philosopher that he never was.[13] It seems to me that Carver does the thinker Marx less than complete justice. Even if, for example, The German Ideology (1845–6) was never more than a collection of fragments, to my mind that doesn’t change much. Even as fragments the texts remain fascinating and contain insights of great theoretical and sociological interest.[14] Marx’s posthumous fame rested on his ideas, compressed into theories, rather than on any activist achievements. His less than spectacular activities for the Communist League and the First International had little to offer the creators of his cult. Friedrich Engels, Karl Kautsky, Georgy Plekhanov and the others, framed Marx as the creator of their doctrine, not as their original super-activist or exemplary underground fighter.[15] That returns us to the question of what it was in these ideas that attracted so many. Marx For All Marx’s intuitive genius, which after his death made his name victorious for a time, consisted in an uncanny ability to combine what seemed uncombinable and to spread his wings to the maximum. While he vigorously denied that he was a utopian, he assuredly was one. In the new communist world envisioned by him all means of production would be socialised under self-managing democratic communes; the state and the great societal divisions of labour would be overcome; scarcity itself would be overcome, and with it money, ending in a condition where all would receive according to their needs. Marx countered accusations of utopianism by offering proofs that the new communist order was inscribed in history by the sociological laws he had discovered. He thought of himself as a man of science. It doesn’t really matter whether Marx’s philosophical exploits were of sufficient stature to call him a philosopher; or whether Das Kapital is to be regarded as a scientific or as a metaphysical work, whether on our present standards or on those of 1867. What matters here is only that Marx projected an image of himself as a scientist. Whether we call it “Marxism” or not, what Marx worked out represented an unusually attractive proposition, appealing to those caught in the romantic allure of communist utopianism as much as to the less euphoric radical attracted to science and rationality. This pattern of balance repeats itself over and over again. In the Communist Manifesto, Marx called out the proletariat for the battle of democracy. In his comments on the Paris Commune he embraced radical participatory democracy. But Marx also accepted the need of repressive measures to ward off “slave-owners’ rebellions” against the victorious proletariat, while over the years, together with Engels, referring to a future “dictatorship of the proletariat”. The power of Marx’s formula rested precisely in this ambivalence. Both radical democrats and those temperamentally inclined to harsh measures and dictatorship could feel represented by him. Not surprisingly, Social Democrats and Bolsheviks alike were happy to recognise this man as their founder. Again, if Marx insisted that communism can strike root only in highly-developed industrial societies, he did not in fact rule out proletarian revolution in backward countries, thus accommodating socialists both from advanced, industrial and from economically backward nations. Marx represented modern capitalism as a system of exploitation of wage-labour resulting in the gradual pauperisation of the industrial workers. The notion of “surplus value”, produced by the workers but appropriated by the capitalist class, possesses great mobilising power in conditions where exploitation and poverty reign. But Marx’s conceptual apparatus was encompassing enough to allow his followers to cast their nets far beyond these conditions. The concepts of “alienation” and “commodity fetishism” allowed later Marxists to remain in business to critique conditions in prosperous, post-industrial consumer societies, a form of society not even in existence in Marx’s own lifetime. Coherence The question remains of how to define the structure of Marx’s thought. How did Marx himself deal with his own thinking’s remarkably wide range and its concomitant ambivalence and contradictoriness? Where all these many ambivalent elements somehow welded together into an overarching intellectual structure, or were the contradictions indeed irreducible? Was there a system in Marx at all? There was surely not, insofar as his views on philosophy, history, politics, and economics do not hang together logically, but are best seen as separate endeavours. But it does not follow that he would not have been bothered by obvious inconsistencies and incoherence. Marx’s preoccupations shifted. Whereas the “Young Marx” was preoccupied with the problem of alienation, that theme later receded into the background, with the question of exploitation taking centre stage. But shifting interests are a far cry from contradiction. Marx regarded exploitation and alienation as the two downsides of the same coin of any social order based on private ownership, division of labour and the state. “Marxism” can, then, easily be framed as a single theoretical perspective speaking to the two conditions of exploitation and consumerism. It does not seem to have bothered Marx overly much that many of his extraordinary insights remained mere attempts, false starts, and fragments. Nobody stopped him from working out a formal definition of “class”, a crucial concept in his work. Marx could easily have accomplished that task, but he never did. Neither did he work out theories of the state or the nation, entities he wrote about all the time. Even his expositions of what came to be called “historical materialism” remained few and far between, and they were formulated loosely, sometimes downright sloppily, and in very general terms. Not a system builder, then. But this is not the whole story. Das Kapital follows a carefully crafted, deductive plan, based on clear and unequivocal definitions of “value”. Marx was immensely proud about his “discovery” that workers sell not their “labour” but their “labour power”, a conclusion that made his system logically flawless and allowed him to deduce “surplus value”. His argument that the expropriation of surplus value, i.e. capitalist exploitation, is based on equal exchange between workers and capitalists betrays great logical elegance. Marx was certainly not uninterested in coherence across the board. Achieving it could even be an obsession. All my three recent articles on Marx touch on the problem of coherence. They discuss, respectively, “permanent revolution”; Marx’s racism, which I argue was substantial and to a point theoretically grounded; and his views on the human passions as drivers of the developing productive forces and of revolution.[16] My particular interest goes out to such elements in Marx’s work as might be regarded as marginal but which on a closer look were significant. I find it especially interesting to explore how and if Marx made such eccentricities consistent with his other views more familiar to us, i.e. the problem of coherence. In exploring a historical personality’s thought, my primary interest goes out to its structure, how and to what degree it all hangs together—if at all. I realise that “finding coherence” not only carries the risk of finding what one seeks but also goes against the grain: the spirit of the times is rather about finding incoherence. Those affected with the postmodern sensitivity take pleasure in demonstrating that the apparent order we discover in theoretical structures really exists only the eye of the beholder. With the postmodern primacy of language and the discarding of the author as centred subject, the coherence-seeking thinker becomes a deeply counter-intuitive proposition. Postmodernity echoes the Buddhist view of the mind as a loose collection of fragments only weakly monitored by an illusionary sense of self. On the contrary, I work under the assumption that the individual mind to a point is centred and will attempt to hold the fragments together to avoid disintegration. This is never more than a hypothesis. Sometimes I have to admit defeat; as when, after much fruitless puzzling, I had to conclude that, whether the elderly Joseph Stalin’s political philosophy was more of the Marxist or of the Russian-patriot cast was a question he did not know the answer to any more than we do.[17] Permanent Revolution, Race, the Passions Back to Marx. In Löwy’s reading, “permanent revolution” is a highly significant element of Marx’s thought, but at basis remains an alien body. Capitalism must run its course. It must create a developed industrial infrastructure and must have exhausted its capacity for development for conditions of proletarian revolution to become mature. In economically backward conditions proletarian revolution is, then, at best, an odd occurrence—something that really couldn’t happen. Löwy solves the problem by assuming that Marx believed the capitalist and socialist stages exceptionally could be “telescoped” into one. But even then, the revolution must be saved from certain doom by revolutions in other, more developed nations. On this reading, Marx’s permanent revolution remains a very conditional, messy, and ad hoc proposition, inspired by revolutionary impatience. I believe there was considerably more logic and consistency to Marx’s revolutionism. As Larsson argues, in the 1840s Marx was under the impression that, even if industrialisation in most European nations, at best, was only beginning, crisis-prone capitalism had already lost its capacity for developing the productive forces much further. Fifty years later, in 1895, Engels admitted that he and Marx had made that mistaken appraisal.[18] So, Marx’s expectations of proletarian revolution in backward Germany and France did in fact not run counter to his stated view that capitalism must first run its course. Capitalism had run its course! And now that the bourgeoisie had lost its capacity to create the industrial infrastructure necessary for a communist economy, it was only logical for the proletariat to assume that responsibility and take over. “Permanent revolution” did not run counter to Marx’s insights about capitalism and the productive forces; rather, it seems logically to follow from them.[19] As for Marx’s racist views, he and with some different accents Engels too, worked under the assumption that human “races” differ in their inherited talents. Some races possess more excellence than others. Inherited differences in mental make-up between human races supposedly were caused by several factors, such as the soil on which people live; nutrition patterns; hybridisation; and—the Lamarckian hypothesis—adaptation to the environment and the heredity of acquired characteristics. Marx and Engels not infrequently stooped to derogatory and degrading characterisations of nations and races for whom had a low appreciation. Marx’s racism is acknowledged and deplored in the existing literature, but authors tend to read it as a strange anomaly incompatible with Marx’s overall system and, therefore, as an embarrassment rather than a fundamental shortcoming of his thought.[20] This is hard to maintain. As Marx and Engels saw it, systems of production are rooted in certain “natural conditions”—geological, climatic, and so on. Race represents one of these conditions, referring as it does to the quality of the human material. The inherited mental faculties of races, whether excellent or shoddy, help determine whether these races manage to develop their economies successfully. But, crucially, this does not undo or even affect the dependence of “superstructural” phenomena on economic infrastructures. Race is simply not about the relationship between these two great societal spheres. In Marx’s own imagination the race factor added a dimension of understanding to how or if economies come to flourish, but without in any way affecting the deterministic order of his economic materialism, running from the economy to state and political institutions. No incoherence here.[21] Something similar was the case with Marx’s remarkable views about the passions, which I have explored for the early years 1841 to 1846. In my interpretation of the philosophical fragments written in these years, Marx cast humanity as a productive force driven by creative passions: an impassioned productive force. If this reading is correct, this helps us understand why Marx assumed that economic and technological productive forces manifest an inherent tendency to accumulate and improve: it is because we passionately want them to. Conversely, it also helps explain why Marx believed productive stagnation makes revolution inevitable: humanity is too passionate a being to accept being slowed down. Marx’s “materialist” scheme of productive forces and relations of production, then, was predicated upon an essentially psychological hypothesis, a formula of materialised desire and subjectivity.[22] And once again, no incoherence here: the hypothesis of a creative, passionate urge fuelling the productive forces in no way conflicts with the “materialist” assumption of a chain of causation running from stagnating productive forces to the emergence of new relations of production to a new political and ideological order. Marx had remarkable integrative gifts; he was the master of combining the uncombinable. He managed to keep many of his wide-ranging intuitions, running in so many different directions, together in a single frame. Even if that frame often was incomplete and formulated in ramshackle ways, yet he managed to avoid all too glaring inconsistencies and keep a degree of underlying logic intact. Future Marx Does Marx have a future? There is much to suggest that he doesn’t and that the days of his posthumous success are finally over. Whether or not “actually-existing” communism reflected his ideas and ideals, its collapse and discreditation might be impossible for Marx’s ghost to recover from. Some deep processes have further contributed to Marxism’s demise. Marx’s core business was the industrial proletariat and the class struggle. But contrary to his predictions, the manual workers’ share in the industrialised world’s labour force sharply decreased in the second half of the twentieth century. What is more, far from becoming impoverished, the relatively small class of manual workers became spectacularly better off. Newly industrialising countries likely will manifest the same pattern. The new “precariat” of marginal and not well-off workers, often consisting of ethnically-mixed migrant populations, are more difficult to organise than the old proletariat concentrated in large factories. Marxism’s consolidated proletarian basis has, then, largely fallen away. Marxism thrived, too, on national-liberation struggles. National emancipation was an ambition Marx could sympathise with, even if never in a principled way. But he did support German, Italian, Hungarian, Polish, and other struggles for democracy and state independence. Not only class warriors, twentieth-century national-liberation warriors, too, could relate to him. However, with the end of colonialism the heydays of national-liberation wars are now long over. There is an end even to Marx’s scope. Present-day activists have a hard time reconnecting with him. In the new post-modern condition, emancipatory struggles have shifted towards issues of gender, sexual preference, race, ethnicity and religion, and, importantly, the environment—themes Marx’s voluminous works have little if any positive connection with. The new times have at last begun to make the man irrelevant. This is how things look now. But I am not absolutely convinced that Marx is irretrievably on the way out. The structural downsides of capitalism are such that, even if we regard that system as a lesser evil compared to communism, critiques of its downsides will continue to be formulated. Those interested in the more radical critiques of capitalism will unavoidably pick up Marx, still the most radical critic of that system available on the market of ideas. The theory of “surplus value” allows Marx to argue that capitalism exploits wage labour not because of any particularly atrocious excesses but quite irrespective of wage and working conditions. Wage labour is exploitation (and alienation). Marx was all for reforms, but in his book, reforms change nothing in capitalism’s exploitative and alienation-producing nature. That the theoretical basis of this uniquely radical critique of capitalism, the “labour theory of value”, is an empirically untestable, metaphysical construction hardly matters: stranger things have been believed. Whether Marxism will ever make a comeback depends on now unpredictable changing circumstances that would refocus global radical activism to once again target capitalist, rather than, for example, racist or patriarchal structures. Should that happen, Marx’s rediscovery as radical guide is likely. Marx’s ghost is waiting for us in the wings, happy and ready once more to offer us his services. [1] Karl Popper, The Logic of Scientific Discovery (London, New York: Routledge, 2005), 7–9. [2] Geoff Eley, Forging Democracy. The History of the Left in Europe, 1850–2000 (Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, 2002), chapter 2. For a similar interpretation, see for example: Gary P. Steenson, After Marx, Before Lenin. Marxism and Socialist Working-Class Parties in Europe, 1884–1914 (London: University of Pittsburgh Press, 1991), 20–1. [3] Wolfgang Leonhard, Sowjetideologie heute, vol. 2, Die politischen Lehren (/Frankfurt M., Hamburg: Fischer Bücherei, 1962), 106. [4] Terry Eagleton, Why Marx was Right (New Haven, London: Yale University Press, 2011), 16; Steve Paxton, Unlearning Marx. Why the Soviet Failure was a Triumph for Marx (Winchester, Washington: Zero Books, 2021), chapter 1. [5] See: Eley, 2002, 40, 509. Though emphasising the significance of the term “dictatorship of the proletariat” in Marx’s work, Hal Draper agrees that that it signified nothing more than “rule of the proletariat”: The “Dictatorship of the Proletariat” from Marx to Lenin (New York: Monthly Review Press, 1987), 22–7. [6] Michael Löwy, The Politics of Combined and Uneven Development. The Theory of Permanent Revolution (London: Verso, 1981), 189. [7] Ibid., 7–8. [8] Ibid., chapter 1. [9] Reidar Larsson, Theories of Revolution. From Marx to the First Russian Revolution (Stockholm: Almqvist & Wiksell, 1970), 9–11, 24–31. [10] Alvin W. Gouldner, The Two Marxisms. Contradictions and Anomalies in the Development of Theory (London, Basingstoke: MacMillan, 1980). [11] Jonathan Sperber, Karl Marx. A Nineteenth-Century Life (New York, London: Liveright Publishing Corporation, 2013), introduction. [12] Quentin Skinner (1969), “Meaning and understanding in the history of ideas”, History and Theory, 8(1): 3–53. [13] Terrell Carver, Marx (Cambridge, Medford: Polity Press, 2018). [14] On The German Ideology see: Terrell Carver (2010), “The German Ideology never took place”, History of Political Thought, 31(1): 107–27. [15] For the creation of the Marx cult and “Marxism”: Christina Morina, Die Erfindung des Marxismus. Wie eine Idee die Welt eroberte (München: Siedler, 2017). [16] Erik van Ree (2013), “Marxism as permanent revolution”, History of Political Thought, 34(3), 540–63; “Marx and Engels’s theory of history: making sense of the race factor”, (2019) Journal of Political Ideologies, 24(1), 54–73; (2020) “Productive forces, the passions and natural philosophy: Karl Marx, 1841–1846”, Journal of Political Ideologies, 25(3), 274–93. [17] Erik van Ree, The Political Thought of Joseph Stalin. A Study in Twentieth-Century Revolutionary Patriotism (London, New York: RoutledgeCurzon, 2002), 282. [18] 1895 introduction to “Class struggles in France”, Karl Marx and Frederick Engels, Collected Works, vol. 27, Engels: 1890–95 (New York: International Publishers, 1990), 512. [19] van Ree, 2013. More on the permanent revolution in Marx: Erik van Ree, Boundaries of Utopia – Imagining Communism from Plato to Stalin (London, New York: Routledge, 2015), chapter 5. [20] See for example: Roman Rosdolsky, Engels and the “Nonhistoric” Peoples. The National Question in the Revolution of 1848 (Glasgow: Critique Books, 1986), especially chapter 8; Michael Löwy, Fatherland or Mother Earth? Essays on the National Question (London, Sterling: Pluto Press, 1998), 23–7; Kevin B. Anderson, Marx at the Margins. On Nationalism, Ethnicity, and Non-Western Societies (Chicago, London: The University of Chicago Press, 2010), 52 and passim. [21] See for this argumentat in more detail: van Ree, 2019. [22] See for these conclusions: van Ree, 2020. |
Details
Archives
May 2023
Categories
All
|


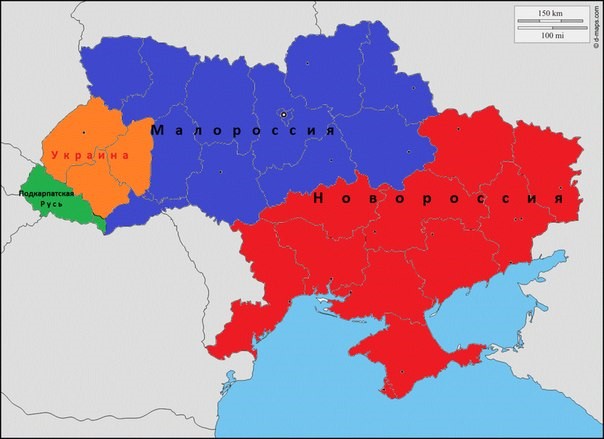


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed