by Marius S. Ostrowski
It has become customary to refer, in something like an air of hushed excitement, to a ‘renaissance in ideology studies’ that has taken place over the last quarter-century. Since the 1990s, so this narrative goes, ideology has emerged from under the long shadows of Marxism, the turn to scientism, the ‘end of ideology’, the ever-narrower self-reinforcing methodological spirals of comparative politics and cultural theory, to once again become a legitimate object of analysis in social research. Not only that, but in a way that it has never previously enjoyed, ideology has begun to move from a topic--one among many—in political philosophy, the history of ideas, social psychology, or sociological theory, to an independent area of study in its own right. The ‘renaissance’ in the study of ideology and ideologies has, in reality, been the ‘naissance’ of ideology studies as a discrete subfield.
Insofar as this ‘re/naissance’ has taken place, it has been in significant part due to the efforts of a handful of key theorists, who have battled to carve out a space for ideology and ideologies in university departments, research centres, and academic journals. One such theorist is Michael Freeden, who in the early 1990s developed the key underlying framework for the morphological school of ideology analysis. Based at the University of Oxford, then the University of Nottingham and the School of Oriental and African Studies, Freeden has played a vital role in the establishment and subsequent expansion of ideology studies through his long tenure as Editor of the Journal of Political Ideologies. In this capacity, he stewarded the journal from its inaugural issue in January 1996, coinciding roughly with France’s final nuclear test in the Pacific, Germany’s first Holocaust Remembrance Day, the release of the programming language Java and the first Motorola ‘flip phone’, as well as the immediate aftermath of the Bosnian War, until September 2020, deep in the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic, which saw the eruption of record-breaking wildfires across the U.S. Pacific coast, the burning of Europe’s largest refugee camp on Lesbos, the declaration by the government of Barbados to remove the monarchy and become a republic, and the outbreak of renewed border conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh. The collection of essays in Ideology Studies gathers together the majority of the editorials that Freeden wrote during the 25 years he spent at the helm of the Journal of Political Ideologies, lightly reframed into 17 substantive chapters. The chapters are grouped together into four themes that cross-cut the exact chronology of the original editorials: ‘Staking out the macro-agenda’ on what it means to study ideology and ideologies; ‘Unfolding vistas and paradigms’, covering some of the main evolving trends in ideology studies and political theory; ‘Boundaries and intersections’ on the thematic overlaps and exchanges between ideology studies and neighbouring subfields; and ‘Lived ideology’, working through some case-studies of how ideology works in society. As Freeden acknowledges at the start of the book, these thematic division perform a dual function. They are an attempt to corral otherwise disparate “contextualised, space and time bound, reactions to events, problems, and epistemological transformations” into an overarching meta-analytic framework of ‘what has been going on’ in ideology studies since the mid-to-late 1990s. But they are also “clues to some of the concerns closest to [Freeden’s] heart” as a seminal ideology theorist, as not just observer but participant in ideology studies’ emergence. To put it morphologically, this collection advances—by a mixture of implicit gestures and explicit statements—our understanding of the core concepts that comprise ‘Freedenism’ as a methodological outlook, as a metatheoretical map with which to navigate ideology and ideologies as objects of research. Yet even here, we already have to draw a careful distinction between several Freedenisms, of which this is only one. The chapters in this volume, even those that deal with substantive questions such as Brexit, the Afghanistan war, ‘cancel culture’, or ‘fake news’, only ever show Freeden in interpretive, ideology-theoretic mode. This is the Freeden of Ideologies and Political Theory (1996), The Political Theory of Political Thinking (2013), and to a lesser extent of Concealed Silences and Inaudible Voices in Political Thinking (2022): the conceptual morphologist, the syncretic, the diagnostician. Yet there is another side of Freeden’s work, another branch of Freedenism, that lies far more subdued in this volume. This is the Freeden who embraces more overtly his particular commitment to liberalism, not just in intellectual-historical interpretive mode, but also in ideological, critical or prescriptive mode: the Freeden of The New Liberalism (1978), Liberalism Divided (1986), Rights (1991), and Liberal Languages (2005). Even in his chapter on ‘Liberalism in the limelight’ as part of this collection, which takes as its starting-point the difficulties liberals face in adequately theorising the context and effects of resurgent fascism, exemplified by then-British National Party leader Nick Griffin’s infamous appearance on BBC’s Question Time in October 2009, Freeden’s own liberal commitments remain firmly in the background. This divide between ‘Freeden the morphologist’ and ‘Freeden the liberal’ reflects one of Freeden’s firmly-held commitments about what ideology studies is, illuminated by a clear description of what it is not. “Ideology studies—unlike their subject-matter—do not prescribe solutions.” Methodological theory is not substantive philosophy, ‘talking about’ is not the same thing as ‘saying that’. In order to preserve its uniqueness and independence as a subfield, ideology studies has to exercise stringent rigour to avoid betraying researchers’ ideological commitments. It has to stay always at one stage of remove: what I have elsewhere called ‘ideologology’, rather than ideology simpliciter. This is not least a profoundly strategic necessity, to preserve the legitimacy of the fragile niche that ideology researchers have carved out for themselves among their peers in the arts, humanities, and social sciences. Part of the uphill struggle that ideology studies has faced is not just against the often instinctive view that ideology is (to put it kindly) not a very good thing, but also against far-reaching scepticism that it is possible to make sufficient space for a diagnostic or historical treatment of ideology that does not just immediately bleed into critique or prescription. Freeden is convinced it is both possible and necessary to do exactly that. “[S]tudents of ideology should be exempted from an expectation to superimpose their personal recommendations on their findings. … They do not have an advocacy role. … [T]heirs is a different project, located in another part of a verdant wood … [that] demands of ideology students an entirely different set of skills.” What is this project? To this, Freeden’s answer is expressed in language that remains unwaveringly similar to that of his earliest interventions in ideology theory: “to explore, map, analyse, and enlarge” the conceptual frameworks we all use to make sense of what is going on in society. Not just the complex, nuanced philosophies of the elite specialist “professional formulators of ideas” but also the mass vernacular thinking of “laypeople, whether well thought-out or casual and under-formulated”. The thinking that is—not the thinking that was (history of ideas) or should be (ethics). Ideology studies in this independent form is needed precisely because it fills a niche of vital, salutary realism that has been bizarrely bypassed in the construction of the accepted boundaries of social theory and social science. Ideology studies does what other areas of social research do all too rarely: take ideas and the connections between them seriously as objects of study on their own terms. But it is not enough to simply affirm and celebrate the fact that ideology studies has been broadly successful in gaining a “permanent, respected, and integrated” place in academic social research. What ideology studies has begun to do, and what Freeden emphasises in some of the key chapters of Ideology Studies, is that ideology studies should now have the confidence to ask: where next? One of the most profound achievements of ideology studies, for Freeden, is to shift understandings of ideology away from “ideational products and arguments” towards the “complex cluster of practices that can be gathered under the container term ‘political thinking’.” Ideas, as combined and arranged into ideologies, do not just exist at the level of abstract universals, but also at the level of particular manifestations. Pace the traditional biases of political philosophy, all of these levels are, and of right ought to be, fair game for ideology analysis proper. Freeden presents this broad orientation towards ideas as well as the “shared identity and action patterns of human communities” that these ideas fashion as an anti-Kantian move, a calling into question of rigid distinctions between theory and practice. The future-facing challenge that Freeden poses to the subdiscipline is how to “unpack and decide what we see and hear when human beings express and conduct themselves in political terms”. Or, to put it differently, to dig more assiduously into what happens when ideology filters through from thinking into behaviour. Freeden frames the immediate next task for ideology studies as that of “relaxing ideology’s link with logocentrism”. For him, this includes “public rites”, “the body-language and conduct of people in positions of authority”, metaphors and tropes, the role of transmission media, “visual imagery” such as architecture and “political telecasts”, and the emotional content of language and memes—every possible form of ideological conformity and non-conformity that belongs to what he describes, evidently led by his recent focus on silence, as “non-verbal performativity”. With that, Freeden has set ideology studies in general, and morphological analysis in particular, on the path of gradually moving beyond exclusively seeing ideology in conceptual terms. Certainly, he remains committed to “[a]dopting the ‘political concept’ as the basic unit of the language of ideology”. Yet he recognises that bridging the false Kantian divide between theory and practice entails broadening this language to include terms that articulate not just the abstract mental content of ideological concepts but also their concrete physical, physiological manifestations. What remains less clear, however, is whether this broadened language also needs to be accompanied by changing or expanding what ideology sees as the ‘basic units’ of ideology analysis: concepts, yes, but alongside them also… what? Elements? Phenomena? Realisations? At the same time, while this certainly widens the terms of reference of ideology studies beyond the purely conceptual, it still implicitly treats the ideational aspect of ideology as primary. There is more to the social implementation, embedding, or entrenchment of ideas and ideology than communication, however generously defined. What is slightly missing is a recognition of just how deeply ideology percolates into the social reality we perceive around us, well beyond anything that could be classed as communication or discourse: our mental and physical outlooks, our routines and procedures, the groups and institutions we belong to, even the circumstances and events we find ourselves caught up in. While these are certainly implicated in morphological analysis à la Freeden, they appear only insofar as they can be deemed to be (quasi-actively) communicating ideas in a specific, narrower sense, rather than (more passively) representing or manifesting them in a broader way. For Freeden, the logocentrism of ideology studies should be relaxed, but not abolished entirely. Nevertheless, there is a hidden radicalism contained in Freeden’s aspiration that could be pushed far further than happens in this volume. In addition to the turn against logocentrism, one of the most important contributions that ideology studies can make to the wider study of how ideas work in society is to inveigh against canonicity—especially but not exclusively in the history of ideas. Freeden’s insistence that “[t]he study of ideology will still involve individual thinkers—but as representatives of an ideological genre” is replete with possibilities for novel analysis. Rather than the model of (pale, stale, male) prominent individuals who pushed and remoulded the boundaries of ‘their’ ideologies through their promethean thoughts and herculean actions, ideology studies has the tools to foreground the collective, interactive formation of ideological maps through groups and networks—from diffuse crowds to disciplined cadres. This includes analysis of the cross-cutting publics and counter-publics that lead to dynamics of ideological hegemony and counter-hegemony (bourgeois versus proletarian, patriarchal versus feminist, and so on), and the subaltern narratives (e.g., ‘people’s histories’) that can be told about how societies change over time. But it also means sharpening the focus on ‘vernacular’ thinking and ‘ordinary’ behaviour to look at how ideologies are not just invented but also replicated and perpetuated through our thinking and behaviour in everyday life. This ‘decanonisation’ mission of ideology studies lends an additional urgency to Freeden’s plea that “the scholarly profile of ideology studies needs to be raised substantially”. For Freeden, this is not just a matter of ensuring ideology theorists do not become complacent about how much they have achieved over the last couple of decades, but also a recognition of how much further there is still to go. To put it brusquely, a lot more ideology theorising is still needed if ideology studies (as part of ‘political studies’) is to catch up “with the parallel bodies of theory available to economics, sociology, psychology, and to the institutional side of political science”. In other words, it is all very well for social researchers who work on ideology to complain (quietly or loudly) that ideology is always the bridesmaid and never the bride—an afterthought in the later weeks of someone else’s syllabus, or in the second- and third-year options in someone else’s degree. If they want to put ideology front and centre, they (we) will have to put in the hard scholarly graft to grow ideology theory to an appropriate scale and complexity. In part, this means keeping up the gradual process of détente towards “political and ethical philosophy on the one hand, and the history of political thought on the other”. In part, it means deepening the areas of cross-fertilisation between ideology theory and other subfields: Freeden explicitly picks out conceptual history in its Koselleckian vein and the Essex school of discourse theory, as well as theories of emotions and rhetoric. But in part, it also means relying on the exponents of “Marxist theories, critical theory, discourse analysis, attitude studies, and everyday preconceptions” to cease their frowning, obstructive reticence whenever the topic of ideology is mentioned. The happier news, for Freeden, is that ideology studies conceived as a subfield offers a ready-made “integrated resting point” where all these fractious perspectives can be housed under one roof. Under Freeden’s scrupulously watchful eye, the Journal of Political Ideologies has acted precisely as a pluralistic forum where scholars who study ideology and ideologies can ply their trade, no matter their methodological creed—as long as their centre of gravity is overwhelmingly diagnostic or historical, rather than critical or prescriptive. But that is only half the story. Really constituting ideology studies as a subfield relies on more than “chance encounters”, and needs the emergence of cross-fertilising exchanges and hybrid approaches that start to thread together different ways of theorising ideology into various models of ideology theory. Without that, ideology studies will only remain a hollow umbrella term that describes bits-and-pieces forms of ideology analysis hived off into mutually incommunicative subfields. Part of this consolidating process will be to thicken the terms of analysis that ideology studies (as opposed to any other subdiscipline) uses to evaluate ideologies. These terms should be autonomous and distinctive, not borrowed from other subfields, which prima facie includes “alter[ing] the assessment criteria of ideological success … from the substantive value-oriented standards political theorists have habitually applied to gauge their ideational produce”. They ought to cover characteristics that are more-or-less unique to ideologies, such as “historical contingency”, “discursive indeterminacy”, “overwhelming detail”, or “interpretative fluidity”—although even within these fairly parsimonious parameters, there is still plenty of room available for evaluative thickening. Freeden first issued this cri de cœur in 2001, but it remains just as apposite in this reissued form over two decades later. Political theory has tried what essentially amount to theoretical half-measures to achieve something like the criteria shift that Freeden has in mind, in the form of the ‘realist’ turn and the ‘political’ turn—both of which Freeden scrutinises in this volume. But neither effort was truly geared towards modifying how ideology studies relates to its own object of analysis. Rather, they were attempts on the parts of disaffected political theorists who did not typically think of themselves as doing ideology research to come up with ways to combat the perceived ‘overreach’ of ethics into how political theory is done today. As far as ideology studies itself is concerned, its innovations have (unsurprisingly) tended to track trends in ideologies themselves, from emerging ecological concerns and successive new waves of ideologies of identity, to “fashions and impulses” such as populism and globalism. Of course, new ideological trends will keep coming, and ideology studies will study them, und das ist auch gut so! But the insufficient depth of introspection on the topic of how we evaluate ideologies is one reason why the “journey” of ideology studies is so “slow—and still unfinished”. A key question for ideology studies as it turns to this task is how it maintains its humble, self-aware commitment to pluralism even while many of the objects it studies are relentlessly monistic and self-asserting. How, in other words, we can come up with distinctive criteria of success and failure while holding onto “a tentativeness about [our] own preferred solution and a toleration of many others”. Besides this, Freeden names a few key areas where ideology studies can afford to delve deeper into the fertile ground it has uncovered over the last few decades. One is a better assessment of the rates at which “the different internal components of an ideology can change … a core usually altering more slowly than the adjacent and perimeter concepts and ideas that encircle it”. Paired with the destabilising and rejuvenating effects of unpredictable social crises on the content of established ideologies, this points towards a greater, more granular micro-level engagement with the moments and processes of rupture, and the essential contestations and decontestations, cooptions and divestments they carry in their wake. Another area of deeper investigation, modelled on Freeden’s assessment of the “birth pains” of the Journal of Political Ideologies, is the “institutional story” that can be told for the key hubs of ideology research—as well, of course, as the apparatuses or dispositifs that act as sites of ideological production in wider society. In this respect, a ‘sociology of the ideology studies subdiscipline’, including a view on why it was only in the 1990s that it finally began to emerge, fits within the more general sociology of knowledge that has existed in broad alignment with ideology research since the time of Karl Mannheim. In one respect, however, the question of ‘where next’ remains unanswered by Freeden’s volume—or rather, perhaps, one avenue of ‘where next’ is kept more-or-less resolutely closed. The relationship, or even the virtual equivalence, between ideology and politics remains a core feature of methodological Freedenism, if anything even more firmly delineated than at the start of his tenure at the Journal of Political Ideologies. “[M]y focus advanced from identifying the features of thinking ideologically to those of thinking politically.” It is not that Freeden’s definition of ideology as “a set of ideas, beliefs, opinion, and values that serves to justify, contest, or change the social and political arrangements and processes of a community” has become more overtly politicised. Rather, he has chosen to subordinate it to a more “expansive view of the ubiquitous nature of politics”. “Thinking ideologically” is the same as “thinking about politics”, and so is necessarily “intertwined” with “thinking politically”. On that basis, ideology theory is a form of political theory, ideology studies is a subfield within political studies, and the study of ideologies is the same as the study of (historical or contemporary) political thought. This dimension of Freeden’s theoretical evolution is arguably the hardest pill to swallow against a societal and intellectual background where unmistakeably ideological dynamics have risen to the fore that sit partly or even wholly in social domains beyond the political. The explosion of (specialist and vernacular) interest in an ideology of ‘neoliberalism’ has uncovered the contestations among proponents of (e.g.) neoclassical, neo-Keynesian, Austrian, Georgist, Marxian, and Sraffian theoretical positions in economic thought that only rarely filter through to the worlds of public policy, electoral democracy, or state administration. The same is true of the running battles between defenders of formalism, originalism, realism, strict constructionism, structuralism, and textualism in legal theory—which, again, have political echoes but are not in themselves primarily political. While it is doubtless fair and theoretically profitable to highlight the political aspects or effects of these avowedly non-political disagreements, it is unnecessarily flattening to restrict the purview of ideological analysis to only these parts of their societal impact. What is at risk of being lost here is the “social and political arrangements and processes” part of Freeden’s original definition of ideology. Even if we want to retain and pay due respect to the familiar alignment between ideology and politics, the rest of society should at least receive an equal amount of airtime too. The broader message we should take from Ideology Studies on this point, however, is that politics is back. If the 1990s were the era of the ‘third way’, ‘post-politics’, triangulation ‘beyond left and right’, and other claims to ‘non-ideological’ pragmatism, the 2020s are a time not only of self-evident division and polarisation, but also of an increased appreciation of the role that politics in all its forms (from mass activism to state action and beyond) can play in changing the face of society. In this way, the ‘renaissance of ideology studies’ has accompanied, almost seamlessly in tandem, the steadily rising disenchantment with the ‘end of history’. As history has returned, in the form of perpetual wars, financial stagnation and collapse, ecological disasters, pandemics, and other aspects of a growing ‘polycrisis’, ideology has come back with it, firmly but quietly clasping history by the hand. In this light, Freeden’s collection of editorials is akin to a chronicle of the journey that ideology and its study has undergone during a key period of ideology studies’ foundation. If ideology studies is, as he argues, still very much a subdiscipline in transition, then this volume represents a considerable milestone on the way to its gradual consolidation. It is a salutary reminder to students and theorists of ideology alike of where we have come from, and where we should go next. by Richard Shorten
Author's Note: The expectation to communicate from personal experience is a crucial driver of modern politics. A recent book I have written, The Ideology of Political Reactionaries, shows how reactionaries have mastered, but subverted, this expectation. Therefore, progressives need to do better. Voice has ‘who’, ‘how’ and ‘what’ aspects that need exploring both more explicitly and more creatively. My short discussion distils voice into six foremost elements: argument style, emotional tone, metaphor, prioritising, humour, and personality. Together, these can be wrested into ways for exercising voice in greater (and more meaningful) equality, co-operation, and solidarity: respectively, to reflect, to feel, to connect, to weigh, to confide, and to become energised.
* * * Academics used to like to define politics as a matter of ‘who gets what, when, and how’. Lately, it has become a matter of who can say what. And how, and when. ‘Culture wars’, ‘wokeism’, and ‘cancel culture’ are all names for things that make people more aware that there is nothing irrelevant or nondescript about voice. Nor is there anything innocent about it. Voice is what people—not just politicians—use to make them real for others. And, it might be added, for themselves. Hence the two parallel expressions, to ‘find one’s voice’, and to ‘give voice’ to others (via an originating act of the giver’s own voice, that is). But ever since the global financial crisis of 2008, progressives have surrendered this ground, and done so meekly. So, in relation to predictable but also unpredictable public issues, reactionaries have grown mutating and enlarging constituencies of support, many proving storm-like and short-lived, but some showing worrying signs of being longer-lasting: enthusiasts for Trumpism post-Trump; immigration and climate change deniers morphing into Covid vaccine sceptics; Zemmouristes, as well as Lepenistes, outlasting the gilets jaunes in France. The Ideology of Political Reactionaries tries to distill the reactionary voice, to break it down into its ingredients and make it plain. There is a baseline unity to reactionary ideology, notwithstanding its varying content across particular iterations: all reactionary ideology (from Euroscepticism in its mild form to neofascism at its strongest) participates in the prominent sounding of a rhetorical core comprising indignation, decadence, and conspiracy. Aside from the getting the historical and contemporary records straight (reactionism has a shady border with conservatism; reactionary ‘nostalgia’ is chimerical because the message is always more embittered than melancholic; the explanation by post-truth ignores the persistent fetishisation of facts), the study is intended as a nudge towards building a more desirable rhetorical public culture. How do language, tone, and style connect reactionaries in and across Europe and America’s past and present? What starts to look enduring at least once the fascination with the apparent novelty of digital media is scaled back just a bit? And what do things look like when we lay out beside one another quite diverse packages of words and gestures for comparison and inspection? Such examination ought to be revealing, even if the lessons for progressives will, in the first instance, have to emerge by default inversion. And equally, it will show that ‘who can say what, when, and how’ is not simply a topical problem of politics and culture. It is actually quite an old one. Reactionaries do not reject the in-vogue imperative to communicate from personal experience. Publicly, and on the surface, they might demean it. But, in truth, they subvert it. Reactionaries know that the authority to speak is closely bound up with personal involvement in what is spoken (i.e., having skin in the game); timing (e.g., taking care not to speak before others have been heard); and manner. They know this, even if their ‘knowing’ should really be understood more as the product of habit and inclination than of implausibly all-seeing calculative intent. On a tentative estimate, they know, and subvert, voice in at least six ways. Argument style Perhaps the first rule of voice in politics is that the task is to make space. Reactionaries recognise this, and one thing they are always sure to do is to make space to reflect. They upend progressive calls to reflection. They do their best, in written and spoken word, to steer any thinking about politics whatsoever through the prior filter of a story about the unstoppability of decline. Such stories—which technically are ‘narratives’ (in the meaningful way, not in the way dulled by generalised over-use to refer to any sense-making exercise whatsoever)—vary in content. But invariably, they are all-absorbing. Progressives ought to do nothing so grandiose as to craft sweeping counter-narratives. But they must find ways to open up, and in due course expand, alternative spaces for reflection, spaces that that are focused around objects of concern that are simultaneously human and humane. Human, because they will resist being formed around immovable abstractions (which is the historical case of adaptable reactionary fixation around ‘revolution’, ‘defeat’, ‘feminism’, etc.).[1]). Humane, because space-shaped reflection would be unapologetically ethical, impatient with the conjuring of ‘liberalism’ into the enemy, or with the celebration of conflict for opposition’s sake. Emotional tone Not only as an afterthought, making the space to feel must take up an important place next to making the space to reflect. The objects of concern created by the reactionary voice are self-referencing: reactionaries pity themselves and those like them. This is the glue that binds. It is also the basis for feelings that are externally directed towards what are made into targets, specifically, targets of anger. The sense conveyed that this anger is not something that has been heard to date—that it has been suppressed, unacknowledged, allowed to fester—is how a circle is squared with the timing rule: licence for reactionaries to speak is to have successfully created the impression that those people being spoken ‘for’ have long been unheard, and remain still unheard. But used creatively in collective life, emotional tone of voice makes people attentive—thereafter receptive—to the vulnerability of others, who, moreover, are others in their fullest diversity. Hence moral philosophers talk of the ‘circle’ of concern. The task, by modulating tone of voice, is to expand that circle, and to do so without de-intensifying attachments in the process. Uplift, good will, faith in others: the promotion of all these things is often made to seem trite, a pathology of the extension of psychotherapeutic language into politics. But that itself is a function of the snare of cynicism in contemporary rhetorical public culture; in turn, a complex cause and effect of reactionary ‘edginess’ in its particular alt-right incarnation. Feelings liable to be dismissed as trite in any case do not exhaust the range of emotions far more likely to be timely to any moment than unspent self-pity: sorrow at wasted lives and livelihoods; outrage, not festering anger, at perpetration, complicity, or indifference. Metaphor Making the space to connect is another capability of voice. Metaphor connects the person to other people; it also helps that person to connect things to things. Reactionaries cement fellow-feeling with others who are not really like them, not in a way that couldn’t be challenged by more plausible connections; connections far more immanent in the the structures of social and political experience. Reactionaries do so by act of making the particular universal, or the part into whole (which more technically belongs to the branch of metaphor that is metonymy). In this way, dethroned monarchs, culturally-mocked millionaires, and failed artists can all be made mirrors to the hardships of the truly vulnerable, because the suffering in each of these scenarios—and the suffering of individuals—becomes representative: not statistically or descriptively representative, but symbolically representative. (Victimhood becomes the state of being belittled in whichever way makes meaning reflect back in this conveniently dangled mirror.) How reactionaries connect things-to-things is by metaphors that are dominantly naturalist and hyper-masculinist. Metaphors from ecology or biology, in particular, dramatise what thereby becomes deep-rooted, health-threatening decline, in idioms that can extend to the frankly carnal. An under-appreciated aspect of the ideology of Eric Zemmour, for example, is the loss of male virility (which, inside his 2014 book The French Suicide, is far more a trope than the national ‘suicide’ of the title). Decoding reactionaries by metaphor is one step towards disarming them, but the next task is to turn the metaphors inside out, to craft them to more humane purpose and effect. One way of doing this is by explicitly reclaiming bodily metaphor, for it is the body which provides human vulnerability with its shared site. Another way of doing so is to take the structure of analogical reasoning (which works on the idea that because you accept something similar already, you will accept something else proposed), to wrest it away from its dominant reactionary or conservative uses (in idealisation of the status quo or status quo ante), and to place it into progressive use. Co-opted analogical reasoning would work on the idea that what has most meaningful prior acceptance is not overtly bound to parochial culture: people’s most pre-existing commitment of all is to be their best selves. Prioritising Prioritising by voice is identifying issues and embracing the task to weigh. Reactionaries weigh issues often with outward portent, but, ultimately, trivially. They do so habitually by lists, or by acts of either linguistic or literary brutalism. List arrangements of projected wrongs and grievances allow for the heaping up of externally-directed criticism and censure, fabricating the illusion of rising gravity. By imagined actions (or sometimes by sheer temerity of existing) migrants, ethnic Others or cartoonised social justice warriors can made to bask in the negative spotlight, and on that basis be made to shoulder blame for whole unlikely catalogues of sins. Brutalism in words and sentences is the creation of heightened urgency by graceless transition, jolting an audience into attention; and, by unfortunate correlation, repeated jolting has the simultaneous effect of deadening human sensitivity. Lists plus brutalism may not exhaust reactionary techniques for deleteriously amplifying concerns, but above all this is a faux seriousness, a seriousness of the shrill or the pompous. What it doesn’t need is more of the same in reply. In the political act of prioritising—which is necessary not primarily because decision-making capacity is finite, but rather because the political imagination is drawn towards specific things and/ or specific persons—the practice of hierarchical ordering is hard to dispel in its entirety, but comes with downsides that may nevertheless be counter-acted. To be sure, listing bona fide wrongs has a dignity that listing imagined injustices does not. However, within contemporary culture, bona fide wrongs have frozen into competitive victimhoods: injury by racism versus class; by sex-based versus gender-based oppression; by historical fascism versus historical colonialism. And one way of chipping away at this (by wakening metaphor again) is to try to introduce alternative spatial orientations into public language: suffering that is neither ‘above’ and ‘below’, nor ‘before’ and ‘after’. Are there ways of juxtaposing experiences that are more consensual than conflictual? Ways that will not cancel out sympathy generated, but render sympathy liable to be reproduced in many directions, even perhaps in ever more fine-grained complexions? Humour Humour in voice is, or can be, a way by which to commune: to confide, to reassure. In reactionary voice, it is anything but. Psychologists of humour talk of humour style, and reactionary styles of humour tend strongly towards the maladaptive, i.e., aggressive. Rarely do reactionaries participate in the affiliative style of humour which (to play upon the original religious meaning of ‘to commune’ from communion) is capable of firming up human relationships by exchange of thoughts and feelings. Reactionary humour is the humour of put-downs and jibes at out-groups, destructive of bridge-building between people. Fairly recently, in the United States, Sarah Palin—the vice-presidential contender and under-emphasised forerunner of Donald Trump—developed a political style that gave a lot of time to unkind mimicry. In British politics, Nigel Farage experimented with a humour style that drifted into bullying, offset only partially by the kind of jocularity that gestured beyond the aggressive by virtue of being self-effacing and buffoonish: the notional punches-upwards could be unceremoniously dumped for punches-sidewards, soon becoming punches-downwards (recall the public humiliation of Herman van Rompuy in the European Parliament). In the terms of theories canvassed across the history of thought, then conspicuously often—to the point of being a rule—the humour of reactionaries matches the comedy identified by Hobbes, operating by ridicule and superiority; not the tension-release by laughter observed by Freud, and still less the comedy that arises out of incongruity (between expectation and occurrence, between unconventionally paired ideas). Alternatively, non-Hobbesian humour is only at a very crude level urbane and elitish, or metropolitan because cosmopolitan. And it is very far from being exclusive since (in a last piece of humour taxonomy) it is open to expression in whole range of types: from the dark, dry and droll, through to the satirical, slapstick, and screwball. In France, currently, Eric Zemmour does possess a more stylish line in witticism. His niche in The French Suicide is to observe paradox, presented as incongruity between the intentions of both leftists and liberals and the effects of their policies. But his paradoxes are not really paradoxes: they are wilfully dark contrasts (such as that gay people were freer when encouraged to be discreet about their sexuality, or that straight women could be less guilty about sex when there existed rigid social norms to police their access to it). And in the process, there may be an instructive lesson about the need to unpick nuances in the uses of dark humour: Zemmour’s are wilful contrasts not only in the sense of being false, but also in the sense of being, ultimately, victim- (and not victimiser-)mocking. As such, shorn of the more appealing victim-empathising quality of ‘gallows humour’, the humour in his book is reduced to word-play. Which is clever, but not funny. Personality Voice also offers, lastly, the chance to inspire, in the possibility of positive response to the comportment of others. This last thing reactionaries know is that expressing viewpoint is simultaneously opportunity to display the virtues one carries. In reactionary practice, those are shallow virtues at best, and misguided inspiration. Charisma is more often bombast. Authenticity is double-edged, and in any event is contradictory to charisma. Bravery is martyring. Bragging should not be mistaken for much inspirational at all. And publicising insider knowledge—Trump’s business prowess, Farage’s Brussels days, Joseph McCarthy’s dogged curiosity—is (as well as in tension with flagging outsider credentials to denigrate ‘expertise’) the accomplice of community-destroying conspiracy claims that are reliably present. This is not collegiality; not integrity or honesty; not gentleness and generosity; not constancy or meaningful self-knowledge. There is, to appreciate, an intrinsic difficulty in trying to craft the progressive articulation of personality in voice: the infra-person location of vocal chords, or the hand-gripped wielding of the pen, point to the hazard of carrying over-exaltation of individual action into the securing of new collective space, pushing against the collective exchange of perspectives. So, minimally, one part of comportment must tasked with trying to find a balance with modesty, as well as with trying to achieve a particular split: between twin tasks of showing one’s skin in the game and bringing others into it. It is here, finally, that some existing conceptualisations of voice on the progressive side of politics are suspect. To be sure, from out of the conventions of academic political science, these present accounts improve vastly on the most established, most frequently-cited account: a 1970 text which makes voice into an alternative to ‘exit’, into a grossly individualised phenomenon, and, fundamentally, a matter of interest, not principle (in effect: ‘I’m not very happy about this, so I’m saying so’). But the dominant, progressive accounts are suspect nevertheless, and suspect, specifically, in respect to the conceptualisation of movement. Rightly, they contest the uniform flatness—the stuckness—of reactionary representations of ‘vox populi’: instead, at their best, they stress the importances of co-creating the meaning of experience, and fashioning demands on that basis. And rightly (albeit from a distinct angle), they stress the ‘situatedness’ of voice. Yet working against these stresses, they tend to portray the who-ness of voice as if the issue were pre-settled. Plus, on the issue of what people ought to do with voice once they get there, they are hesitant, such that they under-estimate the complexities of ‘when’ and ‘how’. Enabling voice, whether for progressives of either a moderate or more radical kind, presently tends to be understood as a single movement: either to or from a single location. Just the direction is reversed. For moderates, the movement is dominantly ‘toward’—in which voice is something graciously presented to somebody, as though receiving a gift-giving guest (‘there you go, here is voice, now use it’). For radicals, the movement is ‘away from’—by beseechment to join something at some distance from a starting point (‘“come to voice” with us’)—and with just a hint that before being exercised, the new joiners’ voices will need to pass through a final stage of screening by older occupants. The future situational pressures on voice cannot, by nature, be foretold. But if the inverted lessons from reactionary practice are instructive, then the desiderata for better voice will—centrally—comprise maximal inclusion, minimal coercion, or pluralism in balance with empathy. From this starting set of features: to reflect, to feel, to connect, to weigh, to confide, be energised. To genuinely co-create. To use voice so that it sounds—then echoes—in a multitude of directions. Above all, to use voice to make space so that others might find space in it of their own. [1] Note that this immovability by abstraction can even be a risk for contemporary progressives, who, following a very timely call for an appreciation of what is ordinary (cf. Marc Stears, Out of the Ordinary: How Everyday Life Inspired a Nation and How It Can Again [Belknap Press, 2021]), can often be drawn towards abstractifying the value of the ‘everyday’. 25/4/2022 Revisiting the original Palaeolithic democracies to rethink the postliberal democracies of the futureRead Now by F. Xavier Ruiz Collantes
Why do we overlook the original democracies?
God created the world six thousand years ago. Human beings are not related to primates. There is no such thing as climate change. The first democracy emerged in classical Athens. There are some important groups that continue to hold fast to certain beliefs, despite the availability of a mass of contrary evidence. One such group is composed of many people interested in history, philosophy and political theories. While there is ample evidence that democratic principles were applied to power relations in Palaeolithic Homo sapiens communities tens of thousands of years, i.e., long before the Athenian democracy of antiquity emerged, a mainstream claim in history, philosophy and political theory discourses continues to be that democracy first emerged in Athens. It has been documented, in the political anthropology and evolutionary anthropology fields, that the first political systems—those that have governed us for most of our existence on this planet—were democratic. The existence of these democracies, which I call the “original democracies”, is confirmed by two types of evidence. Firstly, in different parts of the world, hunter-gatherer communities that have survived in a form close to their original Palaeolithic form, organise themselves politically according to democratic principles, e.g., African peoples such as the Bushmen and Pygmies, Australian and New Guinean Aborigines, indigenous Amerindian peoples, etc. Secondly, Palaeolithic fossil records provide evidence of egalitarian and non-hierarchical societies. Considering just the Upper Palaeolithic,[1] democratic hunter-gatherer communities lasted several tens of thousands of years; in contrast, non-democratic, authoritarian systems only began to emerge less than ten thousand years ago, during the Neolithic,[2] with the consolidation of agriculture and livestock herding and a sedentary way of life. The fact that many historians, philosophers and political theorists hold that democracy first emerged in classical Athens is certainly problematic, yet it is also very significant, because it reflects perceptions of our species derived from the epistemological bias of Western and contemporary culture, determined by extreme chrono-centric and ethno-centric perspectives that run very deep. Ultimately, such perspectives contribute to placing the contemporary white race originating in Western culture at the top of the evolutionary tree and legitimises its usurpation of the planet. Numerous authors, however, when they write about democracy, also refer to Palaeolithic democracies, e.g., Federico Traversa, Kenneth Bollen, Pamela Paxton, Doron Shultziner and Ronald Glassman. [3] Those democracies of the Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer peoples are called “Palaeolithic democracies” by Doron Shultziner, “community democracies” by Federico Traversa and “campfire democracies” and “clan and tribal democracies” by Ronald Glassman. I suggest that these democracies should preferably be called "original democracies”, first, because this term better reflects the importance of these democracies in the evolution of humanity, and second, because it establishes a chronological sequence going back in time, from modern democracies to ancient democracies to the original democracies. The evolution to Homo sapiens: a journey towards democracy Palaeolithic democracies, which emerged in all parts of the world settled by Homo sapiens, undoubtedly represent the most important cultural development of our species, first, because these democracies reflect almost all of human existence, and second, and more importantly, because these democracies have greatly shaped the natural and cultural tendencies of Homo sapiens. Joseph Carroll [4] identifies four different power systems, reflecting periods from the emergence of hominids to the Homo sapiens of today: (1) alpha male domination; (2) Palaeolithic egalitarian and democratic systems; (3) despotic or authoritarian domination as emerged with the Neolithic; and (4) Western Modernity systems deriving from democratic revolutions. Homo species split from the pan species about six million years ago [5]. This evolutionary divergence reflected a journey to democratic communities from the alpha male-dominated despotic communities, typical, for instance, of current great apes species such as chimpanzees and gorillas. The evolutionary journey to Homo sapiens is, therefore, also a journey from despotism to Palaeolithic democracy. Broadly speaking, what we understand by a democratic system for organising and equally distributing political power within a community is specific to Homo sapiens. Various factors led to the disappearance of the alpha male in Homo sapiens hunter-gatherer communities. The advent of lethal weapons meant that subjugated individuals could easily kill an alpha male; the need for cooperation in hunting and raising children generated a communitarian and egalitarian spirit; and the development of hypercognition and language meant that decision-making affecting a community could be based on open and joint deliberation by members. The tens of thousands of years in which humans lived in Palaeolithic democratic communities has left deep marks on our species. These include the development of discursive capacities that enabled deliberation, negotiation and cooperation and also the burgeoning of a certain morality based on the principles of justice and equity. This morality, original, egalitarian and democratic originated in the Upper Palaeolithic, explains why present-day humans are largely repulsed by abusive coercion, non-legitimate power and arbitrary decisions deemed unjust. While humans have inherited (from the hominin species prior to Homo sapiens) a tendency to dominate others, they have also developed al sense of egalitarianism and anti-domination. Our social morality and politics operate within this contradiction. For all these reasons, while we have a tendency towards domination over others, we also tend to reject domination over ourselves and others. The sense of democratic and egalitarian morality that beats in the heart of humans is largely due to the evolutionary development of Homo sapiens living in democratic and egalitarian hunter-gatherer communities of the Palaeolithic. Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer communities, and later tribal societies, did not have a state, as this form of governance developed later from primitive chiefdoms and kingdoms. But the fact that there was no state did not mean that there were no politics and no social power systems. Circumscribing politics exclusively to societies with a state reflects chrono-centric bias. The original Homo sapiens communities clearly demonstrate that politics reached beyond the historical existence of the state. The main problem in considering hunter-gatherer communities to be fully democratic is that, in those peoples that survive to this day, the most important decisions are generally made by adult males. While the exclusion of women would suggest a significant democratic deficit, it is no greater a deficit than that of classical Athens or even, until universal suffrage for men and women was finally introduced, of that of our liberal democratic societies. Nonetheless, this issue has given rise to controversy, as important archaeologists and anthropologists, such as Lerna Lerner, Riane Eisler, and Marilène Patou-Mathis, [6] argue that women during the Palaeolithic had the same prestige and power as men and that this status was not lost until the Neolithic. As evidence, they indicate that the archaeological record does not unequivocally demonstrate that men had a superior status to women, and they further argue that the notion that Palaeolithic women were subordinate is simply a product of the andro-centrism that overwhelmingly dominated early archaeology and anthropology work. If women did indeed possess the same status as men, then those communities were truly democratic. There is a fundamental problem in studying Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer communities from similar communities that have survived to the present day, namely, that, in recent centuries, many of the surviving communities have seen their original way of life contaminated, degraded or radically suppressed by other cultures and by domination exercised by other cultures, especially modern and Western empires. This is an accelerating process and, as time passes, it becomes increasingly difficult to obtain reliable data on the original political life of hunter-gatherer and tribal peoples. The domination and influence of states, empires and large business corporations, aided by the new technologies, today reach into all corners of the earth. The consequences for the original hunter-gatherer peoples is that they no longer preserve their original forms of life and culture. Democratic systems in Palaeolithic communities Democratic systems and decision-making bodies existed in both hunter-gatherer and mobile tribes, according to anthropological studies, which document organs of power such as community assemblies, functional leadership and community chiefs. Space does not allow for an extensive explanation of the political organisation of hunter-gatherer communities. However, some brief considerations are necessary, because despite being limited and even reductionist, they can also be very illustrative. Although the records that throw light on these early political power systems are drawn from peoples who have lived within their original systems until recently, in what follows the past tense will be used because those communities are assumed to have existed during the Upper Palaeolithic. We can, for instance, point to the existence of “community assemblies”, which were meetings of all adults to discuss, deliberate and reach agreements on fundamental issues affecting their community’s future. All adult members of the community, men and women, participated in these assemblies, although, from some of the known present-day communities of hunter-gatherers and horticulturists, we can deduce that smaller and more formal assemblies were composed only of adult males. In many cases, the women stood around those smaller assemblies, actively participating and making their voices heard. In hunter-gatherer community meetings, decisions had to be made by consensus, as the survival of small communities depended on cooperation between members. The search for consensus often meant that the assemblies were extremely lengthy, while no decisions were even reached if there was no unanimity. Community fusion and fission processes were common in hunter-gatherer communities, and, in cases of great conflict, the solution was for the community to split. Persons who excelled in public speaking skills and persuasive strategies were important and acquired prestige in community assemblies. Kenneth E. Read, [7] in an article describing the political power system of the Gahuku-gama (an aboriginal people of New Guinea), provides an excellent explanation of individual communication strategies aimed at influencing community assemblies. In some hunter-gatherer peoples a group strategy that ensured that no one would try to put themselves above the rest was ridicule and laughter directed at people who used bombastic oratory to impress. We can also distinguish individuals who could be defined as "functional leaders" or "task managers”, i.e., men or women who were expert or skilled at a particular task, e.g., hunting, warfare, healing, birthing, music, dance, various rituals, etc. Leadership was not a designated role; rather, roles were acquired by individuals who demonstrated particular knowledge, experience or skills. Leaders only had the authority as permitted by the community and only for the performance of their assigned tasks. Although they held the most important political position in hunter-gatherer communities, chiefs were typically powerless. That is why they were a major source of surprise for the first Europeans who came into contact with these communities. Roberth H Lowie, who studied the chiefs of Amerindian peoples, such as the Ojibwa, the Dakota, the Nambikuara, the Barana, etc, concluded that chiefs did not have any coercive force to impose their decisions, nor had they executive, legislative, or judicial power. They were fundamentally peacemakers, benefactors and the conduit of community principles and norms. Fundamentally, they functioned as mediators and peacemakers in internal conflicts and resource providers to community members in need, and also provided periodic reminders of the norms and values on which member coexistence and community survival depended. [8] This figure of the powerless chief has been encountered in hunter-gatherer communities around the world. According to Claude Lévi-Strauss, the benefits of being a community chief were so few and the burden of responsibility so high that many refused to assume the role. However, what did motivate some individuals to assume the chiefdom was the associated prestige and a vocation to assume certain responsibilities for the community. [9] The community chief was generally elected by the adult community members—men and women—and could also be removed by the community. An example is given by Claude Levi-Strauss in his explanation of the power system of the Nambikwara in Brazil: if the chief was egoistic, inefficient or coercive, the community dismissed or abandoned him. [10] In some tribes, while war chiefs acquired important executive powers, these could only be exercised in periods of war, and despite the associated prestige, they had few or no powers in peacetime. It can hardly be argued that these hunter-gatherer communities—the original democracies—were not democratic, as argued by some authors. Karl Popper, for instance, stated that they were not "open societies" and were therefore undemocratic. [11] However, this argument is based on a liberal perspective: Popper essentially claimed that they were not liberal societies. Yet those societies were profoundly communitarian and egalitarian and, although they were not what we currently understand as liberal, they were in their way democratic. Political theory and political anthropology In the field of modern Western political theories, the tendency to overlook the relevance of the original democracies in the history of humanity is the outcome of the narrow perspective of our cultural tradition. What we call modern democracies are little more than two hundred years old, yet for some thirty thousand years, the original democracies organised the political power structures of Homo sapiens, with the resulting decisive impact on our evolution and on what we are today. Instead of taking into account the reality of the original democracies, Western thinking has focused on establishing hypotheses—with little foundation in reality—regarding illusory states of nature and assumed contracts between individuals aimed at shaping a society and, further on in time, creating a state. Thus, instead of taking into account the key contributions of anthropology, Western thinkers have explored the contractarian ideas of authors like Hobbes, Rousseau, Locke, and Kant, not to mention other more recent authors inspired by liberal contractualism, e.g., Rawls and Nozick. Human society and its political power systems did not originate from a contract between isolated individuals, but from the evolution of societies and power systems of other Homo species from which Homo sapiens arose. Given that the evolutionary processes that gave rise to the first human societies are known, the contractarian origin myth—a device that legitimises liberal individualism—makes little sense, even as a mere logical hypothesis for reflection. In their introduction to a classic overview of the political systems of African peoples, the anthropologists Meyer Fortes and Edward Evans-Pritchard argued that the teachings of political philosophy were of little help with ethnographic research into the political systems of African peoples as conducted by anthropologists in the field. [12] The philosophy, political and anthropological disciplines may be very different, but both philosophers and political theorists need to take anthropological data into account in their reflections. Political principles of the original democracies Two anthropologists in particular, in their reflections on the political systems of hunter-gatherer peoples, have developed important theoretical models: the French anthropologist Pierre Clastres and the US anthropologist Christopher Boehm. Pierre Clastres, whose thinking has strongly influenced French theorists such as Claude Lefort and Miguel Abensour, drew a novel conclusion from his ethnographic studies of Amerindian peoples in the Amazon region in the 1970s, namely, that hunter-gatherer peoples were not people without a state. Rather, they acted against the state, i.e., their political power systems were designed so that no state would ever emerge. For this reason, communities always tried to ensure that their chief was a chief with little or no power, while the community as a whole and its assembly was considered to predominate over any other political power that might be established. [13] As for Christopher Boehm, he concluded, from a detailed study of a large number of ethnographic works conducted in almost all continents, that the political systems of hunter-gatherer peoples were based on the principle of a reverse dominance hierarchy, in which the communities established formal and informal systems that ensured that a chief never achieved power, that no political body could coerce the community, and that no individual or group could prevent community members from freely making decisions on matters that concerned the community. Systems of control over the power of chiefs or leaders ranged from mild punishments, such as ridicule, to much more serious punishments, such as ostracism, banishment or even execution. For Christopher Boehm, the first genuinely human taboo was the taboo of dominance, and the first individual outlawed by the Homo sapiens community was the individual with aspirations to be the alpha male of the community. [14] Both principles—Clastres’ society against the state and Boehm’s reverse dominance hierarchy—are valid, but neither has been applied to date to develop theories consistent with models of democracy. Of the two principles, I consider the reverse dominance hierarchy to be the more productive principle, among other reasons, because it allows us to think about forms of non-state domination of a community. If, for instance, we transfer this principle to modern societies, it would apply to the dominance of certain groups in our society, not only in relation to the control of state apparatuses, but also to the wealthy, religious leaders, private armed militias, excessively powerful corporations, and media and information and communication systems oligopolies, etc. From my point of view, the reverse dominance hierarchy leads to a model of democracy that separates domination from management. In the original democracies, chiefs could exercise direction and influence but held little or no power; rather, it was the community as a whole, through its deliberative assemblies and other formal and informal decision-making mechanisms, which held power over itself, including over the chief, and also over alpha males aspiring to take power, who would be banned by the community. The reverse dominance hierarchy in original democracies allowed communities to freely take decisions over themselves without the interference and dominance of individuals and powerful groups. Adapting this principle to modern societies would lead to reflection on alternative models of democracy. Why revisit the original democracies? My focus on the original democracies is not intended as an exercise in historical or anthropological scholarship, but is grounded in two needs. First, we need to respect the remaining indigenous and aboriginal communities on our planet, as an enormous reserve of democratic culture, ancestral wisdom and human dignity. In recent centuries, their numbers have been greatly reduced, their communities have been annihilated, and their members have been enslaved and acculturated by Western imperialism and predatory capitalism. Second, we need to revisit the moral and political principles of the original democracies in order to be able to rethink our own democracies and our democratic projects for the future. For instance, I consider the reverse dominance hierarchy principle to be a very fruitful and interesting concept for rethinking the notion of democracy. I also believe that we could reflect on the notion of “people” in accordance with political characteristics of hunter-gatherer communities in defence of freedom and the power of the community as a whole. Liberal democracy, the hegemonic form of democracy today, is clearly in crisis, among other reasons due to its increasingly diminished legitimacy in society. The fact that liberal democracy allows socioeconomic inequalities to grow to a disproportionate degree leads to the suspicion that elected politicians do not really represent the majority of voters, thereby reflecting a profound crisis of representation. Moreover, the alliance between liberal democracy and runaway capitalism and its fostering of senseless consumerism and unbounded economic growth is leading scientists and conscientious citizens to fear the planet and humanity are headed for ecological collapse. An important task for political theorists today is to consider alternative forms of post-liberal democracy that lead to greater equality and freedom. Democracy, in sum, needs to be rethought. While republicanism, since the end of the last century, has developed a line of thinking that seeks to renew democracy by drawing on sources such as classical Greece, the Roman Republic and the Italian republics of the Renaissance, those sources are too close to our own culture; they are, in fact, where our political culture originated. We need, surely, to decentralise more, to seek inspiration in sources more remote from our habitual way of thinking—because, if our thinking is derived from what is familiar, then we will likely continue to think in the same way and devise broadly similar solutions. Rethinking democracy by considering Palaeolithic communities has a number of advantages. Looking back to those cultures so foreign to us could bring us closer to alternative perceptions of the human power relationships, and so opens up perspectives lost to us. Furthermore, those different perceptions would not be fanciful or speculative but anchored in reality, and would reflect deeper and more specific aspects of our nature as a species. Palaeolithic cultures can show us that another way of being human and of being a community is possible because that alternative form of humanity lies in our own evolutionary roots. It is not about appealing for the return to an idealised past, as this is evidently neither possible nor desirable, given the immense differences between the original democracies and modern urban and technologically advanced societies. Rather than some kind of futile anachronistic exercise, it is a matter of seeking new references that break with known modes of thinking. It is about looking forward, but considering what led to our present. And what led to our present is not only a few millennia of human authoritarianism and despotism, but also tens of millennia of egalitarian and democratic communities. Hunter-gatherer peoples may not have a written culture, but they do have a very rich oral culture—even if it is increasingly impoverished by the intrusion of Western culture. The myths that they keep alive are their means for formulating deep political thought; those myths also reveal their way of life and their governance and political systems. Undoubtedly we have much to learn from these original democracies, and much to reflect on and to rethink regarding their practices and the data and reflections of the anthropologists who have studied them. [1] The Upper Palaeolithic dates to approximately 40,000 to 10,000 years ago. [2] The Neolithic dates to approximately 10,000 to 5,000 years ago. [3] See: Glassman, R. M. (2017). The Origins of Democracy in Tribes, City-States and Nation-States. Springer; Bollen, K. & Paxton, P. 1997. Democracy before Athens. Inequality, democracy, and economic development 13-44. Cambridge University Press; Traversa, F. (2011). La gran transformación de la democracia: de las comunidades primitivas a la sociedad capitalista. Ediciones Universitarias; Shultziner, D. (2007). From the Beginning of History: Paleolithic Democracy, the Emergence of Hierarchy, and the Resurgence of Political Egalitarianism Shultziner et al. (2010). The causes and scope of political egalitarianism during the Last Glacial: A multi-disciplinary perspective. Biology & Philosophy, 25(3), 319-346. [4] Carroll, J. (2015). Evolutionary social theory: The current state of knowledge. Style, 49(4), 512-541. [5] Pan species that have survived to this day are the chimpanzee and the bonobo. They are part of the family of the great apes (hominids), which includes humans, gorillas and orangutans. [6] See: Eisler, R. (1987). The Chalice and the Blade: Our History, Our Future. Harper Collins; Lerner, G. (1990). La creación del patriarcado. Editorial Crítica; Conway Hall; Patou-Mathis, M. (2020) L’homme préhistorique est aussi une femme. Allary. [7 Read, K. E. (1959). Leadership and consensus in a New Guinea society. American Anthropologist, 61(3), 425-436. [8] Lowie, R. H. (1948). Some aspects of political organization among the American aborigines. Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, 78(1/2), 11-24. [9 ] Lévi-Strauss, C. (1967).The social and psychological aspects of leadership in a primitive tribe, in Cohen and Middleton, Comparative Political Systems. New York: Natural Historical Press. [10] Lévi-Strauss, C. (1992). Tristes tropiques. Penguin Books. [11] Popper, K. (1966) The Open Society and its Enemies. Routledge & Kegan Paul. [12] Fortes, M., & Evans-Pritchard, E. E. (2015). African political systems. Routledge. [13] See: Clastres, P. (1974). La société contre l'Etat. Minuit; Clastres, P. (1977). Archéologie de la violence: la guerre dans les sociétés primitives. Editions de l'Aube. [14] See: Boehm, C. (2012). Ancestral hierarchy and conflict. Science, 336(6083), 844-847; Boehm, C. (2000). Conflict and the evolution of social control. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 7(1-2), 79-101; Boehm, C. (1999). Hierarchy in the Forest: The Evolution of Egalitarian Behavior. Harvard University Press. by Feng Chen
Ideology has been a central force shaping labour movements across the world. However, the role of ideologies in labour activism in contemporary China has received scant scholarly attention. Previous studies on Chinese labour tend to hold that in China’s authoritarian political context, ideologically driven labour activities have rarely existed because they are politically risky; they also assume that ideologies are only related to organised labour movements, which are largely absent in the country. In contrast to these views, I argue that ideologies are important for understanding Chinese labour activism and, in fact, account for the emergence of different patterns of labour activism.
By applying framing theory, this piece examines how ideologies shape the action frames of labour activism in China. Social movements construct action frames by drawing from their societies’ multiple cultural stocks, such as religions, beliefs, traditions, myths, narratives, etc.; ideologies are one of the primary sources that provide ideational materials for the construction of frames. However, frames do not grow automatically out of ideologies. Constructing frames entails processing the extant ideational materials and recasting them into narratives providing “diagnosis” (problem identification and attribution) and “prognosis” (the solutions to problems). Framing theory is largely built on the experiences of Western (i.e., Euro-American) social movements. When social movement scholars acknowledge that action frames can be derived from extant ideologies, they assume that movements have multiple ideational resources from which to choose when constructing their action frames. Movement actors in liberal societies may construct distinct action frames from various sources of ideas, which may even be opposed to each other. Differing ideological dispositions lead to different factions within a movement. Nevertheless, understanding the role of ideology in Chinese labour activism requires us to look into the framing process in an authoritarian setting. In this context, the state’s ideological control has largely shut out alternative interpretations of events. It is thus common for activists to frame and legitimise their claims within the confines of the official discourse in order to avoid the suspicion and repression of the state. Nevertheless, the Chinese official ideology has become fragmented since the market reforms of the late 1970s and 1980s, becoming broken into a set of tenets mixed with orthodox, pragmatic, and deviant components, as a result of incorporating norms and values associated with the market economy. From Deng Xiaoping’s “Let some people get rich first”, the “Socialist market economy” proposed by the 14th National Congress of the CCP, to Jiang Zeming’s “Three Represents”, the party’s official ideology has absorbed various ideas associated with the market economy, though it has retained its most fundamental tenets (i.e., upholding the Party Leadership, Marxism-Leninism-Mao Zedong Thought, Socialism Road, and Proletariat Dictatorship) crucial for regime legitimacy. Correspondingly, China’s official ideology on labour has since evolved into three strands of discourse: (1) Communist doctrines about socialism vs. capitalism as well as the status of the working-class. (2) Rule of law discourse, which highlights the importance of laws in regulating labour relations and legal procedures as the primary means to protect workers’ individual rights regarding contracts, wages, benefits, working conditions, and so on. (3) The notions of collective consultation, tripartism, and the democratic management of enterprises. These notions are created to address collective disputes arising from market-based labour relations and maintain industrial peace. These three strands of the official discourse, which are mutually conflicting in many ways, reflect the changes as well as the continuity within Chinese official ideology on labour. Framing Chinese labour ideology The fragmentation of the official ideology provides activists with opportunities to selectively exploit it to construct their action frames around labour rights, which have produced moderate, liberal, and radical patterns of labour activism. To be sure, as there is no organised labour movement under China's authoritarian state, the patterns of labour activism should not be understood in strict organisational terms, or as factions or subgroups that often exist within labour movements in other social contexts. The terms are heuristic, and should be used to map and describe scattered and discrete activities that try to steer labour resistance toward different directions. Moderate activism, while embracing the market economy, advocates the protection of workers’ individual rights stipulated by labour laws, and seeks to redress workers’ grievances through legal proceedings. One might object to regarding this position as ideological—after all, it only focuses on legal norms and procedures. However, from the perspective of critical labour law, it can be argued that labour law articulates an ideology, as it aims to legitimate the system of labour relations that subjects workers to managerial control.[1] Moreover, moderates’ adherence to officially sanctioned grievance procedures restrains workers' collective actions and individualises labour disputes, which serves the purpose of the state in controlling labour. Radical activism is often associated with leftist leanings and calls for the restoration of socialism. Radical labour activists have expressed their views on labour in the most explicit socialist/communist or anti-capitalist rhetoric. They condemn labour exploitation in the new capitalistic economy and issue calls to regain the rights of the working class through class struggle. Unsurprisingly, such positions are more easily identified as ideological than others. Liberal activists advocate collective bargaining and worker representation. They are liberal in the sense that their ideas echo the view of “industrial pluralism” that originated in Western market economies. This view envisions collective bargaining as a form of self-government within the workplace, in which management and labour are equal parties who jointly determine the condition of the sale of labour-power.[2] Liberals have also promoted a democratic practice called “worker representation” to empower workers in collective bargaining. To make their action frames legitimate within the existing political boundaries, each type of activist group has sought to appropriate the official discourse through a specific strategy of “framing alignment”.[3] Moderate Activism: Accentuation and Extension Accentuation refers to the effort to “underscore the seriousness and injustice of a social condition”.[4] Movement activists punctuate certain issues, events, beliefs, or contradictions between realities and norms, with the aim of redressing problematic conditions. Moderate labour activists have taken this approach. Adopting a position that is not fundamentally antagonistic to the market economy and state labour policies, they seek to protect and promote workers’ individual rights within the existing legal framework, and correct labour practices where these deviate from existing laws. Thus, their frame is constructed by accentuating legal rights stipulated by labour laws and regulations and developing a legal discourse on labour standards. Moderate activists’ diagnostic narrative attributes labour rights abuses to poor implementation of labour laws, as well as workers’ lack of legal knowledge. Their prognostic frame calls for effective implementation of labour laws and raising workers' awareness of their rights. Extension involves a process that extends a frame beyond its original scope to include issues and concerns that are presumed to be important to potential constituents.[5] Some moderate activists have attempted to extend workers’ individual labour rights to broad “citizenship rights”, which mainly refer to social rights in the Chinese context, stressing that migrant workers’ plight is rooted in their lack of citizenship rights—the rights only granted to urban inhabitants. They advocate social and institutional reforms for fair and inclusionary policies toward migrant workers. While demand for citizenship rights can be seen as moderate in the sense that they are just an extension of individual rights, it contains liberal elements, because such new rights will inevitably entail institutional changes. To extend rights protection beyond the legal arena, moderate activists are instrumental in disseminating the idea of “corporate social responsibility” (CSR) and promoting it to enterprises. This aims to protect workers’ individual rights by disciplining enterprises and making them comply with labour standards. Liberal Activism: Bridging Frame bridging refers to the linking of two or more narratives or movements that have a certain affinity but have been previously formally unconnected. While the existing literature has paid more attention to “ideologically congruent but structurally unconnected frames regarding a particular issue or problem”,[6] “bridging” can also be understood as a means of “moral cover”.[7] That is, it splices alternative views to the official discourse, as a way of creating legitimacy for the former. This is a tactic that China’s liberal labour activism has used fairly frequently. Liberals support market reforms and seek to improve workers’ conditions within the current institutional framework, but they differ from moderates in that their diagnostic narrative attributes workers’ vulnerable position in labour relations to their absence of collective rights. Meanwhile, their prognostic narrative advocates collective bargaining, worker representation, and collective action as the solution to labour disputes. The ideas liberal activists promote largely come from the experiences of Western labour movements and institutional practices. As a rule, the Chines government regards these ideas as unsuited to China’s national conditions. To avoid being labelled as embracing “Western ideology”, liberal activists try to bridge these ideas and practices with China’s official notions of collective consultation, tripartism, and enterprise democracy, justifying workers’ collective role in labour disputes by extensive references to the provisions of labour laws, the civil law, and official policies. These are intended to legitimise their frame as compatible with the official discourse. Radical Activism: Amplification Amplification involves a process of idealising, embellishing, clarifying, or invigorating existing values or beliefs.[8] While the strategy may be necessary for most movement mobilisations, “it appears to be particularly relevant to movements reliant on conscience constituents”.[9] In the Chinese context, radical activists are typically adherents of the orthodox doctrines of the official ideology, either because they used to be beneficiaries of the system in the name of communism or they are sincerely committed to communist ideology in the Marxist conception. Unlike moderates and liberals, who do not oppose the market economy, radicals’ diagnostic frames point to the market economy as the fundamental cause of workers’ socioeconomic debasement. They craft the “injustice frame” in terms of the Marxian concept of labour exploitation, and their prognostic frame calls for building working-class power and waging class struggles. Although orthodox communist doctrines have less impact on economic policies, they have remained indispensable for regime legitimacy. Radical activists capture them as a higher political moral ground on which to construct their frames. Their amplification of the ideological doctrines of socialism, capitalism, and the working class not only provide strong justification for their claims in terms of their consistency with the CCP’s ideological goal; it is also a way of forcefully expressing the view that current economic and labour policies have deviated from the regime’s ideological promises. Conclusion These three action frames have offered their distinct narratives of labour rights (i.e., in terms of the individual, collective, and class), and attributed workers’ plights to the lack of these rights as well as proposing strategies to realise them. However, this does not mean that the three action frames are mutually exclusive. All of them view Chinese workers as being a socially and economically disadvantaged group and stress the crying need to protect individuals’ rights through legal means. Both moderates and liberals support market-based labour relations, while both liberals and radicals share the view that labour organisations and collective actions are necessary to protect workers’ interests. For this reason, however, moderates have often regarded both liberals and radicals as “radical”, as they see their conceptions of collective actions as fundamentally too confrontational. On the other hand, it is not surprising that in the eyes of liberals, radicals are “true” radicals, in the sense that they regard their goals as idealistic and impractical. It is also worth noting that activist groups have tended to switch their action frame from one to another. Some groups started with the promotion of individual rights but later turned into champions for collective rights. The three types of labour activism reflect the different claims of rights that have emerged in China’s changing economic as well as legal and institutional contexts. While the way that labour activists have constructed their frames indicates the common political constraints facing labour activists, their emphasis on different categories of labour rights and strategies to achieve them demonstrates that they did not share a common vision about the structure and institutions of labour relations that would best serve workers’ interests. The lack of a meaningful public sphere under tight ideological control has discouraged debates and dialogues across different views on labour rights and labour relations. Activists with different orientations have largely operated in isolation, and often view other groups as limited and unrealistic—a symptom of the sheer fragmentation of Chinese labour activism. Yet the evidence shows that, although they have resonated with workers to a varying degree, these three patterns of activism have faced different responses from the government because of their different prognostic notions. Both liberal and radical activism have been met with state suppression, because of their advocacy of collective action and labour organising. Their fate attests to the fundamental predicament facing labour movements in China. [1] For this perspective, see J. Conaghan, ‘Critical Labour Law: The American Contribution’, Journal of Law and Society, 14: 3 (1987), pp. 334-352. [2] K. Stone, ‘The Structure of Post-War Labour Relations’, New York University Review of Law and Social Change, 11 (1982), p. 125. [3] R. Benford and D. Snow, ‘Framing Processes and Social Movements: An Overview and Assessment’, Annual Review of Sociology 26 (2000), pp. 611–639. [4] S. Tarrow, Power in Movement: Social Movements and Contentious Politics (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2012). [5] R. Benford and D. Snow, ‘Framing processes and social movements: An overview and assessment’, Annual Review of Sociology 26 (2000), pp. 611–639. [6] Ibid. [7] D. Westby, ‘Strategic Imperative, Ideology, and Frames.” In Hank Johnstone and John Noakes (Eds.), Frames of Protest (New York: Rowman & Littlefield, 2005), pp. 217–236. [8] R. Benford and D. Snow, “Framing Processes and Social Movements: An Overview and Assessment.” Annual Review of Sociology 26 (2000), pp.611–639. [9] Ibid. by Noam Hadad and Yaacov Yadgar
How are we to understand a self-proclaimed “religious-nationalist” ideology if we take seriously the critical insights of a wide field of studies that question the very meaning of and distinction between the two organs of this hyphenated identity (i.e., religion and the supposedly secular nationalism)?
A wide field of studies (what is usually termed post-secularism or critical religion) have convincingly situated the emergence of the modern usage of these categories or concepts in specific historical and political configurations of power, debunking the (nevertheless prevalent) notion that they are universal and supra-historical concepts, the distilled essences of which can be found everywhere and everywhen in human history, only the outer appearance of them changing from place to place and from time to time. These critical studies caution us not to accept the assumed distinction between irrational, apolitical and private religion and secular, public and rational politics as a natural “given”. Instead, they encourage us to highlight exactly the specific political and historical makeup of the configuration of power that motivates the very construction and usage of these concepts. We take Religious-Zionism as a case study to explore the manner in which the so-called religious identity of an ideology whose foundational values are those of nationalism and the nation-state, is shaped. We also explore the ways in which this ideology, bent on “hyphenating” nationalism and religion, deals with the ideational challenges posed by an epistemology that insists that the two are mutually exclusive. The Western construction of “religion” and “the secular” Popular imagery, as well as the discourse prevalent in large swaths of the academic field tend to view religion and the secular as universal (that is, culturally agnostic), almost natural and obviously neutral categories, that are used to describe—and to analyse—any given social and political reality. Religion is described in this context as a primordial, non-rational (or irrational) basis of human society, and secularism or secularisation as a rational, enlightened release from the archaic bonds of religion. Powerful critiques reject this construction of both religion and the secular. Critics retrace the emergence of the conceptual binary to its historical and cultural (modern, Christian, largely Protestant, European) context, and warn against employing this binary as if it were supra-historical and universal.[1] The prevailing concept of religion, they show, has developed in the context of the emergence of the modern, secular nation-state. Religion is charged with a (negative) normative load, often captured in what secularist partisans depict as the violent and irrational nature of religion. The critics further show that the secular is constructed as the mirror image of religion, associated with a positive normative load of reason, rationality, and progress. Most importantly, these critiques highlight the ways in which this Western construction of religion serves the politics of the nation-state, while delegitimising competing claims for authority as religious, hence irrational and danger. This construction of religion and the secular nourished on Protestant ideas, especially the depiction of religion as a personal, apolitical matter. The Church, this view would claim, should avoid interfering in matters of politics, leaving it for the secular state to conduct. The outcome of this segregation of religion and its distancing from politics is thus inherently political: it dictates that one’s loyalty should be given exclusively to the state. Loyalty to God (and the teachings taught in God’s name by tradition) is to be depoliticised, neutralised of its public power. The secularist discourse is thus presented with a dilemma when considering the phenomenon of religious nationalism: How to account for this obviously modern “hybrid”, that professes political loyalty to both God and nation-state? The academic discourse on Religious-Zionism, which for the most part has been bound into the secularist discourse suggests that the key for understanding this phenomenon is in the balance of power between the two organs: religion and nationalism. Many of these studies have employed the concept of fundamentalism to study Religious-Zionism.[2] Other studies reject fundamentalism as an irrelevant framework, describing instead this ideology as existentially torn between its competing, incompatible commitments to secular Zionism and the religious Judaism.[3] What all these approached has in common is their insistence on employing the secularist epistemology, analysing Religious-Zionism through the contrast and tension between a secular nationalist ideology (i.e., Zionism), and religion. Religious-Zionism’s self-perception Yet a critique of the ways in which academic literature based on secularist epistemology has struggled to understand Religious-Zionism is not in itself sufficient to overcome this hurdle. This is so since spokespeople and thought leaders of Religious-Zionism themselves also rely on the bipolarity that pits religious tradition against secular politics as an infrastructure of their thought. Religious-Zionism has for decades based its self-perception on this bipolarity, viewing itself as tasked with the challenge of synthetising or reconciling this apparent binary of a thesis and its antithesis. This is the background against which to appreciate far reaching changes in the ways in which Religious-Zionists have understood the meaning of their religious commitments and allegedly secular nationalist loyalties. Much of the history of the Religious-Zionist thought in the past half-century can thus be explained as a struggle to reconcile what its carriers viewed as an inevitable conflict between the two, potentially conflicting but equally cherished cores of their identity. As practically all scholars agree, the June 1967 Six Days war mark, in this regard, a watershed, further motivating this ideological soul-searching.[4] But its effect took time to emerge into the foreground. The two decades immediately following the war saw Religious-Zionists continuing to view their guiding ideology as offering a unique combination of secular and religious values into a whole, consistent system of thought. Some viewed this combination as achieving wholeness, while others insisted on preserving the distinction between the two separate yet interlocked arms. The “Western” (i.e., Euro-American) conceptual toolkit remained their primary framework for understanding their politics. This was especially apparent when spokespeople for Religious-Zionism took a leading role in resisting what they depicted as the separation of religion from state politics, demanding that certain aspects of Jewish tradition are granted a substantial place in public life. The epistemological tension entailed in trying to combine and unify what are, according to the very fundamentals of the secularist discourse, separate and mutually exclusive organs has been apparent. Even when it was clear that the writers are acutely aware of the tension, they were unable to solve it, invested as they were in the conceptual framework that nourished it in the first place. This tension was rapidly coming to a head during the early 1990’s when the Israeli government and the Palestinian Liberation Organisation were negotiating and signing what became known as the Oslo Accords. Religious-Zionists commentators, who read the Accords as an Israeli capitulation, led by secular Zionist leaders, could no longer accept the principal legitimacy of secular dimension of Zionism. They began to question the legitimacy of the so-called secular element in Zionist thought. It is the thin ideological bedrock of secular nationalism, these spokespeople argued, that results in the Israeli inability to safeguard Zionist fundamentals. The only remedy against this precariousness of the Zionist commitments is, they concluded, religion. It is religion, in other words, that safeguards nationalism and guarantees that it is not undermined. Religious-Zionist writers thus solved, in this context, the tension between secular nationalism and religion by transforming the (allegedly secular, even by their own measures) nation-state into a supreme religious value. In effect, this solution meant that any secular Jewish-nationalism is not properly Zionist, since it is only Religious-Zionism that fits bill of authentic Zionism. Yet this solution, too, remains wedded to the same conceptual framework, where religion and nationalism are understood to be distinct from each other. In retrospect, it is clear that it has not gained much ground. It was during the Religious-Zionist campaign against the Israeli “Disengagement” (namely, the withdrawal of Israeli settlers and armed forces from the Gaza Strip and the northern West Bank) in 2005 that religion, in its Western-constructed manner, was no longer presented as a foundational element in Religious-Zionist identity. Neither was religion used to distinguish Religious-Zionism from general, secular Zionists. Instead, Religious-Zionist spokespeople focused on the notion of Judaism, which they saw as identical to Zionism writ large. Moreover, there were also calls from within the Religious-Zionist camp to separate religion from realpolitik, or at least to substantially limit its footprint, since it was limiting Religious-Zionism’s ability to confront this realpolitik of the state. While in the past Religious-Zionist spokespeople sought to legitimate religion as worthy of playing a role in politics, they now started to question religion’s political worth, and to position it at the lower ranks of Religious-Zionist ideology, assigning it a utopian more than politically practical and influential role. In other words, we can see here a renewed “Protestanisation” of Jewish religion among Religious-Zionists. Jewish tradition, seen as mere personal and spiritual “religion,” was gradually pushed aside from matters of national politics, which were fully dominated by the state. Ironic as it may sound, we can speak here of a Religious-Zionist trend of separating religion from politics, that gained power against the background of the Israeli “Disengaging Plan”. Nationalism and Territory—the Land of Israel The effects of the secularist, Western epistemology are also apparent when considering the ideological principle of the settlement of the national territory (the Land of Israel) with members of the sovereign nation, a central foundation of Zionist ideology generally. Scholars and commentators of various kinds have tended to single out the principle of settlement as the very core of Religious-Zionism. Critically, they have interpreted it as a matter of Religious-Zionism’s Judaic, religious commitments, depicting Religious-Zionism as promoting the achieving or fulfilling of this end or “commandment” by all available means, including the nation-state, and Zionist ideology itself. At the very least, these scholars have explained the settlement of the Land of Israel as an independent religious value, to which Religious-Zionism is committed as a matter of its religious orthodoxy, regardless of or in parallel to this ideology’s commitment to the nation-state. Accordingly, scholars subscribing to this view have explained various conflictual flash-points—especially since the onset of Religious-Zionist led settlement of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip—as putting Religious-Zionism in an existential dilemma, torn between its religious commitment to settle the land and its political, secular commitment to the state. (Some even presented the latter as a matter of religion too). Yet careful examination of Religious-Zionist public discourse during the half-century since the June 1967 war shows that the value of settling the Land of Israel was rarely granted an independent, self-fulfilling status. Instead, it was usually tied to and dominated by a broader nationalist view, at the center of which stands the state, the nation and nationalist ideology. The idea of the “undivided Land of Israel”, central and important as it has been in Zionist thought generally and in Religious-Zionist thought specifically, has not been elevated to the status of an absolute value, but remained subservient to the sanctification of nationalism and sovereign statehood. Moreover, the Religious-Zionist public discourse has not focused on a theological discussion of the sanctity of the Land of Israel (a religious principle from which this ideology allegedly nourishes its commitment to colonising the land, according to the scholarship mentioned above.) Instead, most spokespeople have dedicated most of their and their readers’ attention to matters that are commonly identified as secular (primarily issues of security and strategic concerns, but also those of demography), ultimately revolving around one core issue: sovereignty over the national territory. Thus, for example, one of the central arguments in the Religious-Zionist discourse on the Land of Israel (mostly following the occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip in 1967) was about the “historical right”—not the theological one—of the nation-state to rule over the land. This right was presented as an axiom that needs neither proof nor explanation; it is clearly seen as part of a universal, political concept of sovereignty. Another major argument made by spokespeople for Religious-Zionism to defend their maximalist stance on matters of territory had to do with matters of security. Often, these security concerns have overshadowed all other arguments regarding the Land. They have argued that exercising sovereignty and military control over the territory and colonising it are a necessary condition for guaranteeing the security of the state. It is the latter—the state, its security—that held the status of the absolute value. The Land of Israel—and the project of settling it—were presented as one of the most important means to achieving this primary end, not an ideological absolute in and for itself. Certainly, they were not made into a theological end. Moreover, even when the Land and settlement were dressed in a “religious” garb, they still formed part of a theopolitical argument, that is: as a nationalist, Zionist matter of Jewish nation-statism, not as a traditional Judaic value. Militarism as the expression of the modern nature of Religious-Zionism The values of militarism and security, which have gradually grown in dominance, culminating in their occupying the very center of Religious-Zionist ideology in the past decade or so, are also a rather stark expression of the all-encompassing commitment of this ideology to the politics of the sovereign nation-state. Militaristic political ideals that sacralise the security of the state and the nation, rendering this an absolute value and justifying in its name violence and bloodshed are indeed by definition bound to nation-statist thought. Religious-Zionist ideology’s valorisation of the state’s security was most explicitly pronounced in the context of justifying and rationalising the death of Israeli soldiers as the price demanded for guaranteeing this security. This became all the more pronounced against the background of violent conflicts around which there was no consensus among Jewish-Israelis. Especially when critics (usually coming from the Zionist Left) doubted whether such deaths were justified, questioning the necessity, reason and morality of the violent conflicts into which the Israeli government sent its armed forces, Religious-Zionist pronouncements became all the more dominated by intensive, militant militaristic discourse. Indeed, a dominant theme in the Religious-Zionist militaristic discourse surrounding these events has been the demand that the Israeli military is sent to fight, even if this necessarily entails the death of Israeli soldiers. (This demand was made against a background of public debate which questioned the merit of this military adventures, exactly because of their price in human lives.) The prevalent argument heard over Religious-Zionist platforms (either explicitly or implicitly) was clear: the security of the state is an absolute value, that justifies the highest of sacrifices, that of soldiers’ lives. Even more pronounced was this valorisation of the state’s security when what was at stake were the lives of civilians from the enemy’s side. There has been little doubt among formulators of the Religious-Zionist stance on these armed conflicts that such conflicts are a normal feature of the lifecycle of states, and that in this context the killing of civilians on the enemy’s side during war, unfortunate as it may be, is wholly justified and acceptable. A striking feature of this Religious-Zionist militaristic discourse is its utter indifference to the kind of language, argumentation and reasoning that would usually (that is, when seen through the prevalent religious-secular binary) be put under the heading of “religious.” One would be hard pressed to find such “religious” aspects of this militaristic thought, with its focus on “secular” values of security and statism. God and theopolitics How are we, then, to understand the theological aspect of Religious-Zionist political thought? One crucial part of the answer has to do with the nature of these theological language and argumentations: they do not fit what the prevalent discourse will mark as the category of “religion”. This mainstream discourse does not consider the traditional Jewish elements within so-called “secular” Zionist ideology to be “religious”, no matter how deeply rooted they may be in what this same discourse sees as “religion”; instead, it would view the appearance of these elements within Zionism as a product of their “secularisation.” This theological language and argumentation is seen as essentially modernised, politicised and “rationalised”, and it is ultimately aimed at the politics of the nation-state: it fits neither within an apolitical, individual and a-rational notion of religion, nor within the frame of “fundamentalism”, which would put the interest of the state under a higher religious diktat. Furthermore, it cannot be framed as one side of an alleged ideological “synthesis” of two organs that are allegedly separated-in-principle. The Religious-Zionist nation-statist commitment (or its patriotism) does not clash with, serve, or complement theology; rather, it is the very essence of this theology. Like many other modern cases, the political theology at hand sanctifies the modern, supposedly secular and rational nation-state, and positions it in the role of savior, who accordingly demands absolute loyalty and functions as the center of the political order. As William Cavanaugh (2003, 2) puts it (referring, of course, to the general genus of which Religious-Zionism is but a case), “supposedly ‘secular’ political theory is really theology in disguise”.[5] Or, in Carl Schmitt’s famous phrasing, “All significant concepts of the modern theory of the state are secularised theological concepts.”[6] The God, who has traditionally occupied the very center of Jewish theology, was now joined, if not even pushed aside, by the state. At best, God is seen as sanctifying the state, shifting the focus away from Him to the (political, this-worldly) sovereign. Either way, Religious-Zionist theopolitics marks nationalism and the state, not God, at the ultimate purpose. A continuing process of blurring the distinctions between theology, Judaism and nationalism has culminated in the relegation religion to the private realm, barred from the field of politics. “Religion” was replaced in the context of this argumentation by “Judaism” or “Jewish identity”, as these are understood by the modern, nationalist, Zionist discourse. Like the founding ideologues of the Zionist movement, a growing number of Religious-Zionist spokespeople, too, came to argue (either implicitly or explicitly) that Judaism is not necessarily (or not even primarily) about “religion”: rather, it is about (political) nationalism, and its primary value is patriotism. We argue, then, that Religious-Zionism is best understood when considered as a nationalist, Zionist ideology, at the center of which stand not religion or traditional Judaism, but nationalism and the state. Contrary to this ideology’s self-perception, and against a prevalent stream within the academic field that similarly un-self-reflectively employs a modernisation-and-secularisation discourse to construct the meaning of religion and nationalism, we argue that Religious-Zionism should be viewed primarily as a quintessentially modern-Western ideology of the nation-state. The State of Israel, relying on its military power (in which context it is “security” concerns that dominate all others); Zionism; and nation-statist sovereignty over a territory to which the nation claims a “historical right”—these are all the very core of Religious-Zionist ideology, and not merely means to achieving some hidden theological ends such as redemption or the observance of religious praxis. Conclusion An understanding of the strong gravitational force of the notion of the nation-state that dominates Religious-Zionist ideology necessitates the release of its analysis from the grip of the Western, secularist epistemology, which developed as in the context of the emergence of the modern, secular nation-state. The modern epistemology serves primarily the state, depicting it as “secular”, thus legitimising it, while rendering some of its competitors “religious” hence illegitimate. Overcoming the dominance of this epistemology allows us to see how its conceptual toolkit shapes Religious-Zionist identity—both in constructing the meaning of its religiosity, and in situating the state as its ultimate value. [1] W. T. Cavanaugh, The Myth of Religious Violence: Secular Ideology and the Roots of Modern Conflict (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009); T. Fitzgerald, Discourse on Civility and Barbarity (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007); D. Dubuisson, The Western Construction of Religion: Myths, Knowledge, and Ideology (Baltimore, PA: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007); T. Asad, Genealogies of Religion: Discipline and Reasons of Power in Christianity and Islam (Baltimore, PA: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1993). [2] G. Aran, ‘Jewish Zionist fundamentalism: The Bloc of the Faithful in Israel (Gush Emunim)’, in M. E. Marty and R. S. Appleby (Eds.), Fundamentalisms Observed (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 1992), 265–344; C. S. Liebman and E. Don-Yehiya, Civil Religion in Israel: Traditional Judaism and Political Culture in the Jewish State (Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1983); M. Inbari. Messianic Religious Zionism Confronts Israeli Territorial Compromises (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012); A. Horowitz, ‘Religious-Zionism – from Zionist radicalism to religious-national fanaticism’, in D. Arieli-Horowitz (Ed.) Religion and Politics in Israel (Tel-Aviv: The Centre for Jewish Pluralism, 1996), 41–55. [3] For example, M. Hellinger et al., Religious Zionism and the Settlement Project: Ideology, Politics, and Civil Disobedience (Albany, NY: SUNY Press, 2018); E. Don-Yehiya, ‘Messianism and politics: The ideological transformation of religious Zionism’, Israel Studies, 19 (2014), 239; A. Cohen, ‘Patriotism and religion: Between coexistence and confrontation’, in Ben-Amos, Avenr and D. Bar-Tal (Eds.) Patriotism: Homeland Love (Tel-Aviv: Haqibutz Hameuḥad and Dyonon, 2004), 453–78. [4] A. Sagi and D. Schwartz, Religious Zionism and the Six Day War: From Realism to Messianism, trans. B. Stein (London: Routledge, 2018). [5] W. T. Cavanaugh, Theopolitical Imagination: Christian Practices of Space and Time (London: Bloomsbury T&T Clark, 2003), 2. [6] C. Schmitt, Political Theology: Four Chapters on the Concept of Sovereignty (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2006), 36. by Nicolai von Eggers
The presidency of Donald Trump and the rise of far-right movements and politicians across the globe has triggered a resurgence in the use of the concept of fascism to describe our contemporary political situation. Former US foreign minister, Madeleine Albright, wrote “a warning” about the similarities between Trump and former fascist leaders, while philosopher Jason Stanley published a bestseller on the tell-tales of fascist discourse.[1] Both books focused on discourse and the role of the leader, while less attention was given to forms of organisation, political ideology, or more ingrained cultural factors.
But while both books got a lot of attention, they were also widely criticised by critics who held that we are by no means living in a fascist moment, that Trump and similar acts by no means possess the kind of mass organisations that enabled fascism, and that for all of their ultra-populist shortcomings these leaders did not hold ‘core-fascist’ beliefs or aspirations to totalitarian rule.[2] The mainstream debates over the nature of fascism and whether it is a useful category for understanding contemporary politics reflects a wider debate within the study of fascism and political ideologies more widely. Is fascism an ideology on a par with the other ideologies such as liberalism, socialism, and conservatism? Or is it a rather a subset or perversion of one or more of these ideologies? Or is it something entirely different, like a purely negative ideology—antiliberal, anticommunist—as Noberto Bobbio once argued?[3] Such debates over the exact definition of fascism may seem overly academic, but they are nonetheless important, for the way we define fascism has consequences for how we understand fascism today—whether it exists, whether it should be taken seriously, how widespread it may be said to be, how much of a danger it consequently poses, and ultimately how it should be fought. This discussion, however, often makes little sense in the abstract and only becomes concrete through contextualised analyses of concrete movements, political situations, and the ideological output of specific currents. One ideological current that has received some attention in recent years is the so-called European New Right, which has influenced not only currents such as the alt-right and the Identitarians but also political parties and public debate more widely. Specific identifiably far-right talking-points and language, such as ‘the great replacement’ and a ‘ethnopluralist’ way of speaking about ‘tradition’, ‘cultural difference’, and ‘defence of European values’ have increasingly moved out of the fringe culture of the far right and into mainstream discussions. Researchers have long debated how exactly this current should be understood. Most researchers have settled on the somewhat vague definition of the European New Right as ‘neo-fascist’, which some use to emphasise the current’s ideological relation to fascism (thus emphasising the fascist part) while others argue that the current is better understood as something altogether new and different (thus emphasising the neo part).[4] One of the main reasons for doing so is the lack of reference to biological race theories, the lack of reference to white supremacy (which was substituted for the idea of ethnopluralism), and, most importantly, the lack of references to a uniformed mass movement led by a Führer or Duce and a concomitant imperialist-nationalist agenda. Within New Right ideology this has been replaced by the idea of federalism and a ‘Europe of a hundred flags.’ Thus, Steve Bastow argued some time ago that the New Right’s turn to federalism took the movement out of fascist ideological space more broadly construed.[5] The question, however, is how exactly we should understand federalism as it is promoted by the New Right. One way to answer this is to look more closely at how the key ideologue of the European New Right, Alain de Benoist, has defined, understood, and deployed the concept of federalism. A key point of reference for Benoist’s conception of politics, I argue in a recently published article, is the French Revolution.[6] Positioned thoroughly within the reactionary, counter-revolutionary tradition of political thought, Benoist sees the French Revolution as the Fall, the moment in which European society went decisively awry.[7] According to Benoist, the French Revolution saw the rise of two opposed movements, two opposed logics of politics and societal organisation. One, he calls ‘Jacobinism’, by which he understands a modernising, rationalising project based on individual liberties and the rights of man, centralising administration, and governing through universal laws and standardised systems of administration. This also entails a culturally unifying and homogenising project, which seeks to render all members of society equal independently of gender, language, status, occupation, and area of origin. Thus, in France, ‘Jacobinism’ introduced universal education, a universal language (French), and universal laws, all animated by a central, singular entity: the French state. Against Jacobinism, and what Benoist sometimes calls ‘the ideology of the Same’, Benoist argues that an antagonistic counter-project of federalism was born. Benoist identifies this counter-revolutionary, federalist tradition with the anti-revolutionary uprising in the Vendée and, more generally, with the aristocratic counter-offensive against the revolution. But federalism first and foremost signifies a much deeper logic of society and politics. Unlike the ideology of the Same, federalism is an ideology of difference, according to Benoist. Thus, Benoist champions the causes of local ‘peoples’, such as Bretons, Flemings, Catalans, and so on, to preserve their own language, culture, and identity in the face of ‘Jacobin’ encroachments. Benoist does not deny the existence of France and Frenchness, but he is critical of what he views as its tendency to wipe out local identity.[8] Thus, Benoist rather views ‘nationalist’ identity as one of scale: local identity, national identity, and regional (i.e. European) identity. Thus, it is possible to be both Breton, French, and European. What is not possible, however, is to be both ‘foreign’ and French and European. To believe so would be to succumb to the ideology of Sameness. What is at stake for Benoist and the New Right is instead to understand identity as fundamentally based on difference: Difference between various regional peoples who are nonetheless members of the same national and regional ‘family’, and difference between Europeans and non-Europeans who are different on a much more fundamental level. This conception of identity is based on a mythico-historical—but ultimately essentialist—conception of human beings, which conflates culture, politics, and ethnicity. According to Benoist, it can meaningfully be said that an Indo-European ethnicity exists. In some of his texts, Benoist even lends credence to the so-called Hyperborea-Thule-thesis, which is quite widespread among some segments of the far right, and which is a polygenetic theory of human evolution holding that the Indo-European ‘race’ originated in Northern Europe and was only later, and only partially, mixed with other races originating in the South.[9] Benoist weighs his words carefully, but it is clear that these texts toy with a conception of ethnic purity as the road towards happiness and the good life. And in less esoteric texts, Benoist still argues that there is a direct connection between ethno-cultural roots and values and political systems. Thus, Benoist has argued that “unlike the Orient, absolute despotism has been rare in Europe”, and that in “Indo-European societies, kings were usually elected”.[10] This quote precedes a paragraph in which Benoist goes on to praise the electoral processes of the Germanic tribes described by Tacitus, while in other places Benoist refers to the Icelandic Althing as proof that a democratic culture was deeply embedded in premodern European life. Benoist’s political model is therefore not one of a mass-party led by a Führer engaged in expansionist, militarised politics. What he envisions instead is a federalist Europe of purified local peoples that will govern themselves in accordance with their supposed ‘original’ political culture, and which will furthermore federalise on a European level in order to draw up agreements and protect themselves against a foreign, non-European enemy. In contrast to an ideology of the Same, which according to Benoist “annihilates” differences between peoples, the federalist project is to be built on an ideology of difference that respects these ‘original’ ethno-cultures.[11] Does federalism then take the New Right out of the fascist space, as Steve Bastow has argued? I will argue that it does not. The federalist element only provides the New Right with a specific version of core fascist beliefs, not something different from them. I here largely agree with Roger Griffin that fascism should be defined as the attempt to bring about the rebirth of mythical ‘nation’ through struggle, which also entails purifying it of contaminating elements.[12] Thus, as Griffin has emphasised elsewhere, “the single party, the secret police, the public displays of Caesarism, even the presence of the Führer are not necessarily attributes of fascism”.[13] This also means that many “features highlighted in the ‘check-list’ definitions of fascism . . . have been ‘accidental’, contingent on the way the vision of the total politico-cultural renewal of the ‘people’ was conceived in the unique conditions of interwar Europe”.[14] There are, in this sense, various contemporary forms of fascist ideology, and I believe the notion of ‘federalist fascism’ best captures the specific New Right tendency. There are three reasons as to why I think the notion of ‘federalist fascism’ is a useful category when it comes to understand the ideology of the New Right. First, ‘federalist fascism’ incorporates a term—federalism—that Alain de Benoist himself sees as the best description of his own political-ideological beliefs. It goes a long way to describing the adherents of the political ideology of the New Right in the same terms in which they understand themselves. Further, ‘federalist fascist’ is a promising way to redescribe the potentially misleading term ‘ethnopluralist’. Ethnopluralist language, which speaks about the right to defend local identity against modernity, often confuses what is really at stake— namely, ethnic cleansing and the belief that the true nature of a people can only be realised through living in ethno-cultural, homogenous, traditional communities (which is clearly an essentialist and fascist conception of human beings and the good life). ‘Federalist fascist’ is much clearer in that regard, because it emphasises that we are not dealing with standard notions of white supremacy, biological racism, and imperialist ambitions but rather a more defensive project, ‘protecting’ European values and the ‘Europe of a hundred flags’. The notion of ‘federalist fascism’ thus has the double function of describing the New Right ideology partially in terms that lie at the heart of the New Right’s own self-understanding (federalist), while at the same time refusing to rely on that self-description entirely and consequently also redescribing the movement in terms of a social-scientific assessment that uses a widely accepted and well-established typology of political ideologies (fascism). Second, the notion of ‘federalist fascism’ points in the direction of what we might call the political (organisational, governmental) aspect of the New Right. As we have already seen, the party, secret police, Caesarism, and the Führer are more incidental or contingent expressions of fascism. In other words, the specific political form of fascism may vary according to specific political situations— historically, geographically, culturally, etc. The question then is what political form fascism takes today. It does not necessarily take one single form, and the form it does take can be malleable, in the sense that the question of what political form to take often depends on what is strategically feasible. Still, when it comes to the New Right, the political form is closely linked to the notion of ‘federalism’. This means potentially arguing in favour of some level of democracy, of focusing on inter-regional and international collaboration (against the common enemy of the Other, often identified with Muslims and the Arabic world), and having a flatter movement structure than was the norm under traditional fascism. Identifying fascism too closely with the Führer principle, dictatorship, the mass party, and military hierarchy can make it hard to identify real fascists who do not quite fit this mould, and thus to understand what exactly is going on. The more fine-grained notion of ‘federalist fascism’ works better, I believe, when trying to understand who can meaningfully be described as fascist and who cannot. Third, the notion of ‘federalist fascism’ underlines the direct links the New Right has to the fascist tradition. It has been argued that the New Right is not really fascist, or not directly fascist, because it does not invoke figures such as Hitler or Mussolini and the politics they stood for.[15] But this is a very narrow definition of the fascist project and overlooks the fact that many currents of various beliefs assembled under the banner of fascism for a variety of reasons. Furthermore, the New Right does in fact draw explicitly on an avowedly fascist tradition—namely, what we may call the ‘aristocratic-intellectual’ current within the larger tent of the fascist movement. This included intellectuals such as Julius Evola, Pierre Drieu La Rochelle, Martin Heidegger, Ernst Jünger, and Carl Schmitt. Especially the former is a key point of reference for the New Right. What these thinkers have in common is a critique of many of the völkisch aspects of actually-existing fascism as well as the mass political nature of the fascist project. What they championed instead was an aristocratic fascism that emphasised spiritual races and the leadership of an elite, drawing on the traditionalist idea of a priestly warrior caste of officers. The ideal here is not the Führer embodying the vulgar spirit of the people but that of intellectual aristocracy taking care of politics. This intellectual current is what is widely known as ‘the conservative revolution’, a term coined by the Swiss fascist, Armin Mohler, who after World War II tried to delink this part of the broader fascist movement from actually-existing fascism. Mohler, who worked as Jünger’s secretary and since became a major influence on the New Right, explicitly referred to ‘federalism’ as one of the “fundamentals of conservatism”, of the revolutionary (i.e., aristocratic, fascist) kind he himself promoted.[16] The New Right is thus a direct descendent of the conservative revolution, which was an integral part of the broader movement that made up actually-existing fascism. Referring to it as ‘federalist fascism’ highlights this connection. Overall, ‘federalist fascism’ is a better concept for understanding New Right ideology than the concept of ‘neo-fascism’, which remains diffuse and insufficiently clear in its indications of what exactly is ‘neo’ about new forms of fascism, such as that of the New Right. ‘Federalist fascism’ has the merit of highlighting the ethnopluralist ideas of the new right, its tendency to experiment with organisational and potentially governmental forms that are different from the hegemonic current within traditional fascism, while retaining the key insight that we are dealing with a fascist ideology which believes in ethno-cultural homogeneity as a prerequisite for the good life. In this way, the notion of ‘federalist fascism’ can contribute to the debate on what fascism is in the 21st century, what forms it takes, and how best to counter it. [1] Madeleine Albright, Fascism: A Warning (HarperCollins, 2019), Jason Stanley, How Fascism Works (Random House, 2018). [2] Dylan Riley, “Introduction to the Second Edition” in The Civic Foundations of Fascism in Europe (Verso, 2019), pp. xxii-xxx; Enzo Traverso, The New Faces of Fascism (Verso, 2019), p. 21l; Ross Douthat, “Is Donald Trump a Fascist?” in New York Times, 3 December 2015. [3] Norberto Bobbio, ’Lïdeologia del fascismo’ in Daæ fascismo alla democrazia (Baldini & Castoldi, 1997). [4] Amongst the former is Tamir Bar-On Where Have All the Fascists Gone? and Rethinking the French New Right; Thomas Sheehan, focusing on the early period of the New Right, argues in favour of employing the notion of fascism, see Thomas Sheehan, ‘Myth and Violence: The Fascism of Juluis Evola and Alain de Benoist,’ Social Research 48, no. 1 (1981): 45-73; Roger Griffin, ‘Between Metapolitics and “Apoliteia”: The Nouvelle Droite’s Strategy for Conserving the Fascist Vision in the “Interregnum”,’ Modern and Contemporary France 8, no. 1 (2000); Nigel Copsey with reference to Bar-On opts for defining the New Right as a ‘revisionist permutation of neo-fascism’ see Nigel Copsey, ‘“Fascism… But with an Open Mind”: Reflections on the Contemporary Far Right in (Western) Europe,’ Fascism: Journal of Comparative Fascist Studies 2, no. 1 (2013): 13. Somewhat more hesitant to employ the notion of fascism are Pierre-André Taguieff, Sur la Nouvelle droite ; 351-168; Alberto Spektorowski, ‘The French New Right: Differentialism and the Idea of Ethnophilian Exlcusionism,’Polity 33, no. 2 (2002) and ‘The New Right: Ethno-Regionalism, Ethnopluralism and the Emergence of a Neo-Fascist Third Way,’ Journal of Political Ideologies 8, no.1 (2003): 111-130. [5] Steve Bastow, “A Neo-Fascist Third Way: The Discourse of Ethno-Differentialist Revolutionary Nationalism,” Journal of Political Ideologies 7:3 (2002). [6] Nicolai von Eggers, “Federalist Fascism: The New Right and the French Revolution,” Fascism: Journal of Comparative Fascist Studies 10, pp. 298-322, available online via open access: https://brill.com/view/journals/fasc/10/2/article-p298_3.xml. [7] For this tradition, see Zeev Sternhell, The Anti-Enlightenment Tradition (Yale University Press, 2009) and Darrin McMahon, Enemies of the Enlightenment (Oxford University Press, 2001). [8] Benoist’s project is decidedly anti-modern, and the mythical nation that is to be revived is that of tribal, pre-statal Europe. Benoist himself is a pagan because he sees Christianity as a perversion of European culture, and his writings are sprinkled with references to Georges Dumézil and his theory of an ‘original’ tripartite division of society into priests, warriors, and commoners (the so-called trifunctional hypothesis). Benoist furthermore draws on Julius Evola’s esoteric belief that it is the rule of a spiritually superior warrior caste that will redeem society and cast of the yoke of modernity. Such ideas provide an identity for members of the new right who see themselves as warriors fighting to implement the ‘original’ social structure of Indo-European societies, and is reflected in the Generation Identity’s use of the symbol ‘lambda’, which for them represents the Spartan military class and its self-sacrifice in defending ‘Europe’ against the ‘Barbarian’ enemy at Thermopylae. [9] Alain de Benoist, Indo-europeans: In Search of a Homeland (Arktos, 2016) and Runes and the Origins of Writing (Arktos, 2021). [10] Alain de Benoist, ‘Democracy Revisited,’ Telos, no. 93 (1993), 66-67. [11] Alain de Benoist, ‘Jacobinisme ou fédéralisme?’ from alaindebenoist.com, no date (ca. 2000). All translations from French and German are mine. [12] Roger Griffin, The Nature of Fascism (Pinters Publisher, 1991) and for a good discussion of this definition in relation to the current state of the art ‘Studying Fascism in a Postfascist Age: From New Consensus to New Wave?’ Fascism: Journal of Comparative Fascist Studies 1, no. 1 (2012). [13] Roger Griffin, ‘Introduction,’ in Where Have All the Fascists Gone?, Tamir Bar-On (Aldershot: Ashgate, 2007), xi; Griffin, ‘Studying Fascism in a Postfascist Age,’ 17. [14] Griffin, ‘Between Metapolitics and “Apoliteia”,’ 38. [15] Following Mohler, Benoist himself has made this argument on several occasions, as has Pierre-André Taguieff and Paul Piccone, who in the 1990s and 2000s as editor of the journal Telos published a series of articles by Benoist alongside a series of articles discussing his works and related topics. Similar lines of argumentation often pop up in public debate and, to a lesser extent, in the academic literature. [16] Armin Mohler, Die Konservative Revolution in Deutschland 1918-1932: Ein Handbuch (Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, 1972), p. 236. by Marius S. Ostrowski
In May 2021, the British broadcaster ITV launched a new advertising campaign to showcase the range of content available on its streaming platform ITV Hub. In a series of shorts, stars from the worlds of drama and reality TV go head-to-head in a number of outlandish confrontations, with one or the other (or neither) ultimately coming out on top. One short sees Jason Watkins (Des, McDonald & Dodds) try to slip Kem Cetinay (Love Island) a glass of poison, only for Kem to outwit him by switching glasses when Jason’s back is turned. Another has Katherine Kelly (Innocent, Liar) making herself a gin and tonic, opening a cupboard in her kitchen to shush a bound and gagged Pete Wicks (The Only Way is Essex). A third features Ferne McCann (I’m a Celebrity… Get Me Out of Here!, The Only Way is Essex) rudely interrupting Richie Campbell (Grace, Liar) in the middle of a crucial phonecall by raining bullets down on him from a helicopter gunship. And the last, most recent advert shows Olivia Attwood (Love Island) and Bradley Dack (Blackburn Rovers) distracted mid-walk by an adorable dog, only to have a hefty skip dropped on them by Anna Friel (Butterfly, Marcella).
The message of all these unlikely pairings is clear. In this age of binge-watching, lockdowns, and working from home, ITV is stepping up to the plate to give us, the viewers, the very best in premium, popular, top-rated televisual content to satisfy every conceivable taste. Against the decades-long rise of subscription video-on-demand streaming, one of the old guard of terrestrial television is going on the offensive. Netflix? Prime? Disney+? Doesn’t have the range. Get you a platform that can do both. (BAFTA-winning drama and Ofcom-baiting reality, that is.) More a half-baked fighting retreat than an all-out assault? Think again; ITV is “stopping at nothing in the fight for your attention”. Can ITV really keep pace with the bottomless pockets of the new media behemoths? Of course it can. Even without a wealth of resources you can still have a wealth of choice. The eye-catching tagline for all this: “More drama and reality than ever before.” In this titanic struggle between drama and reality, the central irony—or, perhaps, its guilty secret—is how often the two sides of this dichotomy fundamentally converge. The drama in question only very rarely crosses the threshold into true fantasy, whether imagined more as lurid science-fiction or mind-bending Lovecraftian horror; meanwhile, reality is several stages removed from anything as deadening or banal as actual raw footage from live CCTV. Instead, the dramas that ITV touts as its most successful examples of the genre pride themselves on their “grittiness”, “believability”, and even “realism”. At the same time, the “biggest” reality shows are transparently “scripted” and reliant on “set-ups” and other manipulations by interventionist producers, and the highest accolade their participants can bestow on one another is how “unreal” they look. Both converge from different sides on an equilibrium point of simulated, real-world-dramatising “hyperreality”; and as we watch, we are unconsciously invited to ask where drama ends and where reality begins. In our consumption of drama and reality, we are likewise invited to “pick our own” hyperreality from the plethora of options on offer. The sheer quantity of content available across all these platforms is little short of overwhelming, and staying up-to-date with all of it is a more-than-full-time occupation. Small wonder, then, that we commonly experience this “wealth of choice” as decision “fatigue” or “paralysis”, and spend almost as much if not often more time scrolling through the seemingly infinite menus on different streaming services than we do actually watching what they show us. But the choices we make are more significant than they might at first appear. The hyperrealities we choose determine how we frame and understand both the world “out there” within and beyond our everyday experiences and the stories we invent to describe its horizons of alternative possibility. They decide what we think is (or is not) actually the case, what should (or should not) be the case, what does (and does not) matter. Through our choice of hyperreality, we determine how we wish both reality and drama to be (and not to be). Given the quantity of content available, the choice we make is also close to zero-sum. As the “fight for our attention” trumpeted by ITV implies, our attention (our viewing time and energy, our emotional and cognitive engagement) is a scarce resource. Even for the most dedicated bingers, picking one or even a few of these hyperrealities to immerse ourselves in sooner or later comes at the cost of being able to choose (at least most of) the others. We have to choose whether our preferred hyperreality is dominated by “glamorous singles” acting out all the toxic and benign microdynamics of heterosexual attraction, or the murky world of “bent coppers” and the rugged band of flawed-but-honourable detectives out to expose them; whether it smothers us in parasols and petticoats, and all the mannered paraphernalia of period nostalgia, or draws us into the hidden intricacies of a desperately-endangered natural world. In short, we have to choose what it is about the world that we want to see. * * * We face the same overload of reality and drama, and the same forced choice, when we engage with the more direct mediatised processes that provide us with information about the world around us. Through physical, online, and social media, we are met with a ceaseless barrage of new, drip-fed, self-contained events and phenomena, delivered to us as bitesize nuggets of “content”. Before, we had the screaming capitalised headlines and one-sentence paragraphs of the tabloid press. Now, we also have Tweets (and briefly Fleets), Instagram stories and reels, and TikTok videos generated by “new media” organisations, “influencers” and “blue ticks”, and a vast swarm of anonymous or pseudonymous “content providers”. All in all, the number of sources—and the quantity of output from each of these sources—has risen well beyond our capacity to retain an even remotely synoptic view of “everything that is going on”. Of course, it is by now a well-rehearsed trope that these bits of “news” and “novelty” content leave no room for nuance, granularity, and subtlety in capturing the complexities of these events and phenomena. But what is less-noticed are the challenges they create for our capacity to make meaningful sense of them at all from our own (individual or shared) ideological stances. Normally, we gather up all the relevant informational cues we can, then—as John Zaller puts it—“marry” them to our pre-existing ideological values and attitudes, and form what Walter Lippmann calls a “picture inside our heads” about the world, which acts as the basis for all our subsequent thought and action.[1] But the more bits of information we are forced to make sense of, and the faster we have to make sense of them “in live time” as we receive them—before we can be sure about what information is available instead or overall—the more our task becomes one of information-management. We are preoccupied with finding ways to get a handle on information and compressing it so that our resulting mental pictures of the world are still tolerably coherent—and so that our chosen hyperreality still “works” without too many glitches in the Matrix. These processes of information-management are far from ideologically neutral. As consumers of information, our attention is not just passive, there to be “fought over” and “grabbed”; rather, we actively direct it on the basis of our own internalised norms and assumptions. We are hardly indiscriminately all-seeing eyes; we are omnivorous, certainly, but like the Eye of Sauron our voracious absorption of information depends heavily on where exactly our gaze is turned. In this context, what is it that ideology does to enable us to deal with information overload? What tools does it offer us to form a viable representation of the world, to help us choose our hyperreality? * * * One such tool is the iterative process of curating the “recommended-for-you” information that appears as the topmost entries in our search results, home pages, and timelines. The cues we receive are blisteringly “hot”, to use Marshall McLuhan’s term; they are rhetorically and aesthetically marked or tagged—“high-spotted” in Edward Bernays’ phrase—to elicit certain emotional and cognitive reactions, and steer us towards particular “pro–con” attitudes and value-judgments.[2] They “fight for our attention”, clamouring loudly to be the first to be fed through our ideological lenses; and they soon exhaust our capacity (our time, energy, engagement) to scroll ever on and absorb new information. To stave off paralysis, we pick—we have to pick—which bits of information we will inflate, and which we want to downplay. In so doing, we implicitly inflate and downplay the ideological frames and understandings attached to them in “high-spotted” form. Then, of course, the media platform or search engine algorithm remembers and learns our choice, and over time gradually takes the need to make it off our hands, quietly presenting us with only the information (and ideological representations) we “would” (or “should”) have picked out. “Siri, show me what I want to see.” “Alexa, play what I want to hear.” No surprise, then, that the difference in user experience between searching something in our usual browser or a different one can feel like paring away layers of saturation and selective distortion. The fragmentary nature of how we receive information also changes how we express our reaction to it. The ideologically-exaggerated construction of informational cues is designed to provoke instant, “tit-for-tat” responses. At the same time, the promise of “going viral” creates an algorithmic incentive to move first and “move mad” by immediately hitting back in the same medium with a response that is at least as ideologically exaggerated and provocative as the original cue if not more. Gone are the usual cognitive buffers designed to optimise “low-information” reasoning and decision-making. Instead, we are pushed towards the shortest of heuristic shortcuts, the paths of least intellectual resistance, into an upward—and outward (polarising)—spiral of “snap” judgments. The “hot take” becomes the predominant way for us to incorporate the latest information into our ideological pictures of the world; any longer and more detailed engagement with this information is created by literally attaching “takes” to each other in sequence (most obviously via Twitter “threads”). As this practice of instantaneous reaction becomes increasingly prominent and entrenched, our pre-existing mental pictures are steadily overwritten by a worldview wholly constituted as a mosaic of takes: disjointed, simplistic, foundationless, and subjective. As our ideological outlook becomes ever more piecemeal, we turn with growing urgency to the tools and structures of narrative to bring it some semblance of overarching unity. Every day, we consult our curated timelines and the cues it presents to us to discover “the discourse” du jour—the primary topic of interest on which our and others’ collective attention is to focus, and on which we are to have a take. Everything about “the discourse” is thoroughly narrativised: it has protagonists (“the OG Islanders”) and a supporting cast (“new arrivals”, “the Casa Amor girls”), who are slotted neatly into the roles of heroes (Abi, Kaz, Liberty) or villains (Faye, Jake, Lillie); it undergoes plot development (the Islanders’ “journeys”), with story and character arcs (Toby’s exponential emotional growth), twists (the departure of “Jiberty”) and resolutions (the pre-Final affirmations of “Chloby”, “Feddy”, “Kyler”, and “Milliam”). We overcome both the sheer randomness of events as they appear to us, and the pro–con simplicity of our judgments about them, by reimagining each one as a scene in a contemporary (im)morality play—a play, moreover, in which we are partisan participants as much as observers (e.g., by voting contestants off or adding to their online representations). How far this process relies on hermetically self-contained, self-referential certainty becomes clear from the discomfort we feel when objects of “the discourse” break out of this narrative mould. The howls of outrage that the mysterious figure of “H” in Line of Duty turned out not to be a “Big Bad” in the style of Buffy the Vampire Slayer, but instead a floating signifier for institutional corruption, shows how conditioned we have become to crave not only decontestation but substantial closure. The final element in our ideological arsenal that helps us cope with the white heat of the cues we receive is our ability to look past them and focus on the contextual and metatextual penumbra that surrounds them. To make sure we are reading our fragmentary information about the world “correctly”, we search for additional clues that take (some or all of) the onus of curating it, coming up with a take about it, and shaping it into a narrative off our hands. This explains, for instance, the phenomenon where audiences experience Love Island episodes on two levels simultaneously, first as viewers and second as readers of the metacommentary in their respective messenger group chats, and on “Love Island Twitter”, “Love Island TikTok”, and “Love Island Instagram”. In extreme cases, we outsource our ideological labour almost entirely to these clues, at the expense of engaging with the information itself, as it were, on its own terms. “Decoding” the messages the information contains then becomes less about knowing the right “code” and more about being sufficiently familiar with who is responsible for “encoding” it, as well as when, where, and how they are doing so. Rosie Holt has aptly parodied this tendency, with her character vacillating between describing a tweet as nice or nasty (“nicety”) and serious (“delete this”) or a joke (“lol”), incapable of making up her mind until she has read what other people have said about it. * * * Together, these elements create a kind of modus vivendi strategy, which we can use to cobble together something approaching a consistent ideological representation of what is going on in the world. But its highly in-the-moment, “choose-your-own-adventure” approach threatens to give us a very emaciated, flattened understanding of what ideology is and does for us. Specifically, it is a dangerously reductionist conception of what ideology has to offer for our inevitable project of choosing a hyperreal mental picture that navigates usefully between (overwhelming, nonsensical) reality and (fanciful, abstruse) drama. If a modus vivendi is all that ideology becomes, we end up condemned to seeing the world solely in terms of competing “mid-range” narratives, without any overarching “metanarratives” to weave them together. These mid-range narratives telescope down the full potential extent of comparisons across space and trajectories over time into the limits of what we can comprehend within the horizons of our immediate neighbourhood and our recent memory. What we see of the world becomes limited to a litany of Game of Thrones-style fragmentary perspectives, more-or-less “(un)reliable” narrations from myriad different people’s angles—which may coincide or contradict each other, but which come no closer to offering a complete or comprehensive account of “what is going on”. The tragic irony is that the apotheosis of this information-management style of ideological modus vivendi is taking place against a backdrop of a reality that is itself taking on ever more dramatic dimensions on an ever-grander scale. Literal catastrophes such as climate change, pandemics, or countries’ political and humanitarian collapse raise the spectral prospect of wholesale societal disintegration, and show glimpses of a world that is simultaneously more fantastical and more raw than what we encounter as reality day-to-day. Individual-level, “bit-by-bit” interpretation is wholly unequipped to handle that degree of overwhelmingness in the reality around us. Curating the information we receive, giving our takes on it, crafting it into moralistic narratives, and interpreting its supporting cues is a viable way to offer an escape (or escapism) from the stochastic confusion of the “petty” reality of our everyday experience—to “leaven the mundanity of your day”, as Bill Bailey puts it in Tinselworm. But it falls woefully short when what we have to face is a reality that operates at a level well beyond our immediate personal experience, which is “sublimely” irreducible to anything as parochial as individual perspective. How unprepared the ideological modus vivendi calibrated to the mediatisation of information today leaves us is shown starkly by the comment of an anonymous Twitter user, who wondered whether we will experience climate change “as a series of short, apocalyptic videos until eventually it’s your phone that’s recording”. If it proves unable to handle such “grand” reality, ideology threatens to become what the Marxist tradition has accused it of being all along: namely, an analgesic to numb us out of the need to take reality on its own ineluctable terms. That, ultimately, is what Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels were trying to provide through their accounts of historical materialism and scientific socialism: an articulation of a narrative capable of addressing, and as far as possible capturing, the sheer scale and complexity of reality beyond the everyday. We do not have to take all our cues from Marxism—even if, as often as not, “every little helps”. But we do have to inject a healthy dose of grand narrative and metanarrative back into the ideologies we use to represent the world around us, even if only to know where we stand among the tides of social change from which the “newsworthy” events and phenomena we encounter ultimately stem. The trends driving the reality we want to narrate are simultaneously global and local, homogenised and atomised, universal and individuated. We cannot focus on one at the expense of the other. By itself, neither the “Olympian” view of sweeping undifferentiated monological macronarratives (Hegelian Spirit, Whig progress, or Spenglerian decline) nor the “ant’s-eye” view of disconnected micronarratives (of the kind that contemporary mediatisation is encouraging us to focus on) will do. The only ideologies worth their salt will be those that bridge the two. How, then, should ideology respond to the late-modern pressures that are generating “more drama and reality than ever before”? Certainly, it needs to recognise the extent to which these are opposite pulls it has to satisfy simultaneously: no ideological narrative can afford to lose the contact with “gritty” reality that makes it empirically plausible, nor the “production values” of drama that make it affectively compelling. At the same time, it has to acknowledge that the hyperreality it creates and chooses for us is never fully immune to risk. Dramatic “scripting” imposes on reality a meaningfulness and direction that the sheer chaotic randomness of “pure” reality may always eventually belie. Meanwhile, the slavish drive to “accurately” simulate reality may ultimately sap our orientation and motivation in engaging with the world around us of any dramatic momentum. The only way to minimise these risks is to “think big”, and restore to ideology the ambition of “grand” and “meta” perspective, to reflect the maximum scale at which we can interpret both what (plausibly) is and what (potentially) is to be done. [1] Walter Lippmann, Public Opinion (Blacksburg, VA: Wilder Publications, Inc., 2010 [1922]), 21–2; John R. Zaller, The Nature and Origins of Mass Opinion (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992), 51. [2] Edward Bernays, Propaganda (Brooklyn, NY: Ig Publishing, 2005 [1928]), 38; Marshall McLuhan, Understanding Media (New York, NY: McGraw–Hill, 1964), 22ff. by Iain MacKenzie
Twenty years ago, the lines of debate between different versions of critically-oriented social and political theory were a tangled mess of misunderstandings and obfuscations. The critics of historicist metanarratives were often merged under the banner of postmodernism, grouped together in (sometimes surprising) couplings—postmodernism and poststructuralism, poststructuralism and post-Marxism, deconstruction and postmodernism—or strung together in a lazy list of these terms (and others) that usually ended with the customary ‘etc.’. Although this was partly the result of ‘posties’ still figuring out the detail of their respective challenges to and positions within modern critical thought, it was also a way of finding shelter together in a not altogether welcoming intellectual environment.
This is because it was not only the proponents of various post-isms who were unsure of what they were defending, it was also that the critics of these post-isms were indiscriminately attacking all the post-isms as one. They would cast their critical responses far and wide seeking to catch all in the nets of performative contradiction, cryptonormativism and quietism. ‘Unravelling the knots’ proposed one way of clarifying one post-ism—poststructuralism—as a small step toward inviting other posties to clarify their own position and critics to take care to avoid bycatch as they trawled the political seas.[1] That was twenty years ago: has anything changed? In many respects, yes; but not always for the better. Within the academy, taking course and module content as a rough indicator, poststructuralism has become domesticated. Once a wild and unruly animal within the house of ideas, it is now a rascally but beloved pet that we all know how to handle.[2] In political studies, this domestication has come in two ways.[3] First, it has become customary to acknowledge one’s embeddedness within regimes of power/knowledge, such that almost everyone of a critical orientation is (apparently) a Foucauldian now. Second, it has become commonplace to study discourses and how they shape identities, adding this to the methodological repertoire of political science. These two simple gestures often merit the titular rubric ‘A Poststructuralist Approach’ and yet they often remain undertheorised in the manner discussed in the original article. Often, there is neither a fully-fledged account of the emergence of structures nor an account of how meaning is constituted through the relations of difference that define linguistic and other structures. Without such in-depth accounts, we are left with empirically rich but ultimately descriptive accounts of how social forces impinge on meaning, which can have its place, or the treatment of language as a data source to be mined in search of attractive word clouds (or equivalents), which can also have its place. Whatever these claims and methods produce, however, it is not helpful to call them ‘poststructuralist’. There is still a need for the exclusive but non-deadening definition of this term, so that it is not confused with the tame house pet with which it is associated today. Part of the problem is that the discussion of how structures of meaning emerge and how they function through processes of differentiation before any dynamics of identification requires, let’s say in a Foucauldian tone, the hard work of genealogy: the patient, gray and meticulous work of the archivist combined with the lively critical work of the engaged activist.[4] But, these days, who has the patience, and the energy, for genealogy? And, in many respects, the difficulties associated with constructing intricate ‘histories of the present’ have led to a tendency to short-circuit the genealogical process (and other poststructuralist methods[5]) under the name of ‘social constructivism’. It is a shorthand, however, that has generated new entanglements, new knots, that have come to define what those of us with a long enough memory can only regret are now frequently labelled the culture wars. On one side, there are the alleged heirs of the posties, awake to the constructed nature of everything and the subtleties of all forms of oppression. On the other side, there are the new defenders of Enlightenment maturity striving to protect science from constructivism and to guard free-speech from the ‘cultural Marxists’. This epithet, of course, is the surest sign that we are in a phoney war—albeit one with real casualties—as it mimics the trawling habits of previous critics but industrialises them on a massive scale. Claims about the deleterious effects of ‘cultural Marxists’ and their social constructivist premisses simply scrape the seabed and leave it barren. But much like the debate twenty years ago, those seeking to defend ‘social constructivism’ cannot swim out of the way unless they specify that this, and other phrases like it, should never be used to end an argument. There is no use in proclaiming a social constructivism if, after all, the social itself is constructed. Shorthand is always helpful but only if we know that it is exactly that and that it will always need careful exposition and explication when critics raise the call. Moreover, what is often forgotten, in the heat of battle, is that the task is not simply to clarify one’s own claims in response to critics but to reflect upon the nature of critical exchange itself. One side of the culture wars take lively spirited debate as the signal of a flourishing marketplace of ideas. Those on the side of social construction appear to agree, simply wanting it to be a regulated marketplace of ideas. What poststructuralism brings to market is succour for neither side. Forms of critical engagement bereft of analyses of the current structures of socially mediated critical practice will always fall short of the poststructuralist project and typically dissolve into the impoverished forms of communicative exchange that never rise above the to-and-fro of opinion. It is incumbent, therefore, on poststructuralists to have a view on the nature of public interaction through social media and how these interlock with different forms of algorithmic governmentality.[6] In this way, the social constructivist shorthand can be given real critical purchase by delving deeply into the nature of public discourse and the technological forms that sustain it, particularly because these make state intervention in the name of ‘the public’ increasingly difficult (even though they can also be used, to a certain extent, for statist purposes). That said, the culture wars obfuscate a deeper misunderstanding about poststructuralism. To grasp this, however, it is important to be reminded of the overarching project of poststructuralism: it is a project aimed at completing the structuralist critique of humanism. It is important to specify this a little further. Humanism can be understood as the project of bringing meaning ‘down to earth’ so that it is in human rather than divine hands. Given this, we can articulate structuralism in a particular way: it was a series of responses to the ways in which humanism tended to treat the human being as a surreptitiously God-like entity and source of all meaning. Structuralism was the project aimed at completing the founding gesture of humanism. Poststructuralism simply recognises that there are tendencies within structuralism that similarly treat structures as analogous to God-like entities that serve as the basis of all meaning. In this respect, poststructuralism is the attempt to complete the project of structuralism, which was itself aimed at completing the project of humanism. When we understand poststructuralism in this manner it is an approach to thinking (and doing) that seeks to remove the last vestiges of enchanted, supernatural, forces, entities and explanations from all theoretical and practical activity, including science but also philosophy and the arts (broadly understood). Given this, there is no room for a pseudo-divine notion of the social that often haunts ‘social constructivism’. Indeed, given this articulation of its project, poststructuralism is hardly anti-science (as some in the culture wars might claim); rather, it is a project of understanding meaning in every respect without reinstating a source of meaning that stands ‘outside’ or ‘above’ or ‘beyond’ the world that we inhabit. In fact, poststructuralists (though not all posties) are rather fond of science and they certainly do not want to undermine the natural sciences in the name of lazy ‘social constructivism’. It is, in fact, a way of seeking better science with help of philosophy, and a way of seeking better philosophy with the help of science (and for the full sense of what’s at stake, this gesture should be triangulated through inclusion of the arts). But how can there be a ‘better’ if the posties, including the poststructuralists, are sceptical of metanarratives? This question brings us to one of the more fruitful aspects that has changed in the last twenty years. The most interesting challenge faced by poststructuralists in recent times has come from the emergence of forms of neo-rationalism looking to reinvigorate critical philosophy through pragmatically oriented forms of Kantianism and non-totalising forms of Hegelianism.[7] From the neo-rationalist perspective, poststructuralism has failed in its attempts to naturalise meaning, to take it away from explanations that rely upon supernatural forces, to the extent that it is reliant upon a transcendent notion of Life that treats the priority of becoming over being as given. This immanent critique of poststructuralism cuts much closer to the bone than the Critical Theory inspired fishing which cast their nets wide but always from the harbour of their own shores. At the heart of this dispute is whether or not what we know about the world and how we know what we know about the world can be articulated within a single theoretical framework. For the neo-rationalist, it is (in principle, at least) possible to work on the assumption that there is an underlying unity between ontology and epistemology founded upon a specific conception of reason-giving. For poststructuralists, exploration of the conditions of experience suggests a dynamic distance between the what and the how, such that the task is to secure the claims of philosophy, art and science as equal routes into our understanding of both. While this reconstitutes a certain return to the pre-critical debates between rationalists and empiricists, it is equally indebted to the critical turn with respect to the shared task of legitimating knowledge claims, but with a pragmatic or practical twist. Both the neo-rationalists and the poststructuralists pragmatically assess the worth of the knowledge produced by virtue of the challenges they proffer to arguments that rely upon a transcendent God-like entity and the dominant form of this today; namely, the sense of self-identity that underpins capitalist endeavours to maximise profit. This critical perspective, perhaps surprisingly, was seeded within the fertile soil of American pragmatism. For the pragmatists—and we might think especially of Pierce, Sellars, and Dewey—it is the practical application of philosophy that engenders standards of truth, rightness and value. Admittedly, in the hands of its founding fathers, this practical application was often guided by the idea of maintaining the status quo. But that is not essential. Neo-rationalists and poststructuralists have found a shared concern with the idea that philosophical practice should be guided by the critique of capitalist forms of thought and life. As such, they share a common ground upon which meaningful discussion can be forged, aside from the culture wars (which are simply a reflex of capitalist identitarian thinking). While deep-seated divisions remain—does the knowledge generated by social practices of reason giving trump the experience of creative learning or are they on the same cognitive footing?—the shared sense of seeking a critical but non-final standard for what counts as better (better than the identity-oriented thinking sustaining capitalism) is driving much of the most productive debate and discussion at the present time. Work of this kind reminds us that poststructuralism is still a wild animal rather than a domesticated house pet, that it is a critical project but also one that has political intent. That said, it is not always easy to convey the political dimension of poststructuralism, especially given the vexed question of its relationship to ideology. As discussed in the original article, part of the initial excitement about poststructuralism was that its major figures distanced themselves from the idea of ideology critique. However, this was only ever the beginning of a complex story about the relationship of poststructuralism to ideology and never the end.[8] While Marxist notions of ideology were critiqued for the ways in which they incorporated notions of the transcendental subject, naïve versions of what counts as real and over-inflated notions of truth, poststructuralists have always endorsed the power of individual subjects to express complex notions of reality and historically sensitive and effective notions of truth, and to do so against dominant social and political formations. These formations are often given unusual names—dispositif, assemblages, discourses, and such like—but the aim of unsettling and ultimately unseating the dogmatic images and frozen practices of social and political life is not too distant from that animating Marxism. Of course, as Deleuze and Guattari expressed it, any revised Marxism needs to be informed by significant doses of Nietzscheanism and Freudianism (just as these need large doses of Marxism if they are to avoid becoming critically quietest and practically relevant for the critique of capitalism).[9] What results, though, is an immanent version of ideology critique rather than a rejection of it tout court: there are many assemblages/ideologies that dominate our thoughts, feelings and behaviour and it is possible to learn how they operate by making a difference to how they function and reproduce themselves. In searching for the natural bases of meaningful worlds it is no surprise that poststructuralists have become adept at diagnoses of how natural processes can lead to systems of meaning that import supernatural fetishes into our everyday lives, and how these are sustained in ways even beyond merely serving the interests of the economically powerful. There appear to be an endless number of these knots that need untying. If we want to untie at least some of them, then unravelling the knots that currently have poststructuralism tangled up in a phoney culture war is another small step on the road to bringing a meaningful life fully down to earth. [1] I.MacKenzie, ‘Unravelling the knots: post-structuralism and other “post-isms”’, Journal of Political Ideologies, 6 (3), 2001, pp. 331–45. [2] I. MacKenzie and R. Porter, ‘Drama out of a crisis? Poststructuralism and the Politics of Everyday Life’, Political Studies Review, 15 (4), 2017, pp. 528–38. [3] One of the interesting features of the recent history of poststructuralism is that it is not the same across disciplines. Of course, this need for disciplinary specificity with respect to how knowledge is disrupted, new forms of knowledge established and then domesticated is part of what poststructuralism offers. That said, much of what follows can be read across various disciplines in the arts, humanities, sciences and social sciences to the extent that the legacies of humanism and historicism traverse these disciplines. [4] M. Foucault, ‘Nietzsche, Genealogy, History’, in D. Bouchard (ed.) Language, Counter-Memory, Practice: Selected Essays and Interviews by Michel Foucault (New York: Cornell University Press, 1992 [1971]), pp. 139–64. [5] B. Dillet, I. MacKenzie and R. Porter (eds) The Edinburgh Companion to Poststructuralism (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2013). [6] A. Rouvroy, ‘The End(s) of Critique: data-behaviourism vs due-process’ in M. Hildebrandt and E. De Vries (eds), Privacy, Due Process and the Computational Turn. Philosophers of Law Meet Philosophers of Technology (London: Routledge, 2012), pp. 143–68. [7] See R. Brassier’s engagment with the work of Wilfrid Sellars, for example: 'Nominalism, Naturalism, and Materialism: Sellars' Critical Ontology' in B. Bashour and H. Muller (eds) Contemporary Philosophical Naturalism and its Implications (Routledge: London, 2013). [8] R. Porter, Ideology: Contemporary Social, Political and Cultural Theory (Cardiff: Wales University Press, 2006) and S. Malešević and I. MacKenzie (eds), Ideology After Poststructuralism (Oxford: Pluto Press, 2002). [9] G. Deleuze and F. Guattari, Anti-Oedipus: Capitalism and Schizophrenia (New York: Viking Press, 1977). This triangulation of the philosophers of suspicion, with a view to completing the Kantian project of critique, is one especially insightful way of reading this provocative text: see E. Holland, Deleuze and Guattari’s Anti-Oedipus: Introduction to Schizoanalysis (London: Routledge, 2002). by Glyn Daly
What can porn shoots tell us about the functioning of ideology? This can be approached through a critique of externalism. In externalist thinking there is always the image of a full presence, something substantial to which all distortion can be referred. In modern discourse, this is ultimately the position occupied by the (mythic) phallus: an autonomous self-sustaining One that stands apart and effectively overdetermines all relations of distortion: desire, narcissism, envy, and so on as so many orientations toward it.[1] Put in other terms, it reflects Jacques Derrida’s critical charge of phallogocentrism—where the symbolic order tends always to centre on notions of (masculinised) presence and identity—that he levels against psychoanalysis.[2] But what this misses is the way in which the privileging of the phallus in psychoanalysis is simultaneously a non-privileging. What the phallus names in psychoanalysis is essentially movement and/or treachery: gaining an erection when one least wants it and losing it when it is most required. Far from any autonomy or positivity of presence, the phallus reflects an autonomy of negativity. In other words, the phallus is “privileged” only insofar as it signifies lack as such. This is why Jacques Lacan repeatedly refers to the phallus as a “wanderer” and as “elsewhere”: that which denotes a permanent alibi at the very heart of the symbolic order. Indeed the whole of psychoanalysis can be seen as predicated on the basic absence not only of phallic consistency (a phallogo-decentrism in this sense) but also all externality.
It is this lack of externality that is reflected in porn shoots where, in order to get in “the zone”, male pornstars themselves typically have to resort to watching porn. Far from being a site of authentic sexual production, the porn shoot reflects a kind of game of mirrors, or metonymy of distortions, without any externality. The phallus in its “naked” form (as full presence) does not exist as such; it only ex-sists in its relation to an elsewhere, in referral to an Other site of imaginary existence (a fantasy scenario) where it finds its authentication. Nobody really has It (the phallus) and consequently there are no figures of ultimate phallic enjoyment blocking our access to full (and impossible) presence and identity. The problem of ideology, on the other hand, can be characterised in terms of a certain “phallic” anxiety. That is to say, ideology always retains some idea of an external figure who is somehow in possession of It and is thereby responsible for all the distortions (unemployment, crime, lack of resources, global viruses, and so on). In every instance there exists a projection of an image of a unitary identity (“the Jew”, “the Muslim”, “the Mexican”…) that is held to be responsible. It is here that we should locate today’s fashionable idea of “red pilling”—a reference to The Matrix where, in a metaphorical sense, one takes a red pill in order to perceive the truth behind all the surface distortions and deceptions. This is also what lies at the root of all those groups from QAnon and the “deep state” believers to the antivaxxers and even those who recently stormed the Capitol. In each case the same basic mythology is reflected: that behind the scenes there is an “intelligent design”, a Lacanian subject-supposed-to-know. This mythology is perfectly embodied in the current “Plandemic” conspiracy theory—i.e., the view that coronavirus and the vaccines have been designed for the purpose of enslaving humanity—which by definition implies the existence of a planning entity behind the global pandemic: an entity that must be exposed. Again we have the same motif of a unified Other at work: that the systemic beast (in all its abstraction, algorithmisation of power, and so on) is secretly ruled by a sovereign, a beastly sovereign perhaps. Across the spectrum of the various dark elite perspectives—Illuminati, shape-shifting reptilians, Fourth Reich, etc.—there exists a basic fantasmatic attempt to resurrect (res-erect?) the phallus: the sense of a full presence behind all the distortion, a prime mover that would explain the nature and functioning of the system. Nor is this mythology restricted to extreme right-wing conspiracy theory. Chomsky, for example, is famously dismissive of the idea of “speaking truth to power” affirming instead that “power knows the truth already, and is busy concealing it”.[3] In other words, there exists a power cabal (a master entity) that is operating at a point beyond distortion where truth is fully transparent and is consciously manipulated/distorted by that cabal in order to secure its underlying interests. Yet what Chomsky misses is the way in which power is itself subject to the same kind of illusions of transparency, rationality, holism, and so on. If we take Brexit, for example, it is not simply that power (however defined) has engaged in mass deception in order to secure its “objective economic interests”—the purely economic arguments for and against Brexit were essentially undecidable. The point is rather to see how, mediated through ideology, the pro-Brexit interests were themselves constituted in such a way as to be perceived as fully in accord with serving and advancing the “national interest”. There was/is nothing inauthentic about the idea that the UK will be better off once it is free from the shackles of the “Brussels’ dictatorship”. On the contrary, the authenticity of the pro-Brexit mobilisation derived from the sincerely held belief that Britain will be able to secure its integrity, reassert itself globally, and restore its national greatness (etc.). Consequently we should not seek to identify an ultimate, or positivistic, source of capitalist manipulation/distortion. There is no Capitalism (with a capital “c”) in this sense. Capitalism only functions historically in its “impure” forms: liberal, authoritarian, fascist, democratic, religious, secular, communist, and so on. In other words, there exist only distorted (fantasmatic) versions of capitalism, all of which rely on the same kind of fiction of an antagonism-free (neutral) capitalism that is best for “the people”. Marx already knew this, arguing that (along with the proletariat) the bourgeoisie are also subject to an entire mode of production in which they internalise, and are simultaneously motivated by, the dimensions of not only enrichment and narcissism, but also the greater good, work ethic, social opportunity, sacrifice, and so on. This is also how we should read Marx’s assertion that capital is essentially a social power: i.e., a way of reproducing the very sense of “the social” without any pre-given content or orientation. In Althusserian language, capital is a system in distortion that seeks to naturalise its basic principles through all of its adjectival (impure) forms. Capitalists, no less than porn actors, are equally inscribed into an economy of distortions that both enables and directs their very sense of agency. Far from the traditionalist view of straightforward deception and mystification, ideology functions rather as a certain kind of revelatory discourse of disclosure and unmasking—precisely as a way of protecting a substantialist notion of reality. Against the Deleuzian insight that that the mask does not hide anything except other masks, the ideological mission is always one of unmasking, of establishing a positive account. And it is in this context that Laclau’s view of ideology as the illusory concealment of basic lack needs to be supplemented. The ideological mechanism effectively consists of a double distortion.[4] On the one hand, there is the distortive illusion of a social fullness (Laclau) but on the other there exists a simultaneous reciprocal distortive illusion of an external obstacle to that fullness (deep state, dark elites, threatening-yet-inferior groups, and so on). The illusion of social rapprochement can only be sustained via its opposite: the identification of social blockage. In a Hegelian twist, the ideological illusion of an antagonism-free world is generated through antagonism itself. Far from blocking me from the full constitution of my identity, the presence of an enemy is the very condition for supporting an image of full identity. In the words of Blofeld in Spectre, the positive function of (ideologised) antagonism is to provide an “author of all your pain”, a determinant figure to which we can seek redress for pure antagonism (i.e., antagonism that resides at the very heart of all identity). This is why Lacan refers to the subject as constitutively split (the S-barred or $): the subject is divided in terms of a pure/inherent antagonism between its historical symbolic content and its transhistorical void, the persistence of radical negativity that thwarts all symbolic constitution. Mediated through ideology, antagonism thus becomes a way of protecting us from the traumatic knowledge that there is no author of our pain/blockage. Through the externalisation of antagonism (the construction of the Other-as-blockage) we avoid the unbearable inherency of pure antagonism as such. It is against this background that the radicality of Lacan’s critique of castrative anxiety can be discerned. In Freud, anxiety arises through an affect of generalised loss premised on castration: the sense of privation. Lacan, however, completely turns this around and affirms that what the subject fears is not the loss as such but rather the loss of the loss: that is, the loss of an externalised figure that is projected as the embodiment of loss, negativity, and/or the impossibility of Society. Without such a figure, the subject is faced with the radical anxiety of freedom: the anxiety that arises from the knowledge that we are not constrained by an exterior obstacle or big Other. This is also how we should approach Ernst Hoffmann’s story of the eponymous and uncanny “Sandman” who haunts and torments the tragic character of Nathaniel throughout his short life. For Freud, the Sandman embodies the archetypal castrating father—reflected in his unfathomable desire/demand “Eyes out, eyes out!” for an obscure alchemical ritual. Yet what ultimately destroys Nathaniel is not so much the Sandman (a projected image of blockage) but his own inability to act or come to terms with the intricacies and pressures of forging meaningful relationships with “flawed” human beings—it is precisely when the way is open to a romantic union with Clara that Nathaniel’s madness/anxiety descends and he shrinks back from the act, fatally hurling himself from the market gallery. In this respect, the Sandman functions rather as a figure that regulates a critical distance with the anxiety of freedom. So when Slavoj Žižek affirms in his classical formulation that the “function of ideology is not to offer us a point of escape from our reality but to offer us the social reality itself as an escape from some traumatic, real kernel”, the only (Hegelian) point to add here is that the ideological escape from the Real is supplied through the Real itself: that is, through a certain simulation of the Real, giving it a semblance—the various “Sandmen” of today’s interlopers, malefactors, enemies of the people, and so on—rendering it manageable in some way.[5] How do we get out of this predicament? Here perhaps Joseph Stalin provides some inadvertent help. Towards the end of his life, Stalin confided to Lavrentiy Beria (the head of the secret police during Stalin's leadership) "I'm so paranoid that I worry that I am plotting against myself". Since Freud, psychoanalysis has long been aware of how paranoia functions as a desperate attempt to overcome the feeling of inexistence: the subject constructs enemies as a way of (over-) confirming their identity and thus avoiding what Stephen Grosz calls the “catastrophe of indifference”, the sense of drifting away into the void.[6] Those suffering from paranoia are in fact passionately attached to their antagonistic constructs—as Lacan puts it, paranoiacs “love their delusions as they love themselves”.[7] The paranoiac invents a world in which they can continue to have and eat their cake. In paranoia, the subject strives to keep both the possibility of a resolution (full presence) and the obstacle(s) to it—the obstacle serves as support to the (illusory) resolution. So the problem with the paranoiac is that, in a way, they are not paranoid enough. That is to say, they still cling to the idea of some kind of resolution (however remote or abstract). The way to confront paranoia is not by addressing the validity of specific claims but virtually the opposite: to radicalise paranoia in the affirmation of a paranoia without enemies or resolution. So Stalin was right in a certain sense: the negation is precisely an inherent one, a reflection of an inward contradiction between the idea of oneself and its attendant void. At the same time, what Stalin was unable to do was to realise the emancipatory potential of accepting the traumatic truth of this fundamental contradiction—and in this regard he remained fully within the terms of ideology. In Hegel, an emancipatory path is only opened once we abandon the continuous attempts to overcome contradiction (auto-negativity) and instead inscribe this contradiction as the very “foundation” of existence. This is why for Hegel there can be no resolution, only reconciliation. [1] This traditional notion of the One functions in idealised terms: something external and indivisible, comprising a positive ground for substance in general [2] Phallogocentrism is a neologism (combining both phallocentrism and logocentrism) deployed by Derrida to designate a double privileging: the privileging of logos (a positive view of the symbolic order in which meaning appears as both immediate and directly communicable) within Western metaphysics, and within logos the privileging of the phallus (i.e. a dominant paradigm of universalised masculine presence, authority and priorities). [3] Chomsky cited in T. Eagleton (2016), ‘The Truth Speakers’, New Statesman (3 April 2016) [4] G. Daly (2021), ‘Obstacles and Distortions: A Speculative Approach to Ideology’, Journal of Political Ideologies (forthcoming). [5] S. Žižek, The Sublime Object of Ideology (London: Verso, 1989), 45. [6] S. Grosz, The Examined Life: How We Lose and Find Ourselves (Toronto: Random House Canada, 2013). [7] J. Lacan, The Psychoses (New York: Norton, 1993), 215. by Fernando Lizárraga
When pursuing the clarification of socialism’s core concepts, according to the methodology advocated by Michael Freeden for the study of political ideologies, equality stands out as one of the undisputed ideas on that complex, variegated, and often quarrelling tradition. The other key concepts or conceptual themes that form the kernel of socialism are, according to Freeden, “the constitutive nature of the human relationship, human welfare as a desirable objective, human nature as active, … and history as the arena of (ultimately) beneficial change”.[1] The method leading to this list involves a particular understanding of political ideologies which differs from the usual approach taken by political theory or political philosophy. It requires a thorough study into the main currents of socialism—not only of the Marxist version—and the specification of the relevant concepts through a process of decontestation. The research aimed at specifying those core concepts is also necessary when it comes to depicting the ideas that comprise the adjacencies and periphery of the socialist ideology. There is a particular difficulty that arises when looking into socialism’s morphology, namely, the fact that socialism is both a critique of capitalist society and also a project of a society yet to be brought about: “unlike conservatism, or even mainstream forms of liberalism, socialism is peculiarly prone to a dual temporal existence. It is centrally founded on a critique of the present, yet significantly projected onto a future of which there is as yet little empirical evidence”.[2] This second aspect demands a “leap of faith and imagination”—to use Freeden’s expression.[3] By and large, the self-awareness of socialism—as an ideology containing at the same time a dominant scientific side and a subordinate utopian (normative) dimension—faded away in the face of different dogmatisms promoted by socialist states. But with the collapse of the socialist bloc, there emerged a need for a revision and updating of key elements of the tradition.
Recent scholarship about socialism has largely benefited from the impact of John Rawls’s liberal egalitarianism on several fields of the social sciences and the humanities. After a reckoning of the ethical deficit caused by an extended belief in the scientific prowess of Marxism, a good number of socialist thinkers and activists admitted the need for a normative turn. This is not to deny, of course, the existence of a deep-seated ethical current in Socialism, as it is evident in the works of Eduard Bernstein, R. H. Tawney, G. D. H. Cole, amongst others, but only to highlight the fact that, because of the mainly Marxist anti-moralism, normative work was demeaned and considered powerless in the face of the anticipatory prodigies of historical materialism. This year will mark the 50th anniversary of the publication of A Theory of Justice,[4] and the shockwaves of Rawlsianism are still highly influential. Discussion of the core concepts of socialism, from a normative perspective, have gained a promising place within academia and also within grassroots organisations. Shortly after the turn of the millennium, Alex Callinicos, in his Anti-capitalist Manifesto, advocated a specific form or socialist democracy that embodies four key values of an anti-systemic program: justice, efficiency, democracy, and sustainability, where justice embraces ideals such as liberty, equality, and solidarity.[5] A recent entry on “Socialism” by Pablo Gilabert and Martin O’Neill for the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy singles out equality, democracy, individual freedom, self-realisation, and community or solidarity as paramount values of this tradition.[6] As we can see in these two examples, together with Freeden’s construal, the proposed lists of core concepts do not fully match with each other but have one striking coincidence: equality. This quick exercise seems to support Norberto Bobbio’s famous statement about equality being the Pole Star of the left, as opposed to the anti-egalitarian right. More important, though, is the acknowledgement that values matter to socialism and Marxism in particular, and that it was a shortcoming to eschew any talk of ethical principles, fearfully avoiding a collapse into what Marx and Engels described as petty utopianism. One must only be thankful that this anti-utopianism was not understood as an outright rejection of utopia altogether. So, in defiance of Marx and Engels’s strictures against moral theory, important varieties of moral thinking emerged within the socialist purview, and a strain of ethical socialism came around in the second half of the nineteenth century, paving the way for the post-Rawlsian normative turn. Although the name of Ethical Socialism normally refers to a group of thinkers and activists of the late 1800s in the United Kingdom, it had outstanding representatives in other parts of the world. William Jupp, John Trevor, Thomas Davidson, and Edward Carpenter were key representatives of British ethical socialism. The last two are of particular importance since they were deeply influenced by American Romanticism and immanentism, especially by the works of Henry Thoreau and Ralph Waldo Emerson.[7] In the United States, a provincial writer destined to become an almost involuntary political protagonist of the Gilded Age, Edward Bellamy, can be counted as one of the few who, despite the widespread dismissal of utopias, decidedly resorted to this genre—inherent to socialist critique and history—to carry out a double task: to cast a harsh indictment on capitalism as a predatory and unjust system, and to advance a vernacular conception of egalitarianism, which was the most cunning way to bring socialism and Marxist themes to the American public. He was also under the influence of American immanentism, transcendentalism, and the experiences of intentional utopian communities such as the famous Fourierist Brook Farm in Massachusetts. Bellamy’s ideas had a profound impact on the organised labor movement, especially among the Knights of Labor. Eugene Debs, founder of the Socialist Party in the United States, revealed that he became a socialist thanks to Bellamy and even met with the writer in his last days.[8] Daniel De Leon, too, is said to have started his revolutionary career under “Bellamy’s inspiration”;[9] and Charlotte Perkins Gilman, the leading feminist activist and writer, was also a prominent member of the Bellamyist movement.[10] John Dewey famously wrote that Bellamy was “A Great American Prophet”, and remarked that “what Uncle Tom’s Cabin was to the anti-slavery movement, Bellamy’s book may well be to the shaping of popular opinion for a new social order”.[11] In short, and in keeping with the morphological approach, I find it plausible to hold that Edward Bellamy’s condemnation of capitalism and the account of the alternative egalitarian society he advocated are founded one a thick idea of equality which, at the same time, involves an outright rejection of the principle of self-ownership. This last rejection, I also sustain, must be either counted as a component of equality as a core idea of socialism or as an adjacent but necessary concept that contributes to making sense of the kind of egalitarianism espoused by Bellamy and, to a large degree, by contemporary egalitarian socialists. It must be noted that the principle of self-ownership, first conceived by John Locke, constitutes the founding tenet of contemporary libertarianism. In its most usual rendition, the principle says that individuals have over themselves the same kind of rights that a master has over a chattel slave and, by implication, those who enjoy self-ownership cannot, as a matter of right, be forced to help others through personal service or any other mandatory scheme of redistribution. Bellamy’s opposition to self-ownership must be understood in the context of his life-long advocacy for egalitarianism, as it is conveyed in his most famous utopian novels: Looking Backward 2000-1887 (1888),[12] and Equality (1897).[13] Such opposition—as I will explain—was founded on the idea of the common ancestry of humankind, on the belief that each person has ha debt to society and past generations; and most importantly, on the notion that it is “fraudulent” to believe that individuals deserve and fully own their natural and social endowments and owe nothing to each other. Looking Backward was one of the most significant literary works in the late 1800s in the United States. It sold millions of copies in a few years and was translated into several languages. The plot, as it normally happens in utopias, is a setting for the development of theoretical propositions. Bellamy uses a time-travelling scheme in which the main character falls into mesmerised sleep in 1887 only to wake up 113 later in his home city, Boston, which in the Year 2000 is part of a perfectly egalitarian society. Julian West, the protagonist, learns about the institutions and ethos of the new world in dialogue with his host, Dr Leete, a retired physician, and his daughter Edith. The sequel of Looking Backward, Equality, is a lengthier description of this new society. Bellamy gained almost immediate international recognition and country-wide acclaim, to the point that he became a keynote speaker for many associations, wrote extensively in his own newspaper, The New Nation, and, eventually, the Nationalist Party was created to advance Bellamy’s ideas. Nationalism, it must be said, was the name Bellamy adopted for his proposal, in an attempt to avoid the word socialism which was associated with violence and social unrest in the wake of the Haymarket Massacre and the mass strikes of the 1870s. An in-depth exploration into Bellamy’s rejection of self-ownership reveals that such a stance is an integral part of his particular form of radical egalitarianism. The writer from Chicopee Falls (Massachusetts) thought that some of the dominant currents of socialism of his time were not radical enough as to how far they were prepared to push in the direction of equality. He thought that Fabians were too attached to the mechanism of retribution according to contribution, whereas Marxists allowed personal assets to have undue influence on distributive matters. These critiques of other varieties of socialism were the basis of his own understanding of equality. Bellamy considered equality to be the only relevant moral relationship between persons. From this uncompromising stance, he mounted a full criticism of the notion of self-ownership and propounded a strong egalitarian principle: “From each, equally; to each equally”.[14] The institutional arrangements of the utopian society that Dr Leete presents to Julian West are carefully designed and crafted to meet this extremely high standard, without giving in to the annulment of singularity or individual tastes. It is well known that William Morris’s News From Nowhere (1890) is a direct response to Bellamy’s vision, from an anarchistic and pastoral perspective, as opposed to the industrialist and somewhat highly regulated Bellamian society. Morris wrote a critical review in which he remarked that Looking Forward should be “considered seriously” but not taken as a “socialist Bible”. He thought that Bellamy only wanted to get rid of the ills of modern life, without changing that life altogether. He described the utopian system as State Communism, criticised its severe discipline, its industrialism, the major role of great cities, and the limited conception of work as productive activity dissociated from pleasure and creativity. But the core of Morris’s critique was aimed at Bellamy’s peaceful “economical semi-fatalism” that lead to the egalitarian society instead of a conscious struggle for a “free and equal life”. Even though Bellamy does not reply to Morris’s review, many of these objections seem to have shaped the more nuanced portrayal of the utopian society in Equality and other writings.[15] At the same time, he comes up with a more straightforward rebuttal of self-ownership. So, when writing in The New Nation, he contends that it would be a “fraudulent” principle that which “would assume that an individual owns himself and has a valid title to the full usufruct of his powers without incumbrance or obligation on account of his debt to the past and his duties toward the social organism of which he is a part”.[16] At the same time, alongside a handful of acute arguments against increasing social inequalities and an outright indictment of monopoly capitalism, Bellamy pulls off a brilliant case against the entailment of the principle of self-ownership which forbids someone from lending assistance to others unless it is done by a consented interpersonal contract. In Equality, he contends that under capitalism it is accepted that “everyone is entitled to … the result of his abilities” and that this is plainly wrong because “they would naturally acquire advantages over others in wealth seeking as in other ways”.[17] Since he thought that abilities and the capacity for effort were due to the mere chance of birth, Bellamy ruled out the claim that the better endowed had a rightful claim over the advantages they could muster by using those undeserved talents. Therefore, it was the mission of social institutions to keep these inequalities from arising. It is easy to see that Bellamy was advancing similar arguments to those that, in the early 1970s, John Rawls used to build his monumental theory of justice as fairness. If Rawls springs up in this account of Bellamy’s thought, it is because, in my view, they represent a deep-seated egalitarian trend both in American political thought and, more importantly, in the socialist tradition. The egalitarianism of Bellamy and Rawls, as noted before, is part of a rich ethical tradition that overcame the staunch anti-moralism of the more orthodox Marxist versions of socialism. Rawls spent two years in Oxford, at a time when G. D. H. Cole, who thought of Bellamy as a mere “populariser of other men’s ideas”, was teaching about utopian socialism; when the Labour Party was divided between friends and adversaries of public ownership; and when Tawney’s new edition of Equality rekindled the debate over and against equality of opportunity,[18] as he advocated a kind of relational egalitarianism that despised the crude distributive view marked by “details of the countinghouse”. Without openly calling themselves socialists, both Rawls and Bellamy were no foes of socialism. On the contrary, Bellamy was convinced that his egalitarian model was even more radical than any socialist program of his time, and Rawls repeatedly emphasised that his theory of justice as fairness can be realised under a system of liberal or democratic socialism. Rawls believed “that the choice between a private-property economy and socialism is left open; from the standpoint of the theory of justice alone, various basic structures would appear to satisfy its principles”.[19] Moreover, after dismissing laissez-faire capitalism, welfare-state capitalism, and state socialism as incompatible with his principles of justice as fairness, he asserted that “property-owning democracy and liberal socialism [in] their ideal descriptions include arrangements designed to satisfy the two principles of justice”.[20] In Bellamy and Rawls we can see proof of that "dual temporal existence" of Socialism identified by Freeden. As already mentioned, socialism encompasses both a critique of the present and a projection into the future. Bellamy chose the utopian genre to accomplish both tasks; Rawls, in the same spirit, called his otherwise unadorned and formal theory a “realistic utopia”. Above all, both political thinkers were adamant in rejecting self-ownership as part and parcel of their egalitarian views. It should come as no surprise that the first systematic challenge to Rawls was launched from within the liberal tradition, in the guise of the libertarian theory of Robert Nozick, whose endorsement of self-ownership leads to a form of rugged anti-egalitarianism. To sum up: I understand that self-ownership has no place in a radical egalitarian version of socialism and that a good deal of theoretical work needs to be done in order to refine our understanding of the precise place of this rejection in a morphology of the socialist political ideology. [1] M. Freeden, Ideologies and Political Theory. A Conceptual Approach (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1996), pp. 425-426. [2] Ibid., pp. 417-418. [3] Ibid., p. 418. [4] J. Rawls, A Theory of Justice. Revised Edition (Cambridge, MA.: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 1999. First published, 1971.) [5] A. Callinicos, An Anti-Capitalist Manifesto (Cambridge, UK: Polity Press), pp. 107-108. [6] P. Gilabert and M. O’Neill, “Socialism”, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2019 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.) <https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2019/entries/socialism/>. [7] M. Bevir, The Making of British Socialism (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2011), pp. 220-227. [8] F. Rosemont, ‘Bellamy’s Radicalism Reclaimed’, in Daphne Patai (Ed.) Looking Backward 1988-1888. Essays on Edward Bellamy (Amherst: The University of Massachusetts Press, 1988), p. 162. [9] Ibid., p. 168. [10] Ibid., p. 176. [11] J. Dewey, ‘A Great American Prophet’, in Boydston, Jo Ann et. al (eds.) John Dewey. The Later Works 1925-1934. Volume 9: 1033-1934 (Carbondale and Edwardsville: Southern Illinois University Press, 1986), p. 106. [First published in Common Sense 3 (April 1934), pp. 6-7). [12] E. Bellamy, Looking Backward. 2000-1887 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007). [13] E. Bellamy, Equality (New York: Appleton, 1897). [14] E. Bellamy, Talks on Nationalism (Chicago, IL: The Peerage Press, 1938), p. 25. [15] Morris, W., News From Nowhere and Other Writings (London: Penguin, 2004), pp. 353-357. [16] E. Bellamy, Talks on Nationalism, op. cit., p. 27. [17] E. Bellamy, Equality, op. cit., p. 107. [18] K. Forrester, In the Shadow of Justice. Postwar Liberalism and the Remaking of Political Philosophy (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2019), pp. 18-24. [19] J. Rawls, A Theory of Justice (Cambridge, MA.: Harvard University Press, 1999), p. 228. [20] J. Rawls, Justice as Fairness. A Restatement (Cambridge, MA.: Harvard University Press, 2001), p. 138. |
Details
Archives
May 2023
Categories
All
|
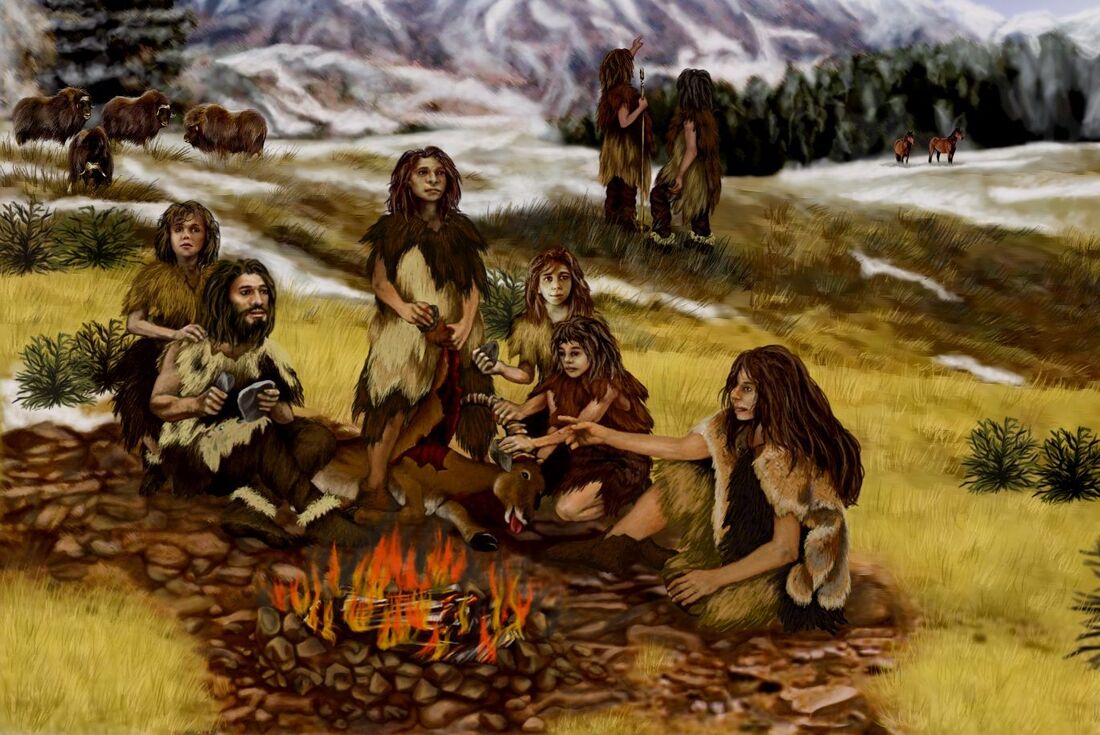









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed